Visitor counter is based on popularly known 4026 decade counter and divider IC with 7 segment displays to display the number of visitors. In this circuit we are using LDR as a sensor for sensing the visitors with few more components. CD4033 is a Johnson counter IC commonly used in digital display. It contains 5 stage Johnson decade counter with decoder which converts the Johnson code to 7 segment decoded output. It means it will convert the input into numeric display which can be seen on 7 segment display or with the help of LED's. It can be used for displaying analogue value, such as temperature with pic- microcontroller, and can be used for counting objects. In this, counter will advance on receiving a high at its clock pin (pin 1).
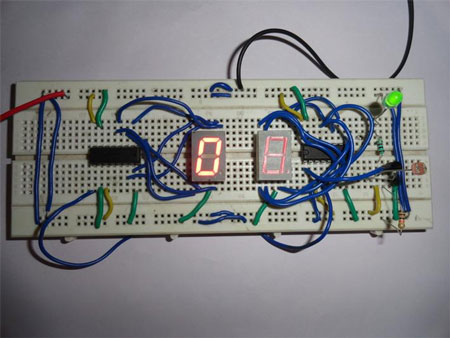
Fig. 1: Prototype of Circuit on Breadborad Showing working of Visitor Counter
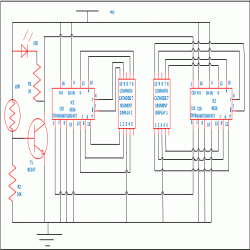
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.