Samsung Electronics, a provider of advanced semiconductor technology, announced that four of its System LSI products received product carbon-footprint label certification from the Carbon Trust — the first of Samsung’s logic chips to do so. Having received the semiconductor industry’s first carbon-footprint accreditation for memory chips from the Carbon Trust in 2019, Samsung has now…
Infineon adds new current ratings to its EconoDUAL 3 portfolio
Infineon Technologies recently launched new current ratings for its EconoDUAL 3 portfolio with TRENCHSTOP IGBT7 chips. With the broad range of current classes from 300 up to 900 A, the portfolio offers inverter designers a high degree of flexibility while also providing increased power density and performance. In addition to solar and drive applications, the portfolio is…
Vishay’s high-voltage chip resistors save board space and component count
Vishay Intertechnology has introduced a new series of AEC-Q200-qualified, thick-film chip resistors with operating voltages up to 3 kV in the 2010 and 2512 case sizes. With their high-operating voltages, devices in the Vishay Draloric RCV-AT e3 series can be used in place of standard resistor chains. This allows designers to save board space in…
STMicroelectronics enhances automation with new, single-chip GaN gate driver
STMicroelectronics’ new STDRIVEG600 half-bridge gate driver is a high-current output and 45ns propagation delay. This offers a close match between the high and low-side outputs to, ideally, handle high-frequency switching of GaN enhancement-mode FETs. Also suitable for driving N-channel silicon MOSFETs at up to 20V, the STDRIVEG600 allows the flexibility to apply up to 6V…
Vishay’s new thin-film chip fuse is AEC-Q200 qualified
Vishay Intertechnology recently introduced a new fast-acting thin-film chip fuse. For automotive applications, the Vishay Beyschlag MFU 0603 AT is AEC-Q200 qualified and features current ratings from 0.5 A to 5.0 A. The device will be used in electric (EV) and hybrid-electric (HEV) vehicles, where it will provide protection for voltage sensing circuits in battery management systems,…
MediaTek offers computing devices 5G connectivity, multimedia & gaming tech
MediaTek announced the launch of its Kompanio 1300T, a SoC designed to power incredible experiences across computing devices. Built on the leading 6nm process technology, the chip is bringing premium performance to tablets with advanced 5G, multimedia, AI and gaming technologies for a premium user experience. Kompanio 1300T allows OEMs to build powerful, lightweight and…
Microchip launches first, single-chip network synchronization 5G solution
The latest 5G technology requires time sources to be synchronized throughout a packet-switched network 10 times more accurately than 4G requirements. Microchip Technology now makes it possible to achieve 5G performance with the first single-chip, highly integrated, low-power, multi-channel integrated circuit (IC), coupled with the company’s widely adopted and reliable IEEE 1588 Precision Time Protocol…
Renesas and Syntiant develop voice-controlled multimodal AI solution
Renesas Electronics Corporation, a supplier of advanced semiconductor solutions, and Syntiant Corp., a deep learning chip technology company, announced the joint development of a voice-controlled multimodal AI solution that enables low-power contactless operation for image processing in vision AI-based IoT and edge systems. These can include self-checkout machines, security cameras, video conference systems, and smart…
STMicroelectronics launches flexible automotive LED driver
STMicroelectronics’ ALED6000 single-chip automotive LED driver with integrated DC/DC converter is a low-BoM (Bill of Materials) solution that allows design flexibility and keeps the lighting intensity consistent as electrical conditions within the vehicle fluctuate. Suitable for exterior lighting such as daytime running lights, headlights, rear lights, stop lights, and turn signals, as well as interior lighting, the…
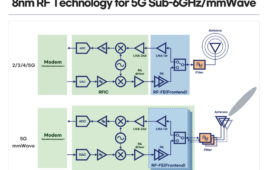
New 8nm RF chip architecture offers up to 35 percent increased power efficiency
Samsung Electronics, a provider in advanced semiconductor technology, is introducing its newest radio frequency (RF) technology based on 8-nanometer (nm) process. This cutting-edge foundry technology is expected to provide a ‘one chip solution,’ specifically for 5G communications with support for multi-channel and multi-antenna chip designs. Samsung’s 8nm RF platform extension is expected to expand the…
COB ICs
The quest to fabricate more and more devices in a minimum Silicon space has been ON since J. K and R. Noyce invented the first ICs. This quest has enabled scientific community to cross various technological frontiers. Sustained efforts to put more and more transistors on a wafer have led us to nanotechnologies. In the commonly used electronic technology, the semiconductor chips (also known as bare-dice) are individually mounted on a package, and wire-bonded to its I/O pins. This package is then mounted on a Printed Circuit Board (PCB). However, not only does packaging of single chip ICs cost more than the cost of the chips they contain, packaging of a chip take relatively large amount of physical space. Using a conventional single chip package and circuit board interconnect strategy, the package and interconnects took up over 50% of the timing budget as well.
Insight – How RFID Tag works
RFID tag is a small device which stores and sends data to RFID reader. They are categorized in two types – active tag and passive tag. Active tags are those which contain an internal battery and do not require power from the reader. Typically active tags have a longer distance range than passive tags. Passive tags are smaller and lighter in size than the active tags. They do not contain an internal battery and thus depend on RFID reader for operating power and certainly have a low range limited up to few meters. There are two important components of a RFID tag – A microchip and a coil (antenna). The antenna receives power and RF signals from the RFID reader and sends those signals to the chip. The chip receives those signals, computes them and sends back the data to RFID reader. We can figure out the précised working of a RFID tag through this diagram.