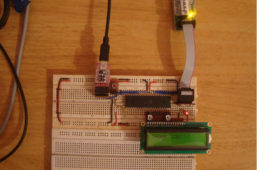
In any microcontroller the Boot-Loader is the first code which executes before the application code does. The major function of the Boot-Loader is to load the application code into the flash memory of the microcontroller and execute it. In AVR microcontroller the Self Programming Mode (SPM) helps the Boot-Loader to load a particular application from where the application binary is stored.The Boot-Loader may receive the code binary from other memory chips, SD-cards or through the serial port of the microcontroller in case of serial programming. It is then with the help of the SPM that the microcontroller write the binary code into the application flash section. In this particular project the operation of a Boot-Loader code using the SPM is demonstrated by re-writing flash memory with the code binary which has already been flashed into the built-in EEPROM of the ATMEGA16. The hardware used in this project includes ATMEGA16 as microcontroller, USBASP as the programmer and the software used are AVR STUDIO4 as IDE and AVR-BURNO-MAT as the burner software.
How to Use SPM for Flash to Flash Programming – (Part 33/46)
The Self Programming Mode (SPM) is a feature which enables a microcontroller to program its own flash memory. Using the SPM a microcontroller can program itself with an SPM code. The SPM is commonly used with the microcontroller Boot-Loader codes which help to program the microcontroller serially. In AVR microcontroller the SPM is available only for the code running in the BLS of the flash memory. With the help of the SPM a code in BLS can rewrite the application flash memory entirely or a part of it. It can even rewrite its own code in the BLS section. The SPM is a key factor of the Boot-Loader code since the major function of the Boot-Loader is to load an application code into the application flash section. The Boot-Loader may receive the code binary from other memory chips, SD-cards or through the serial port of the microcontroller in case of serial programming.
How to Initialize Peripherals from Boot Loader Section- (Part 32/46)
In almost all the microcontroller codes the peripheral initialization functions like uart initialization, spi initialization are written along with the different application codes. These initialization functions are actually repetitions of the original initialization functions. The same is the case with the external hardware initialization like LCD initialization, GSM modem initialization etc. Suppose the case in which the application codes required are stored in a memory chip or SD memory card so that there is an option to select between the applications. If all the application codes have the same functions for peripheral and external hardware initialization that will simply increase the size of the code only and the size of the memory required to store the codes. It will take too much time for the Boot-Loader to load such a large size application and there will be flash memory shortage issues due to the large code size. These issues can be solved by doing the initialization of the peripherals and the external hardware in the code running from the BLS itself.
How to Program in Boot Loader Section- (Part 31/46)
In the AVR microcontroller the flash memory is divided into two parts, namely Application Section and Boot Loader Section. A code can be programmed into either the Application Section or the Boot loader Section (BLS). The code programmed into the Application section runs normally and is used for common applications, whereas the code running in the BLS is provided with some special features. The code running in the BLS section can execute Self Programing Mode (SPM) instructions which are blocked for the code running in the Application section. Using SPM instructions the code from the BLS can rewrite the code in the application section or the code in the BLS itself. The BLS section is normally used for storing the Boot-loader code for the microcontroller. The Boot-Loader code can be used for initializing the peripherals in the microcontroller, initialize the devices connected to the microcontroller, select the application to load and execute from a storage medium, load the selected application to the application section, jump to the application section and execute the application.
Digital Book Cricket with ATtiny 85
The project described here is a digital implementation of “book cricket game” which students normally use to play in their childhood time. The heart of the project is 8 bit MCU from AVR family called ATtiny85. ATtiny85 are small and cheap microcontrollers which are convenient for running simple programs with low footprint. The software used for programming the MCU is Ardunio which is a popular open source IDE. The overall design is kept to a least for simplicity and ease to use. The main components used in the circuitry are 16X2 LCD which is used to display the characters in 2 lines with maximum of 16 characters in one line, a serial in parallel out shift register HEF4094, ATtiny85, 2 push buttons and 7805 voltage regulator which regulates the voltage supply to maximum of 5 volts. Shift register HEF4094 is used because normally when LCD is used it requires 7 connections to the pins on the display. But if shift register is used the number of connections to the MCU can be reduced to only 3 wires.