The sensors and actuators have an important role in IoT. It the sensors and actuators that enable IoT devices to interact with the physical world. The large IoT applications like smart home, smart transportation, smart grid and many others are intelligent systems that connect the world in an automated way to ease human efforts. The collective aim of such systems is to nurture the concept of IoT which is fulfilled with the use of tiny sensors. The whole Sensor Network is tightly coupled directly or indirectly with communication Network (Internet) where intelligent monitoring, management, and data processing can be achieved via the usage of networked cloud computing devices. This sensor network is when interconnected through a wireless interface (like Zigbee in Industrial applications) is referred as Wireless Sensor Network (WSN).
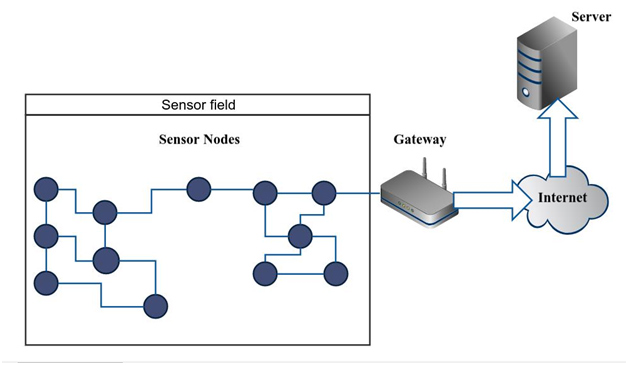
A wireless sensor network consists of several Sensor Nodes which monitor the surrounding through the use of different tiny sensors and provide the outputs in the form of electrical signals which are transmitted to the controller for further processing. The sensor nodes communicate with each other using radio signals when they are on the same network. When the sensor nodes want to send the data to the cloud or they want to communicate with sensor nodes connected to the different network then there is need of a Gateway because these devices do not have TCP/IP stack with them. The Gateway acts as a bridge that does some kind of protocol conversion and transmits the data to the network or to the different devices. The wireless sensor nodes send the information to the Gateway then the Gateway forwards that information to the communication network and the cloud gets the information through the communication network.
The individual sensor nodes in the wireless sensor network are designed to be resource constrained which means they have limited storage capacity, relatively slow processing speed and limited communication bandwidth. But despite of these limitations, they have actually gained rich popularity due to their flexibility in solving problems in different application domains. They have the potential to automate the large scale applications like military applications, area monitoring, transportation etc.
To allow users to access the WSN network from all over the world, it is necessary to deploy the WSN network’s data to the Internet. So, the connection of WSN with TCP/IP network is very important but due to the sensor node’s limitations, it is not possible to install full existing TCP/IP stack into a sensor node. So, to connect WSN and TCP/IP network, a Gateway is needed. At one end of Gateway, the output from WSN network can be provided on the basis of some protocol like UDP or Zigbee then in the middle, it converts the protocol in to protocol compatible with TCP/IP network and finally at the other end, it provides the data to cloud using TCP/IP protocol.
The advantage of this approach is that this way both WSN and internet remain completely independent. It is the responsibility of gateway to do required protocol conversion. But everything depends on gateway. Any point of failure in gateway can stop the transmission of WSN data to Internet.
Fig. 1: Block Diagram showing Wireless Sensor Node Data to Server
Wireless Sensor Network Topologies –
There is a standard to connect the wireless sensor nodes to form a network. WSN nodes are typically organized in one of three types of network topologies – Star topology, cluster topology and Mesh topology.
In star topology, each sensor node connects directly to a Gateway. In a cluster topology, each node connects to a node higher in the tree and then connects to the gateway and the data is routed from the lowest node on the tree to the gateway. In mesh network topology, Nodes connect to each other in a random fashion and pass the data through the most reliable path available. This increases the reliability in system.
Fig. 2: Image showing WSN Network Topologies
WSN Protocols –
There are many wireless protocols and standards which are used WSN networks. Some of them are as follow –
1) IEEE 802.15.4 – This is the main communication standard for the low rates WSN Networks. It defines the physical and link layer for short-range wireless transmission with low power consumption, low complexity and low cost. It is used for purposes other than like Wi-Fi, which offer more bandwidth and require more power.
2) Bluetooth – It is also wireless short range communication protocol defined by Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG). With Bluetooth 4.0 or plus, they have included a low energy protocol which is ideal for low power devices used in IoT.
3) Zigbee – The Zigbee specification enhance the IEEE 802.15.4 standard by adding network layer, security layers and an application framework It is called Zigbee protocol. It covers various application areas like home and building automation, health care, energy and electricity management and telecom services.
There are many other standards which can be used for Wireless Sensor Network. Learn more about these standards from the following tutorial –
Physical and Data Link Layer Protocols for LAN HAN and PAN
WSN Features –
The WSN is characterized by the following features –
1) Power consumption constraints for nodes using batteries – The WSN is specifically designed for low power devices which are usually battery-operated.
2) Ability to cope with node failures – The WSN network works on the principle of distributed work load. So, any node failure does not affect the whole WSN network.
3) Heterogeneity of nodes – The data collected from sensor networks is usually saved on a central base station which allows any individual node to monitor or control wireless sensor network through a web browser.
4) WSN has scalability to large scale of deployment.
5) It has ability to withstand harsh environment conditions.
6) It is easy to use.
In the next tutorial, learn about Zigbee Protocol which is widely used in Wireless Sensor Networks for industrial applications.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Electronic Projects









Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.