Second Generation (2G) technology was launched in the year 1991 in Finland. It is based on the technology known as global system for mobile communication or in short we can say GSM. This technology enabled various networks to provide services like text messages, picture messages and MMS. In this technology all text messages are digitally…
4G Technology
Wireless technology has transformed our lives in many ways. Until very recently, we needed a computer wired to a port, to get online. Even wired telephones are becoming a thing of past. Nowadays, we use our mobile phones for banking, to check ticket availability at a Cinema Hall, and many more. Wireless communication is the transfer of information over a distance without the use of enhanced electrical conductors or “wires”. And, Wireless networking refers to any kind of networking that does not involve cables. It helps in saving the cost of cables for networking in addition to providing the mobility. Mobile networks have evolved tremendously in last three decades. Cellular concept was introduced with 1G (‘G’ stands for generation) networks. Today, 4G technology is getting ready to storm the markets. Not only that, research on 5G technology has already begun.
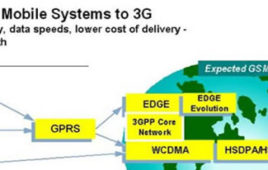
3G Technology
3G is the next generation of technology which has revolutionized the telecommunication industry. Apart from increasing the speed of communication, the objective of this technology is to provide various value added services like video calling, live streaming, mobile internet access, IPTV, etc on the mobile phones. These services are possible because the 3G spectrum provides the necessary bandwidth. Technically speaking 3G is a network protocol which refers to the generations of mobile phones and telecommunication equipments which are compatible with the International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT-2000) standards stated by International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The basic requirement for compiling to IMT-2000 standards is that the technology should provide peak data rates of atleast 200 kbit/s.