The passive RFID tags do not have any power source and hence they have indistinct operational life span. The power needed for functioning is taken from the reader when the tag comes in the vicinity of the reader. They are available in a variety of sizes ranging from sizes which can fit into adhesive label. The passive RFID is basically made up of three parts: Antenna which is responsible for capturing energy and transferring the tag ID, Semiconductor chip appended to the antenna and an encapsulation which maintains the tag integrity. The encapsulation protects the antenna and chip from harsh environmental conditions. These encapsulations can be made up of small glass vial or from a laminar plastic substrate with adhesive on one side so that it can be easily attached to the goods.
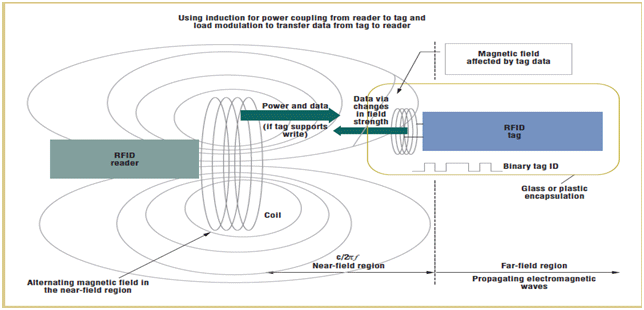
Fig. 1: Diagrammatical Figure Displaying Near Field Technique in passive RFID Tags
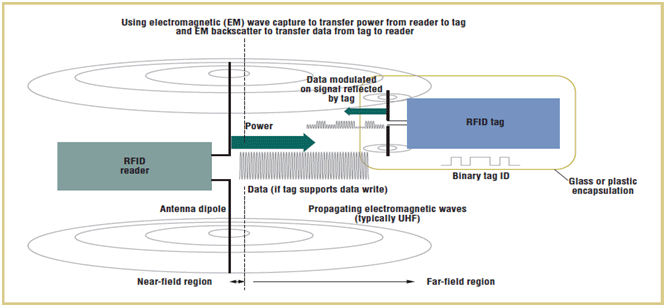
Fig. 2: Diagrammatical Presentation of Far Field Technique in Passive RFID Tags
Filed Under: Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.