In today’s electronic devices, many practical applications use hardware filtering implementation. These applications include electrocardiograms (ECG), image processing cameras, etc. Electrocardiograms are medical devices that record the human heart’s activity using a noninvasive approach by encoding heartbeat into signals. But before reading information from these electrical signals, they are filtered out from unwanted noisy signals introduced by the environment, using many hardware filters like low-pass, high-pass, and notch filters.
In this article, we will try to practice using hardware electronics components by designing some hardware filters to capture their input and output waveforms on the oscilloscope.
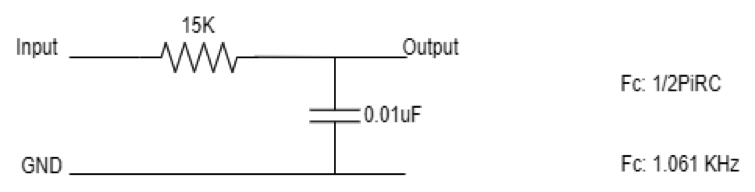
Low-pass filter: As we know, the low-pass filter passes the low-frequency components from any signal without attenuation (decrease in power). Low-frequency components can be defined using the cutoff frequency of the designed hardware filter.
The above design has a cutoff frequency of approx 1KHz. So, this low-pass filter will attenuate the frequencies above 1KHz and pass the frequency components below 1KHz.
The input signal has a peak-to-peak amplitude of 5 Volt.
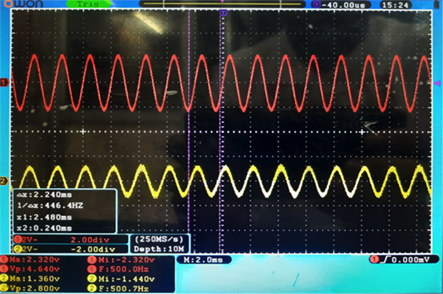
In the oscilloscope screen below, the input is in red, and the output is in yellow. And it is clearly shown that a low frequency of 500Hz is passed through the above-designed filter, which has a cutoff frequency of 1KHz.
There is no attenuation in the output signal.
Red prob – Input signal frequency
Yellow prob – Output signal frequency

Fig. 2: The image shows output variation for a low frequency of 500Hz is passed through the above-designed filter
But when the input signal frequency is increased from 500 Hz to 5KHz. The high-frequency components are attenuated. This can be seen in the figure below. The signal amplitude is attenuated from 5 V to 1 V.

Fig.3: The image shows the attenuated output when the input frequency is increased from 500 Hz to 5KHz
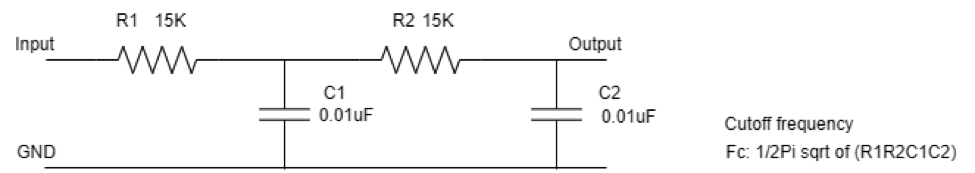
We have studied the first-order low-pass filter, which is designed using a resistor and a capacitor in series. But sometimes, it is not necessary that all the noisy frequency components can be removed using only a single-order low-pass filter.
Thus a designer needs a second-order filter.
Second-order low-pass filter
The second-order low-pass filter can be designed by adding one more low-pass filter stage to the first-order low-pass filter. Higher-order low-pass filters are obtained to remove or attenuate high-frequency components from the input signal completely.
A given formula calculates the cutoff frequency of the second order.
In the above figure, a signal of frequency 300 Hz is passed through a second-order filter with a cutoff frequency of 1 kHz. Thus the above circuit passes the signal frequency below 1 kHz and stops the frequency components above 1 kHz.
When a signal of frequency 3 kHz is passed through the above-designed filter. The output signal is almost lost or attenuated because this low-pass filter attenuates the frequency above its cutoff frequency of 1 kHz.
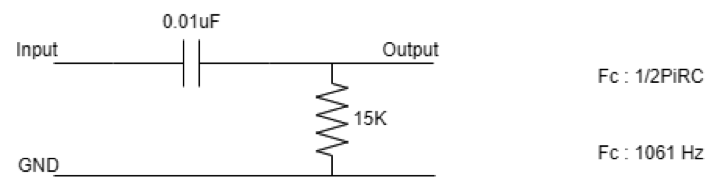
High-pass filter: High pass filter is the functional complement of the low-pass filter. As we have studied, the high-pass filter has high-frequency components in the pass band and low-frequency components in the stop band.
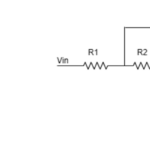
A high pass filter is designed, which has a cutoff frequency of approx 1KHz. The electronic components and their value used in the design are shown in the figure below.
When a signal of 500 Hz is passed through the high pass filter, which has a cutoff frequency of around 1 kHz, This filter attenuates the input signal, as shown in the below figure. The signal’s amplitude goes down to 2.80 V peak-to-peak from 4.64 V.
Red prob – Input signal frequency
Yellow prob – Output signal frequency
And when a signal with high-frequency components is passed from the above circuit. It is observed that the high-frequency components are passed without any attenuation from the filter.
This can be seen in the figure below.
In the above figure, an input signal is 2 kHz (shown in RED color), and the filtered (Output) signal is also 2 kHz (Shown in yellow color). This is how the high-pass filter works.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Hardware Filters, Tutorials






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.