For the people who are doing PCB designing, hobbyist or professionals, there are so many PCB designer softwares available. Most popular among them are diptrace, orcad, eagle, kicad etc. This tutorial is mainly for those people who haven’t tried out any professional pcb designer software yet.
Here is a quick guide, which will help you to get started off with kiCAD. In this tutorial we will be considering a simple astable multivibrator circuit using 555 timer IC. We will be designing a pcb for this well known simple circuit. Let me tell you upfront that I’m not an expert in pcb designing. My intension is only to explain you the necessary steps required in kicad to convert a simple circuit diagram to a gerber file, and also some tips and things to be taken care while doing the designing.
I’m here doing a complete design process and at the same time explaining the steps for you with the help of screenshots of the same. I request the reader to do the same steps in your PC from the beginning to the end for this single example, and next time you will be able to do it on your own.
The kiCAD software mainly has the following utilities:
Eeschema – Schematic editor
Cvpcb – Components to modules
Pcbnew – Pcb editor
Gerbview – Gerber viewer
The main window of the kicad looks like this:

Your recent project might have been listed in the project tree. To start a new project select the “New Project Descr”

The most important thing that you should take care of is that, all the files generated by while doing the project should be saved in a single folder, and the title of all the files should be the same.
So let us save this new project in our project folder. The extension should be .pro

After you have saved the project, the main window will look like this:

Editing the Schematic
1) Editing the schematic
Now you need to convert the circuit diagram into the schematic in kicad. For that you need to select the schematic editor.

The schematic editor window is shown below:

Before start drawing the schematic, we have to do a few important things;
Page settings – To set the page size, title etc.

Page settings window:

When you press OK, you can see the title of your work sheet has been changed like this:

Now we need to set the preference

General options window:

Press OK and then save the preferences:

To make our design process faster we have to use a lot of shortcut keys. We can have a list of currently using shortcuts like the following:

Current hotkey list:

Now we have set most of the necessary things, so we can start drawing the schematic.
It’s all about selecting the right component, placing the component, connecting them and do the annotation.
First we add all the components. To add a component to the worksheet, press A, and the component selection window will open up. If you know the key word for the component, just enter the key word and press OK.
The key word for resistor is R and the capacitor is C, like that
Component selection window:

Use insert key to add the same component again. Press M to move a component after placing the cursor on it. Use ctrl + scroll to move entire page left/right, shift + scroll to move the entire page up/down

So far we have added the resistors and capacitors to the schematic, now we have to add the 555 IC, LED and 3 pin connector. If you don’t know the key word of the component you can use “by library browser” button, which will list you all the library components.

Once you have selected the required component you can use the export to schematic link to add the component to your schematic.
Selecting 555 IC from the component list:

When you finish adding the components for the particular circuit, the schematic editor will look like this.

Now we need to do the connections. You can keep the cursor at any point and press W to add a wire.

After you have finished the connections, it would be better if you add some text labels at the necessary areas. You can do that by using the T button as shown in the above figure.

Now our schematic diagram is almost finished. Next step is to annotate the components. We can automatically annotate the components using schematic annotation button. It will open up the following window.

Press annotate key to automatically annotate the components.

Our finished schematic will look like this:

For this particular tutorial it is not important whether the circuit is correct or not, all I’m trying to explain you nothing but, how to convert your circuit to a pcb.
Now if you wish you can do the ERC (Electric Rules Check) using the “schematic electric rules check” button.

Press “Test Erc” button for the following window:

If there are errors, which mean you have violated some rules. The errors will be shown in the schematic using markers and you can easily identify and correct those errors. If you have no idea about the ERC, don’t worry, it is not going to affect most of the simple circuits in anyway.
Now you must save the schematic like the following:

Components to Modules
2) Components to modules
Next step is to generate a netlist of the components using “Netlist generation” button:

Click the button “Netlist” for the following window:

Save the netlist file using the extension .net:

Now run cvpcb by to convert the components to modules which we can use, while we actually design the circuit board:

The cvpcb window will look like this:

For each component listed we must select the required footprint. It would be better if you list the entire footprint without filtering:

How could I identify which footprint will be appropriate for a particular component??
Which all footprint you will select, it should match up with the physical dimensions of the components in your collection. You can view the entire available footprint in a pdf format using the button as shown below:
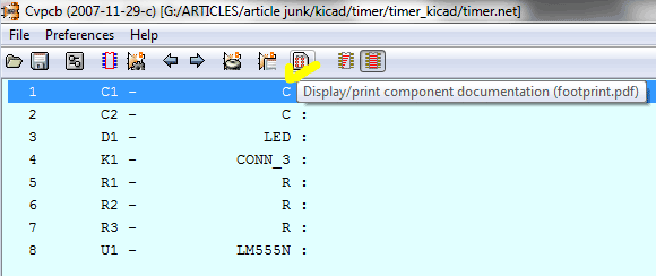
In your pdf viewer, set the zoom to 100% or actual size. Now simply place the component gently over the screen just above the footprints of the particular component and see whether it is matching or not. Note the label of that footprint and simply select the footprint with the same label from the list for that particular component.
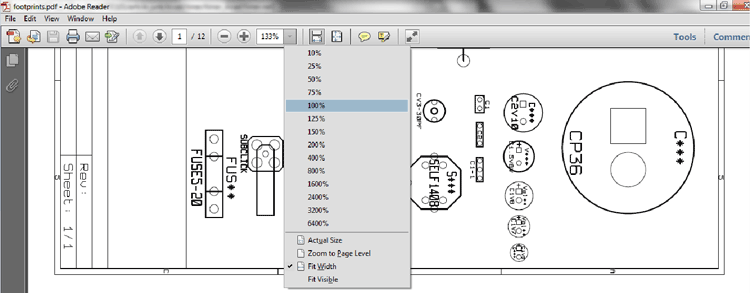
I’ve a couple of small electrolytic capacitor for the circuit which matches the following footprint like:

If you want to see the selected footprint in detail, keep the footprint selected in the list and press view selected part:

Here is the footprint in detail:

If you want to see the component in 3D, you can press the 3D button.
3D view of the component:

Close both the windows and double click the required footprint to get it selected. If you finish selecting the footprints, the page will look like the following:

Save the netlist using the save button:

Now run the pcb editor using the button “Run Pcbnew” either from schematic editor or from the main window.

PCB Editing
3) PCB Editing
Here is the PCBNEW window:

Before we proceed further I recommend you to do the required page settings like we have done for the schematic editor. After that it would be better if we draw an initial outline for the board, which we may change later if required.
Select the current working layer as “Edges Pcb”.

Use the graphic line button to draw the edges. You can set the coordinates at any corner as both zero by keeping the mouse pointer over it and pressing the space bar. Double click to finish the outline as you complete drawing it.
Here I’ve drawn a square outline for the pcb.

Now we are going to link the schematic and the pcb editor by reading the netlist.

Press “read” button for the following window.

In the following figure you can see that the modules corresponding to the components in the schematics have been added to the pcb editor. Now press the cancel button.

Now arrange the components by moving them into appropriate positions and orientations. Use M to select a component to move with the cursor.

After rearranging the components:

Now it seems that the outline of the pcb is too large for the circuit. Now I will show you how to delete items, in this case we are deleting the outline only.
Drag the cursor across the block holding the left button down and then release so that the entire block will get selected. Now right click and select the option delete block.

For this particular case, select the “include edge layer” and press OK.

You can use the same technique to delete the tracks, modules, zones, texts, drawings etc.
After deleting the current outline, we will draw a much smaller one. After rearranging the components and redesigning the outline, the pcb editor will look like this.

At this point you should make sure that your arrangement of components in the board is physically realizable. If it is not, you will run into a lot of troubles while assembling the components. In order to avoid such issues, there is an option for the 3D view of your board. Click the 3D display button.

If you are happy with the arrangement of the components in your board, you can start routing.
Before that you have to set a few things. Go to general options, where you can set the number of layers required, maximum links shown etc.

I’m going to make a 2 layered board, which is actually not required for this simple circuit, but I can show you how to add vias and adding tracks in both the layers.
Press OK button to save the settings:

Now we will be working mainly on the two important layers of our board
1) Copper layer – normal bottom layer if we consider a single layer board, where we do the soldering.
2) Component layer – The opposite side of the board, where we place the components.
Now your pcb editor window will look like this.

You can click on any pins to highlight the corresponding connected pins after you have clicked the “Net highlight” button as shown above.
In the following pins a set of highlighted pins are shown. Now you can add tracks connecting those pins using the “Add tracks and vias” tool. Make sure that you have selected the “Copper (page up)” from the drop down list as marked in the figure.

Now you can place track connecting the pins. Use END key to release the track once you have reached the end point.

In the following figure it is shown that I’m having trouble connecting the pin7 and the pins of two resistors R2 and R1.

So I’m going to place a part of the track in the component layer and connect the rest in the copper layer through vias.
First connect the two ends of the resistors normally. Now start adding track from pin 7, and once you have reached the point where you wish to add the via, right click and select “place Via” or just press V.

Now you can just route through the component layer and connect both the parts through another via as shown in the following figure.

Keep in mind that your component’s pin can also act as a via, as it is Printed Through Hole (PTH), connecting both the layers.
I’ve finished routing and my design is shown below.

Now let us have a 3D view of our board.

Generating Gerber File
4) Generating Gerber file
Select plot after clicking the file, to open the plot window.

Do the things in the plot window as shown in the following figure:

Now go to the main window and click the “gerbview” button to open up the Gerber viewer.

The following figure shows the Gerview window. Select “Load Gerber file”
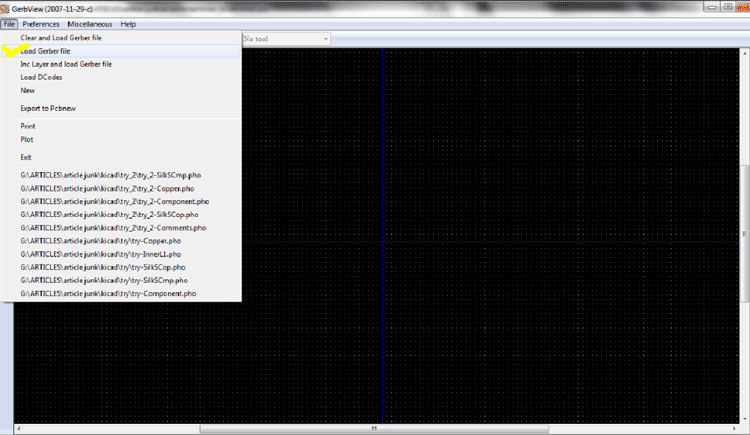
Let us view the copper layer first.

Gerber view for the copper layer:
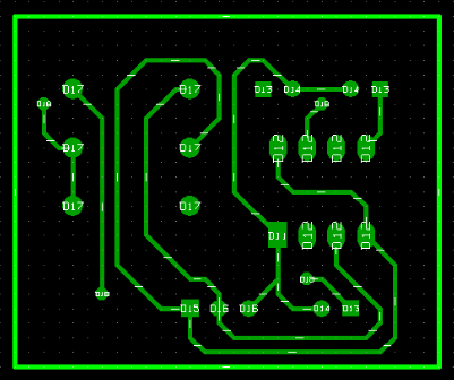
In order to view another file without mixing the view with the previous one, use the option “Clear and Load gerber file”.

This time we select the component layer:

The Gerber view of component layer will look like this:

In order to view all the layers at once use the option “Inc Layer and Load gerber file”.

Gerber view of the selected layers will look like the following:

Now you select the option “Save set up”.

Save the gerview file as the extension .cnf

Now click the save button and we finished. Next step is to send the Gerber files to your PCB manufacturer. Which all files you have to send depends on the pcb manufacturing process they have.
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.