Project has basically two modules:-
1) Wave generator
2) Wave counter

Fig. 1: Overview of LPC2138 ARM Microcontroller based Wave Counter
Wave generator generates square waves of certain frequency. Wave counter counts the positive edges and thus the waves and displays the frequency on a serial device like a laptop or serial LCD etc.
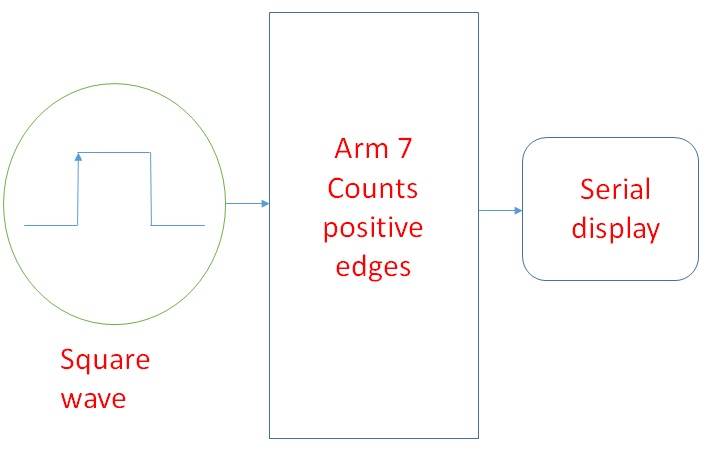
Fig. 2: Diagram showing working principle of Wave Counter
MATERIALS REQUIRED
1) WAVE GENERATOR (OPTIONAL)
– 1 lpc2148 board = Rs 2000
– Or atmega16 board =Rs 250
2) WAVE COUNTER
– 1 lpc2148 board = Rs 2000
– Some serial display
TOTAL=Rs 2000-2200
WORKING
– WAVE GENERATOR (OPTIONAL)
Basically it generates square waves of certain frequency. The concept here used is time scheduling. Timer 0 is set as fast interrupt request and after every 1 ms the interrupt is generated and the ISR is executed. In the ISR a set variable is taken and is given certain value eg=50. So as After every 1 ms ISR is executed a count is incremented and compared with set and as a match is found the output pins initially low are set high that is toggled and count=0. So again as ISR is executed count is incremented and again when count = set output pin is set to 0 (toggled) from high so like this square waves are generated of time period=2*set and the
Frequency= (1000/ (2*set))
Eg set = 50
Time period = 100ms
Frequency = 1000/100 = 10 Hz
And same is found on serial display through wave counter and can be seen in simulation.
WAVE COUNTER
In this input wave is given through I/O pin and then counting begins. Here also time scheduling is used. Timer 0 is set as fast interrupt request and after every 2 us ISR is executed. And a static variable count is incremented and if count==1 the status at I/O pin is stored in pre variable. Then again after 2 us ISR is executed and count is again incremented if count==2 status at input I/O pin is stored in nex variable and count=0. So after this we have previous state in pre and next state in nex. Then pre is compared with 0 and nex with 1 now if pre == 0 and nex == 1 means a positive edge has occurred so another variable num is incremented num++. To keep track of time another variable task[0] is incremented after every 2 us and as it equals 16000 i.e time elapsed = 32000 us or 30-32 ms this is actually done by calibrating task[0]. Now as task[0]==16000 the value stored in num at that time equals frequency of the wave. The same is sent to serial terminal and displayed.
– I used 3 pins 3, 4, 5 of lpc2148 to generate waves and choose set=50 so frequency=10.
– For wave counter i.e second lpc2148 I used 2, 3, 4 pins as input pins.
– I displayed result as follows:-
10 11 10 n
11 11 10 n
Here 3 values represents frequency at 3 pins and if frequency < 40 then letter displayed = n
Otherwise letter displayed = s
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
– IDE used KEILUVISION 4
– SIMULATED on PROTEUS 7.1
– BOARD used LPC2148
– Codes provided
– pulse_gen
– wave_counter
– Hex files provided
– pulse_gen.hex
– wave_counter.hex
– Some additional .h and .c are also provided like delay, uart0, timerfiq etc.
All these are in their respective folders i.e:-
-wave_counter
-wave_generator
-Build schematic on proteus load the provided hex files in respective lpc2148 then run to see output.
Circuit Diagrams
| Circuit-Diagram-LPC2138-ARM-Microcontroller-Based-Wave-Counter | 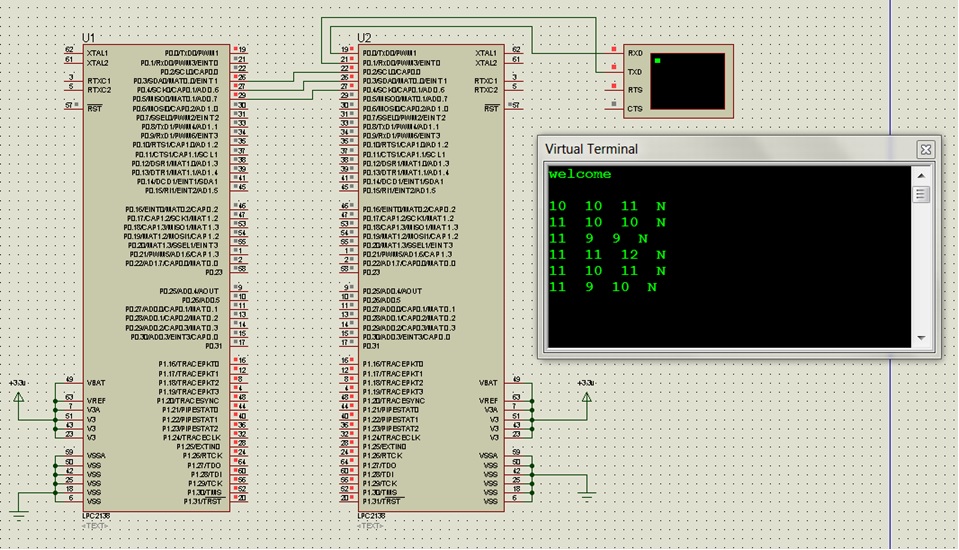 |
| Circuit-Diagram-LPC2138-Microcontroller-Based-Wave-Counter | 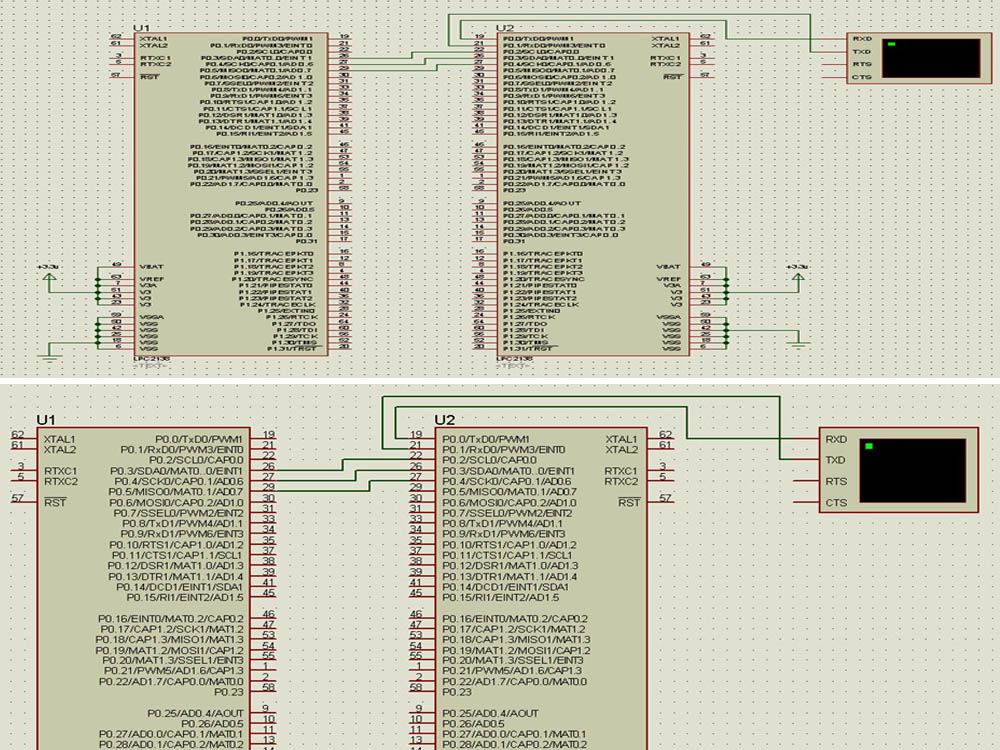 |
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.