This article discusses about how to develop simple game pad hardware and interface it with the Raspberrypi board and also about the technique of interfacing a game code written in HTML5 with the game pad. Here a Snake game written in HTML5 and JavaScript is modified in such a way that it can be played with the new game pad having four push buttons. In this project the techniques of signals, pipe, fork etc. are used get the game running.
The game runs in a browser window and it communicates with the game pad through a Named Pipe or FIFO. There are multiple processes running which can read from the game pad and write the required commands to the FIFO for controlling the game. The JavaScript written in the game code simply reads from the FIFO for the input control data.
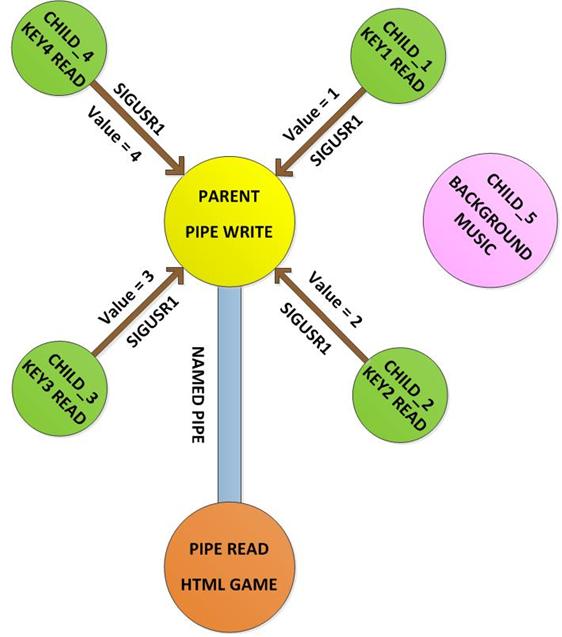
Fig. 2: Block Diagram Of Raspberry Pi Gamepad
Project Source Code
###
#include <bcm2835.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h>#define IN_PIN1 RPI_GPIO_P1_07
#define IN_PIN2 RPI_GPIO_P1_22
#define IN_PIN3 RPI_GPIO_P1_18
#define IN_PIN4 RPI_GPIO_P1_16#define OUT_PIN1 RPI_GPIO_P1_15
#define OUT_PIN2 RPI_V2_GPIO_P1_13
#define OUT_PIN3 RPI_GPIO_P1_12
#define OUT_PIN4 RPI_GPIO_P1_11#define SNAKE_FIFO_NAME "xyz"
void set_pins_input ( void );
void set_pins_output ( void );
void set_output_pins_low ( void );
void button_signal_handler ( int sig, siginfo_t *siginfo, void *context );
void signal_on_state_change_pin1 ( void );
void signal_on_state_change_pin2 ( void );
void signal_on_state_change_pin3 ( void );
void signal_on_state_change_pin4 ( void );
void sig_set_handler ( int signo, void *handler );
void sig_send_val ( pid_t id, int signo, int val );
pid_t child_id [ 5 ];
int st = 0;int main ( void )
{
int i;
int snake_fifo = -1;if (!bcm2835_init())
return 1;
set_pins_output ();
set_output_pins_low ();
set_pins_input ();
delay ( 100 );
sig_set_handler ( SIGUSR1, &button_signal_handler );if ( ! ( child_id [ 0 ] = fork () ) )
{
signal_on_state_change_pin1 ();
_exit ( 0 );
}
else;if ( ! ( child_id [ 1 ] = fork () ) )
{
signal_on_state_change_pin2 ();
_exit ( 0 );
}
else;if ( ! ( child_id [ 2 ] = fork () ) )
{
signal_on_state_change_pin3 ();
_exit ( 0 );
}
else;if ( ! ( child_id [ 3 ] = fork () ) )
{
signal_on_state_change_pin4 ();
_exit ( 0 );
}
else;while ( 1 )
{
system ( "echo x >> xyz" );
delay ( 100 );
}bcm2835_close();
return 0;
}void signal_on_state_change_pin1 ( void )
{
while ( 1 )
{
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN1 ) )
{
delay ( 50 );
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN1 ) )
{
sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 1 );
do
{
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN1 ) )
delay ( 1 );
delay ( 50 );
}
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN1 ) );sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 1 );
}
else;
}else;
delay ( 1 );
}
}void signal_on_state_change_pin2 ( void )
{
while ( 1 )
{
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN2 ) )
{
delay ( 50 );
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN2 ) )
{
sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 2 );
do
{
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN2 ) )
delay ( 1 );
delay ( 50 );
}
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN2 ) );
sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 2 );
}
else;
}else;
delay ( 1 );
}
}void signal_on_state_change_pin3 ( void )
{
while ( 1 )
{
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN3 ) )
{
delay ( 50 );
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN3 ) )
{
sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 3 );
do
{
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN3 ) )
delay ( 1 );
delay ( 50 );
}
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN3 ) );sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 3 );
}
else;
}else;
delay ( 1 );
}
}void signal_on_state_change_pin4 ( void )
{
while ( 1 )
{
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN4 ) )
{
delay ( 50 );
if ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN4 ) )
{
sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 4 );
do
{
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN4 ) )
delay ( 1 );
delay ( 50 );
}
while ( bcm2835_gpio_lev ( IN_PIN4 ) );sig_send_val ( getppid (), SIGUSR1, 4 );
}
else;
}else;
delay ( 1 );
}
}void button_signal_handler ( int sig, siginfo_t *siginfo, void *context )
{
if ( 1 == *( ( int * ) &siginfo -> si_value ) )
system ( "echo u >> xyz" );
else if ( 2 == *( ( int * ) &siginfo -> si_value ) )
system ( "echo r >> xyz" );
else if ( 3 == *( ( int * ) &siginfo -> si_value ) )
system ( "echo l >> xyz" );
else if ( 4 == *( ( int * ) &siginfo -> si_value ) )
system ( "echo d >> xyz" );
else;
bcm2835_gpio_write ( OUT_PIN1, st );
st = ~ st;
}void set_output_pins_low ( void )
{
bcm2835_gpio_write ( OUT_PIN1, LOW);
bcm2835_gpio_write ( OUT_PIN2, LOW);
bcm2835_gpio_write ( OUT_PIN3, LOW);
bcm2835_gpio_write ( OUT_PIN4, LOW);
}void set_pins_output ( void )
{
bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( OUT_PIN1, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_OUTP );
bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( OUT_PIN2, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_OUTP );
bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( OUT_PIN3, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_OUTP );
bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( OUT_PIN4, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_OUTP );
}void set_pins_input ( void )
{
bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( IN_PIN1, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_INPT );
bcm2835_gpio_set_pud ( IN_PIN1, BCM2835_GPIO_PUD_OFF );bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( IN_PIN2, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_INPT );
bcm2835_gpio_set_pud ( IN_PIN2, BCM2835_GPIO_PUD_OFF );bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( IN_PIN3, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_INPT );
bcm2835_gpio_fsel ( IN_PIN3, BCM2835_GPIO_FSEL_INPT );bcm2835_gpio_set_pud ( IN_PIN4, BCM2835_GPIO_PUD_OFF );
bcm2835_gpio_set_pud ( IN_PIN4, BCM2835_GPIO_PUD_OFF );
}void sig_send_msg ( pid_t id, int signo, char *msg )
{
union sigval *sigdata;
sigdata = malloc ( sizeof ( union sigval ) );
sigdata -> sival_ptr = msg;sigqueue ( id, signo, *sigdata );
free ( sigdata );
}void sig_send_val ( pid_t id, int signo, int val )
{
union sigval *sigdata;
sigdata = malloc ( sizeof ( union sigval ) );
sigdata -> sival_int = val;sigqueue ( id, signo, *sigdata );
free ( sigdata );
}void sig_set_handler ( int signo, void *handler )
{
struct sigaction *act;
act = malloc ( sizeof ( struct sigaction ) );
act -> sa_sigaction = handler;
act -> sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;sigaction ( signo, act, NULL );
}
###
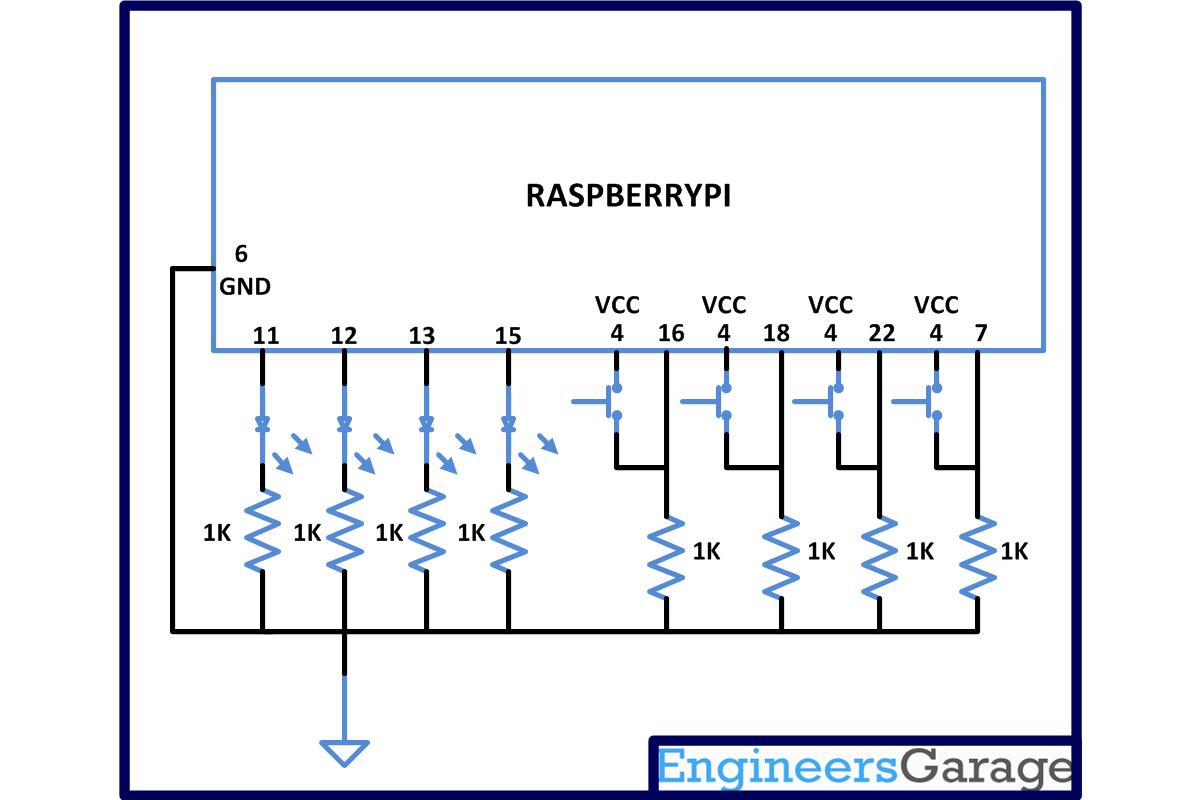
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Raspberry pi.
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, Raspberry pi.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.