Making Watchdog Timer with NRF24LE1 Circuit
Till now in the series on NRF24LE1, we have covered many interesting and special features which differentiate NRF from others. Today we are going to discuss an important functionality of microcontrollers which helps them recover from failure. Suppose, I give you a task to solve in predefined time and you fail to do it in allotted time then you will have to start it from the beginning. The word ‘Timeout’ can be used here to clarify the concept.

Fig. 1: Prototype of NRF24LE1 based Watchdog Timer
But do you know that microcontroller can also keep track of time and if it fails to achieve the task in allotted time, it can restart itself. This is done in order to avoid malfunction and hanging. Or we can say in case of system failure it automatically restarts itself. This also eliminates the need of human for manual restarting. It is an essential part in designing remote and automated systems. The timer which is used to keep track of time is known as Watchdog Timer. The name is itself clear. The Mars Rover also uses this functionality to recover from system failures and malfunction.
Some features of Watchdog Timer in NRF24LE1 are:
• Minimum Watchdog timeout interval : 7.8125ms
• Maximum Watchdog timeout interval : 512 s
• Uses 32.768 KHz frequency clock


| FUNCTIONS | INPUT PARAMETER | OUTPUT | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| hal_wdog_init() | 16-bit start value | – | To initialize the watchdog timer with start value |
| hal_wdog_restart() | – | – | To restart the watchdog timer to avoid reset |
We have written a code to understand the functioning of Watchdog properly.
You may also like:
Project Source Code
###
//Program to#include"reg24le1.h" // I/O header file for NRF24LE1#include"hal_delay.h" // header file containing delay functions#include "hal_wdog.h" // watchdog functions library// main functionvoid main(){CLKLFCTRL = 0x02; // starting 32.768 clockwhile(!( CLKLFCTRL & 0x40)); //waiting for clock to startP0DIR = 0; // port0 as outputP0 = 0xff; // port0 highdelay_ms(200); // wait 200msP0 = 0x00; // port0 lowhal_wdog_init(0x0200); // 4seconds time-outwhile(1); // infinite loop}###
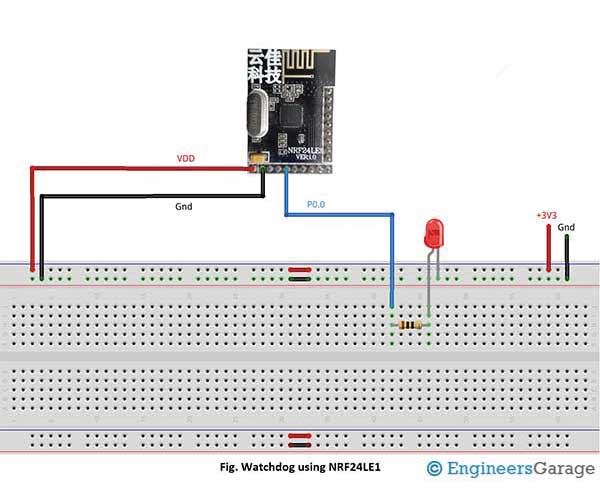
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Tutorials
Filed Under: Tutorials






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.