Camera streaming systems have become popular, enabling users to record and/or live stream a video over the Internet. The Raspberry Pi (RPi) camera is widely used for its streaming feature as it easily captures live images and videos. Plus, it’s straightforward to interface the RPi camera with the Raspberry Pi 2/3/4 — or any other microcomputer.
For this project, we’re designing an online home-surveillance system using the Raspberry Pi Camera V2 and the Raspberry Pi 4B (note, RPi now also offers a high-quality camera for higher-resolution images). It will be possible to view the camera’s live video footage, which is streamed online, from any web browser.
The camera module is easily controlled with clean Python codes. The only condition is that the RPi and the device opening the browser must be connected to the same network.
Components required
1. Raspberry Pi 2B/3B/4B x1
2. Raspberry Pi camera V2 x1
3. Ribbon cable for connecting Raspberry Pi camera x1
Circuit connections
To design this project, it’s necessary to interface the Raspberry Pi camera module with RPi. Fortunately, RPi already has a camera serial interface (CSI).

The CSI port on Raspberry Pi 2/3/4.
First, locate the CSI port on Raspberry Pi, gently removing the plastic clip from the port. Insert the camera module’s ribbon cable in the CSI port such that connectors at the bottom of the cable face the contacts in the port.
Next, place the plastic clip back so that the ribbon cable is secured. Once attached to RPi, the camera module should look like the below illustration.

Securing the ribbon cable to RPi’s CSI port.
The device is now ready for operation. You can secure the entire assembly in a Raspberry Pi camera case as shown here…

The Raspberry Pi camera case.
Configuring Raspberry Pi
Before using the home surveillance camera system, there are a few additional steps:
1. Enable the CSI port in Raspberry Pi.
2. Write the Python code for live streaming from the camera module.
3. Locate the RPi’s IP address to access the live stream.
4. Configure RPi to automatically run the Python code on start-up.
By default, the camera module is disabled in Raspberry Pi. To enable the CSI port, go to the main menu and open the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool. It’s also possible to open this tool from the terminal by typing: sudo raspi-config.

From the configuration tool, select the interfaces tab, making sure the camera is enabled. Raspberry Pi will then reboot with the camera enabled.

The Python code is provided and explained below. You can write the code using Thonny IDE in Raspbian OS, saving the script file by a suitable name.
To check the IP address, open the bash terminal and run this command: pi@raspberry:~ $ ifconfig
This command enlists several network interface parameters. One of these parameters is the IP address of the network, ensuring RPi is connected.

For this project, the IP address is 192.168.29.242. Since RPi’s live stream will be available from port 8000, it could be accessed via the HTTP link: <IP_ADDRESS>:8000.
For us, this is 192.168.29.242:8000. However, the video stream can be captured on any device that’s running a browser via the above HTTP link.
As we’d like the Python script to begin anytime RPi starts, open the profile file in the Bash terminal by executing this command: sudo nano /etc/profile
Save the Python script under the name: onlineHomeSurveillance.py. To do so, scroll to the bottom of the file and add the following lines:
sudo python /home/pi/ onlineHomeSurveillance.py &
Note the ampersand at the end of the line, which lets the script run repeatedly without stopping.
Python script…
How the project works
The Raspberry Pi camera is connected to the CSI port of the Raspberry Pi (RPi). With the support of the picamera library, the camera module can be configured to web stream the video captured by the module.
The code for this project is a recipe from the picamera library. It uses Pytho’s built-in http.server module to use RPi as a video-streaming server. The video is streamed in MJPEG format.
You can find more picamera recipes from the official documentation of the library.
How the code works
The Python code runs a “try and exception” handling routine with an object instantiated from the PiCamera class. It captures a streaming output using the StreamingOutput() class into a variable “Output.”
Here’s what happens next:
- The StreamingOutput() class uses the IO library functions to capture the raw video stream.
- The start_recording() method is called, which begins recording the camera’s object (the video stream).
- The “object server” (from the http.server module) is instantiated to the socketserver by using the StreamingServer() class.
- The video streaming server is configured using the StreamingHandler() class.
- The method server_forver() is called on the server object to run the video streaming server, endlessly.
Take a closer look at the following lines of code:
with picamera.PiCamera(resolution=’640×480′, framerate=24) as camera:
output = StreamingOutput()
#Uncomment the next line to change your Pi’s Camera rotation (in degrees)
#camera.rotation = 90
camera.start_recording(output, format=’mjpeg’)
try:
address = (”, 8000)
server = StreamingServer(address, StreamingHandler)
server.serve_forever()
finally:
camera.stop_recording()
The results

Camera installation site.
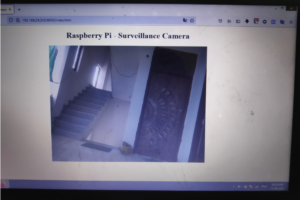
Live video footage from the RPi camera stream.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Electronic Projects