This tutorial is about generating pwm (pulse width modulation) signal with stm32f103 microcontroller using its internal hardware timers. Stm32f103 microcontroller components/peripherals initialization code is generated using stmcubemx ide and code is written and compiled in keil MDK-ARMv6 ide. A simple led is derived on a fixed pwm signal output. Led dims and blinks according to the duty cycle and frequency that a particular pwm pin is outputting. A single Pwm signal is generated/Outputted in the tutorial, but you can generate multiple pwm signals with the same method and settings.
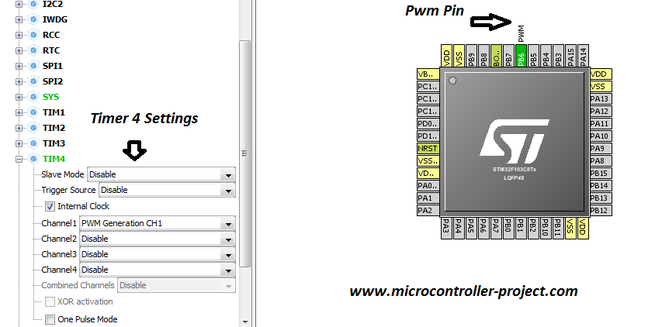
I am going to output a 1 Hz frequency and 50% duty cycle pwm(pulse width modulation) signal using timer-4 of stm32f103 microcontroller. Timer-4 channel-1 is used to output signal. Channel-1 corresponds to PB6 pin of stm32f103 microcontroller. At PB6 an led is connected on which pwm output can be seen. 1 Hz frequency in time domain is T=1/f > T=1/1 Hz > T=1 s. So 1 Hz frequency translates to 1 s and my duty cycle is 50% so the led at PB6 pin will blink at half a second rate.
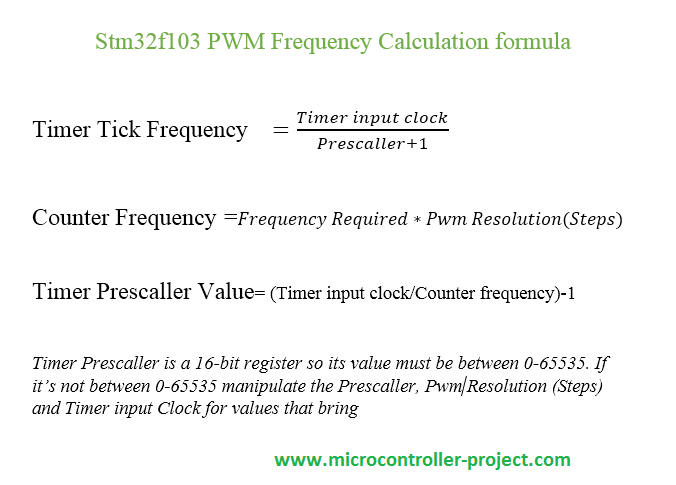
How to Generate Desired/Specific PWM Frequency? Formula derivation and Calculations.
Pwm Resolution
Stmcube-Mx code initializing steps an generating keil MDK-ARM code
I assume that you people are familiar with stmcube mx project creating process and know about the necessary steps. If not then take a simple tutorial
Timer 3 and 4 are stand alone and they do not collide with any other peripheral function. So its good to use them. I am using Timer 4 in the project/tutorial.
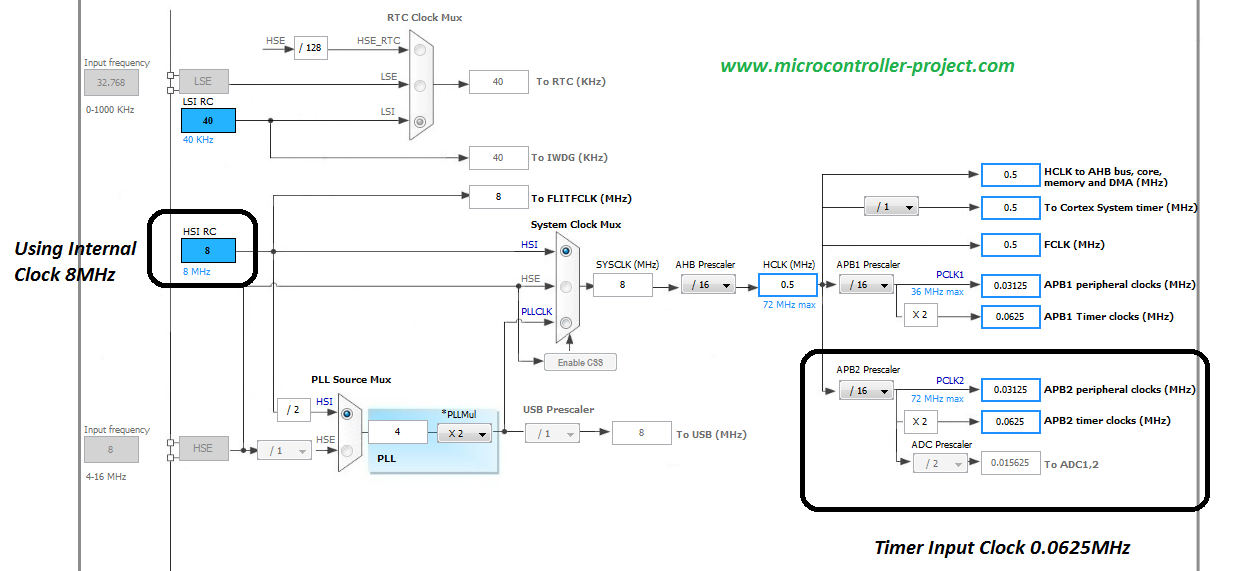
I am using Internal clock source so check this check box in the timer settings. I am using timer 4, channel 1 for pwm output so i selected channel 1. Channel 1 corresponds to PB6 of stm32f103 microcontroller. The settings diagram is given on the right side.
Calculating Values for 1Hz frequency and 50% duty cycle pwm signal output
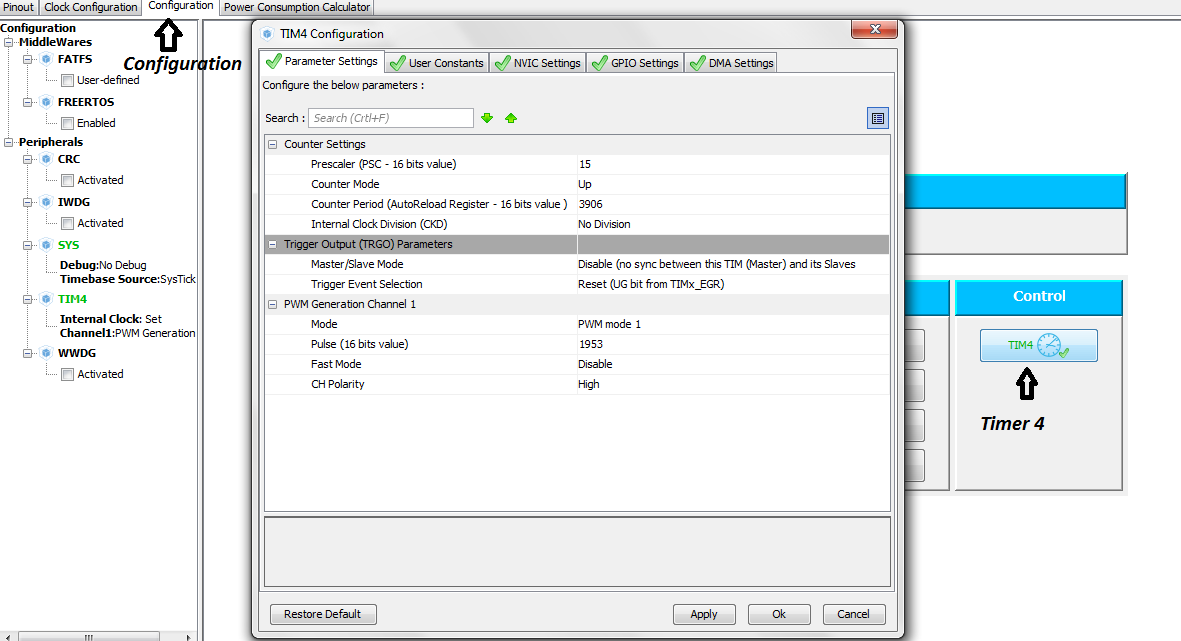
In the final timer settings it’s time to input the Counter Period/Pwm Resolution(Steps), Prescaler value and Pulse required. Pulse is the duty cycle required and in our case its 50%. Lets Solve the upper formula according to the pwm calculation formula’s given above.
Given values:
Timer Input Clock = 0.0625Mhz or 62500Hz
Required Frequency = 1 Hz (In Time Domain 1 second)
Counter Period/Pwm Resolution(Steps) = 3906 (I picked a random value)
Counter Frequency= frequency required * Counter Period
Counter Frequency= 1Hz * 3906 =3906 Hz
Timer Prescaller value=( Timer Input Clock/Counter Frequency)-1
Timer Prescaller value=(62500 Hz / 3906 Hz) – 1 = 15
Now we have both the value’s Timer Presaller value, Counter Period/Pwm Resolution(Steps) and also they are in 16-bit range. Now input the values in the timer 4 configuration. I selected the counter to be in UP mode(Count for 0 to 3906). Pulse is the duty cycle in our case its 50% so 3906*50% > 3906*0.5 = 1953.
Watch the Project Video Here…
You may also like:
Filed Under: Electronic Projects, STM32, STM32.





Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.