This tutorial explains the process of ac to dc conversion and why it is needed. The electricity that is delivered to our home is mainly AC (Alternative Current). Different countries have different standards for domestic AC lines ranging from 100 V to 220 V. Even so, most home appliances are DC (Direct Current)-operated, although devices…
Vishay’s new resonant transformer with integrated inductor simplifies PCB layouts
Vishay Intertechnology has introduced a new resonant transformer for inductor-inductor-capacitor (LLC) applications that feature the transformer and an integrated inductor in a single package. Designed to save PCB space while simplifying layouts and reducing component mounting requirements, the 5.5 kW Vishay Custom Magnetics MRTI5R5EZ offers fully tunable magnetizing and leakage inductance with minimal parasitic variation. The…
Insight: How a current transformer works
Transformer is an electrical device which works on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetism used to step up or step down the input [[wysiwyg_imageupload::]]voltage.Transformers are of different types for example: Power transformers, Current Transformers, Potential Transformers, Pulse Transformer, RF Transformer and Audio transformers. The most common application of Current transformer is to reduce the current and provide galvanic isolation in current sensing devices. Some typical examples include SMPS, motor control and electronic lightning ballasts.Some of you would know how a current transformer works. Windings, Core, connections and other things which many of you have surely seen in the books or in the diagrams.But how many of you have got the chance to see how actually it looks from inside. A small instrument but which works greater than its size. In today’s insight you will know how current transformers are made to work.
TI’s new transformer module technology maximizes EV drive time
Texas Instruments (TI) recently introduced the industry’s smallest and most accurate 1.5-W isolated DC/DC bias-supply module. The UCC14240-Q1 uses a proprietary integrated transformer technology to enable designers to cut their power solution size in half for use in high-voltage environments such as electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid EVs, motor-drive systems, and grid-tied inverters. With the accelerating…
STMicroelectronics launches energy-efficient isolated buck converters
Optimized for isolated buck regulator designs, STMicroelectronics‘ A6986I and L6986I DC/DC converter ICs have a wide input-voltage range and low quiescent current to ensure robust and energy-efficient operation in automotive and industrial applications up to 5W. The isolated buck topology drastically lowers the bill-of-materials in systems that require a regulated non-isolated primary voltage and one or more…
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is an apparatus for converting electrical power in an ac system at one voltage or current into electrical power at some other voltage or current without the use of rotating parts. Transformers have been an essential component in electrical as well as electronic circuits. Apart from stepping up or stepping down the voltages, they are used for providing isolation, for impedance mismatch and so on. Development of new technologies has reduced the usage of transformers, but still they are quite vital in many applications.
Audio Transformer
Amazed by the electronic music of your favorite band? Mesmerized by the way suddenly an electric guitar goes as loud as the singer? Like most of know, there is an expert recording engineer present in the studio to make sure that music instruments and the voices make a perfect blend. A critical device that helps in creating this blend is an audio transformer. Works just like any other conventional transformer; audio transformers are designed to work at audio frequencies, i.e. between 20Hz to 20 KHz. interestingly, the initial need to design to such transformer was to enhance long distance voice communication. Now serving essentially for professional musicians, audio transformers stand as one electronic-audio component. This article will cover technical and applicative features of audio transformers explaining how they are different from the conventional counterparts
Insight – How Pulse Transformers works
We are accustomed to using transformers in voltage stepping applications and in providing isolation to output circuits from the loading and transient effects that affect the input. These transformers work fine in most of the scenarios we encounter in day to day life, like the mobile phone charger, DC Adapter, the Step Down transformer at the nearby electrical distribution pole etc. But, when it comes to applications where square, pulse-like waveforms are required, the conventional transformers output a distorted waveform.Hence, for applications such as digital communications, camera flashes, radar systems and other fields where pulsed form of relatively high voltage is required, special type of transformers, ‘pulse transformers’ are required.
Insight – How Electronic Ballast works
Electronic ballasts are gradually replacing conventional magnetic ballasts (commonly known as choke) from the fluorescent tubes. They have higher efficiency as compared to magnetic ballasts and provide a flicker free start up to the tube. Also it does not produce the ‘hum’ sound which is very annoying with the magnetic ballastElectronic ballast uses semiconductor components and operates at 20 KHz-80KHz unlike the magnetic ballast which operates at 50 -60 Hz. At high frequency the lamp requires less input power, thereby increasing the efficiency. When power supply enters in to the ballast circuit, it first goes through an EMI filtration to block the ballast generated noise. Capacitors are used for the same.
Insight – How Mobile Phone Charger works
Latest mobile chargers are kind of power supply units that use the Switched Mode Power Supply (SMPS) technology. To understand the working phenomenon of a mobile charger, we need to understand the concept of Power Supply Unit (PSU). PSU is a device that transfers electrical energy from one end to another by changing its fundamental characteristics according to the requirements. Example of a PSU is an application that converts AC mains voltage to regulated DC voltage. PSUs can be of two types depending on the mode of operation – Linier and Switching. In these switching mode chargers, energy transfer is done by continuously switching electrical components (inductor, capacitor, etc) on and off. We can control the output voltage/current by varying the duty cycle, frequency or the corresponding phase.
Insight – How Transformer works
TransformerStep up transformer increases the magnitude of voltage while step down transformer decrease the magnitude of voltage. Depending on the ratio of the number of turns in the primary & secondary winding a transformer is characterized as step up or step down. is an electrical device used to step up and down the AC voltages. There are two types of transformers: Step up and step down transformer.When a varying current enters in the primary coil of the transformer, it generates a magnetic flux in the core and thus a varying magnetic field in the secondary coil. This varying magnetic field across the secondary coil produces a voltage in secondary coil. This effect is called mutual induction.
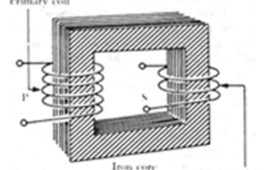
What is Transformer- it’s construction and working
TRANSFORMERS – CONSTRUCTION A transformer primarily consists of three basic parts- a primary winding which receives the electrical energy from the applied voltage source, and a secondary winding which receives the induced electrical energy and a core which provides a circuit of low reluctance for magnetic lines of force. Windings Windings, primary as well as…