Transformer is an electrical device which works on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetism used to step up or step down the input [[wysiwyg_imageupload::]]voltage.Transformers are of different types for example: Power transformers, Current Transformers, Potential Transformers, Pulse Transformer, RF Transformer and Audio transformers. The most common application of Current transformer is to reduce the current and provide galvanic isolation in current sensing devices. Some typical examples include SMPS, motor control and electronic lightning ballasts.Some of you would know how a current transformer works. Windings, Core, connections and other things which many of you have surely seen in the books or in the diagrams.But how many of you have got the chance to see how actually it looks from inside. A small instrument but which works greater than its size. In today’s insight you will know how current transformers are made to work.
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is an apparatus for converting electrical power in an ac system at one voltage or current into electrical power at some other voltage or current without the use of rotating parts. Transformers have been an essential component in electrical as well as electronic circuits. Apart from stepping up or stepping down the voltages, they are used for providing isolation, for impedance mismatch and so on. Development of new technologies has reduced the usage of transformers, but still they are quite vital in many applications.
Audio Transformer
Amazed by the electronic music of your favorite band? Mesmerized by the way suddenly an electric guitar goes as loud as the singer? Like most of know, there is an expert recording engineer present in the studio to make sure that music instruments and the voices make a perfect blend. A critical device that helps in creating this blend is an audio transformer. Works just like any other conventional transformer; audio transformers are designed to work at audio frequencies, i.e. between 20Hz to 20 KHz. interestingly, the initial need to design to such transformer was to enhance long distance voice communication. Now serving essentially for professional musicians, audio transformers stand as one electronic-audio component. This article will cover technical and applicative features of audio transformers explaining how they are different from the conventional counterparts
Insight – How Pulse Transformers works
We are accustomed to using transformers in voltage stepping applications and in providing isolation to output circuits from the loading and transient effects that affect the input. These transformers work fine in most of the scenarios we encounter in day to day life, like the mobile phone charger, DC Adapter, the Step Down transformer at the nearby electrical distribution pole etc. But, when it comes to applications where square, pulse-like waveforms are required, the conventional transformers output a distorted waveform.Hence, for applications such as digital communications, camera flashes, radar systems and other fields where pulsed form of relatively high voltage is required, special type of transformers, ‘pulse transformers’ are required.
Insight – How stepper motor works
Like other motors a stepper motor also converts the electrical power into mechanical rotation. A stepper motor rotates in distinct steps where each step is a fraction of a full circle. Stepper motors are driven with pulses and one set of pulses can move the stepper motor by one step only.The top and bottom mounting plates made up of aluminum with stator in between. The rotor shaft and wires are coming out. A Stepper motor has a stator and a rotor. The rotor has a permanent magnet attached to it. The stator is made up of coils as shown in the image. There are eight coils in this motor. Every coil in the motor behaves as an electromagnet, when they are energized by electrical pulses.
Insight – How DC Motor Works
DC Motors convert electrical energy (voltage or power source) to mechanical energy (produce rotational motion). They run on direct current. The DC motor works on the principle of Lorentz force which states that when a wire carrying current is placed in a region having magnetic field, than the wire experiences a force. This Lorentz force provides a torque to the coil to rotate.When we pass the input DC current to the coil through the brushes, it directly goes to the coil inside the motor body. This makes coil to work as an electromagnet. Magnetic fields of both magnets interact with each other that results in a force which in turn produces the necessary torque required to move the coil.
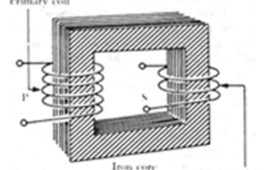
Insight – How Transformer works
TransformerStep up transformer increases the magnitude of voltage while step down transformer decrease the magnitude of voltage. Depending on the ratio of the number of turns in the primary & secondary winding a transformer is characterized as step up or step down. is an electrical device used to step up and down the AC voltages. There are two types of transformers: Step up and step down transformer.When a varying current enters in the primary coil of the transformer, it generates a magnetic flux in the core and thus a varying magnetic field in the secondary coil. This varying magnetic field across the secondary coil produces a voltage in secondary coil. This effect is called mutual induction.