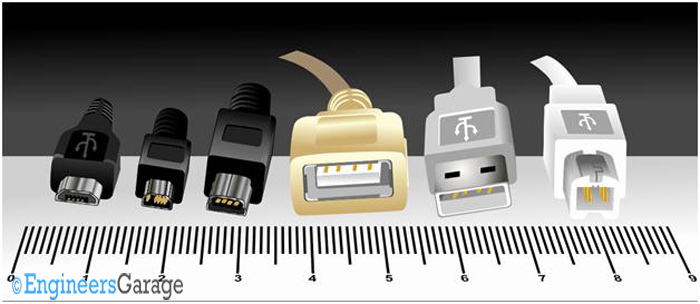
Fig. 1: Image showing different types of USB connectors
The USB standard connectors have both male and female types. The male connectors are usually found at the cables and are commonly referred to as USB plug. The female connector usually found sitting inside the device and are commonly referred to as USB receptacles. USB connectors are polarized connectors, it is impossible to connect the USB plug to the receptacle upside down. No screws or clips are used in USB connectors since they are designed for frequent connection and disconnection. A small amount of force is only required to plug the connector in and out. USB connectors are designed for strength, durability and maximum number of mating cycle.
Let us take a look at the USB standard connectors, their applications and pin-out.
Type-A
These types of USB connectors are identified by their rectangular shaped plug. The plug is always found in the cable and the receptacle is found in the device. They are commonly used with keyboard, mouse, data-cards etc. The image of a type A connector and the pin position is shown in the following image.
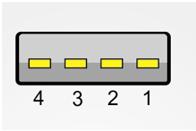
Fig. 2: Representational Image of Type-A USB Connector
The pin-position of Type A USB connector
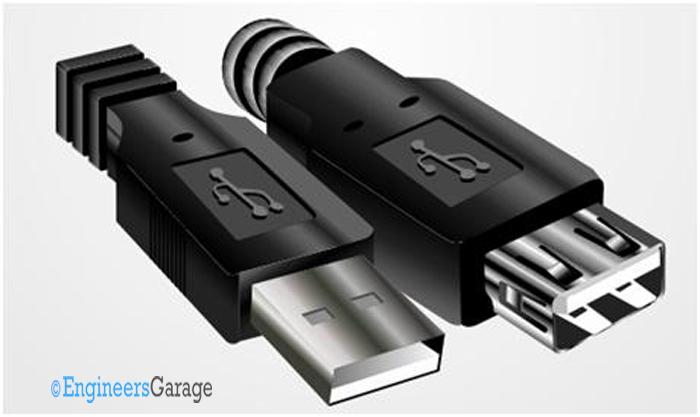

Fig. 3: Image of Type A male and female USB connector
The pin-out of the Type A USB connector
PIN 1 ——————- VBUS
PIN 2 ——————- D –
PIN 3 ——————- D+
PIN 4 ——————- GROUND
Type-B USB Connector
Type-B
The Type-B connectors are designed to be used with devices which are meant to be connected with the device having Type-A receptacle. These connectors are square shaped with beveled exterior corners. They are found in USB devices like printers, USB to serial converters, simple USB powered devices like battery chargers etc. The image of a type B connector and the pin position is shown in the following image.
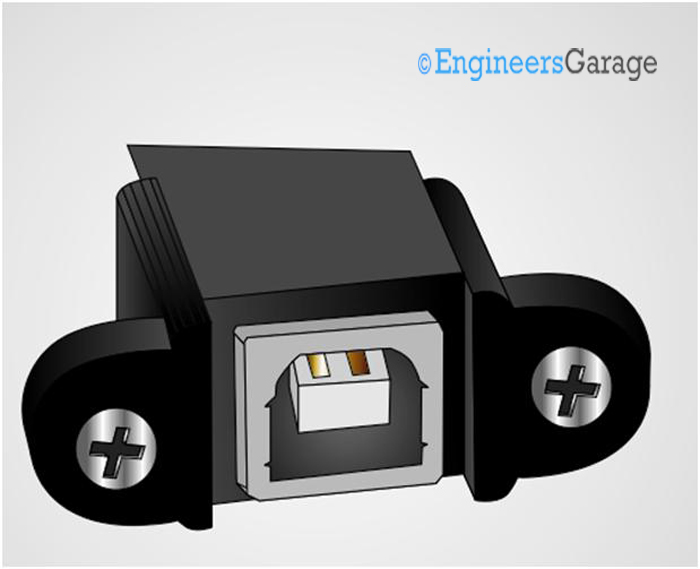
Fig. 4: Image of Female Type B USB connector 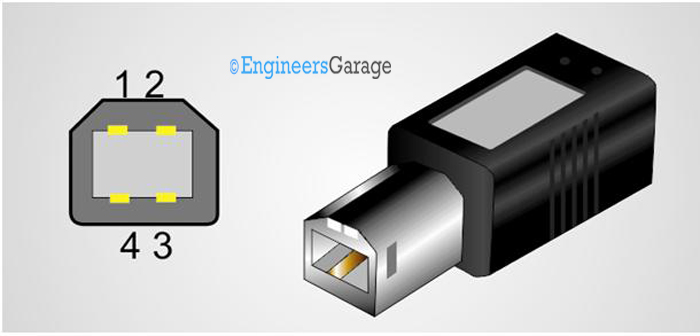
Fig. 5: Image of Male Type B USB Connector and the pin position of the type B USB connector
The pin-out of the Type A USB connector
PIN 1 ——————- VBUS
PIN 2 ——————- D –
PIN 3 ——————- D+
PIN 4 ——————- GROUND
Mini USB Connectors
Mini-A and Mini-B
The Mini-A and Mini-B connectors are use with USB devices which are meant to be connected to Type A receptacles. But these connectors are smaller than the Type B connector. They are designed to be connected with small sized USB devices like camera, mobile phones etc.

Fig. 6: Image of Mini A and Mini B USB male connector and their pin positions
The pin-out of the Mini USB connector
PIN 1 ——————- VBUS
PIN 2 ——————- D –
PIN 3 ——————- D+
PIN 4 ——————- ID
PIN 5 ——————- GROUND
Micro-A Micro-B
Micro USB Connectors
The Micro-A and Micro-B connectors are introduced to replace the Mini-A and Mini-AB connectors. They are smaller in size than the Mini connectors. They have up to 10, 000 mating cycles. The Micro connectors are used with small devices like mobiles, smart phones, PDAs etc.

Fig. 7: Image of Micro-A and Micro-B USB connectors and their pin positions
The pin-out of the Micro USB connector
PIN 1 ——————- VBUS
PIN 2 ——————- D –
PIN 3 ——————- D+
PIN 4 ——————- ID
PIN 5 ——————- GROUND
Sample specification:
Voltage rating —————————- 30 VAC(rms)
Current rating —————————- 1 Amp .
Contact resistance ———————- 50 m Max.
Insulation resistance ——————– 100 M Min.
Dielectric strength ———————– 100 VAC Min.
Summary
Universal Standard Bus (USB) is design with a motive of standardizing all the existing standard connections into a single universal standard
· {C}{C}{C}{C}{C}{C}USB connectors defined in the standard are available as Type A, Type B, Mini A, Mini B, Mini AB, Micro A and Micro B.
Mini A, Mini AB and Micro A connectors are found rarely yet all other connectors are widely used in electronic gadgets.
Filed Under: Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.