EMC test is known as Electromagnetic Compatibility, a certification for electronic devices to maintain their limitation of electromagnetic waves. As discussed in the previous article, there are two types of EMC tests – emission (EMI) and immunity (EMS). EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) tests measure the magnetic waves emitted by the device, and EMS (Electromagnetic Susceptibility) tests are performed to test emission handling immunity of the device.
This article is about some of the most common EMS or immunity tests performed at EMC test labs on electronic devices. The tests performed along with the EMI test can vary according to the application of the equipment under test (EUT). The most common immunity test is given below.
The EMC immunity test is commonly performed on either continuous or transient phenomena. EMS is also known as EMC immunity. EMC immunity testing measures the device’s ability to survive in the presence of interference generated by other devices.
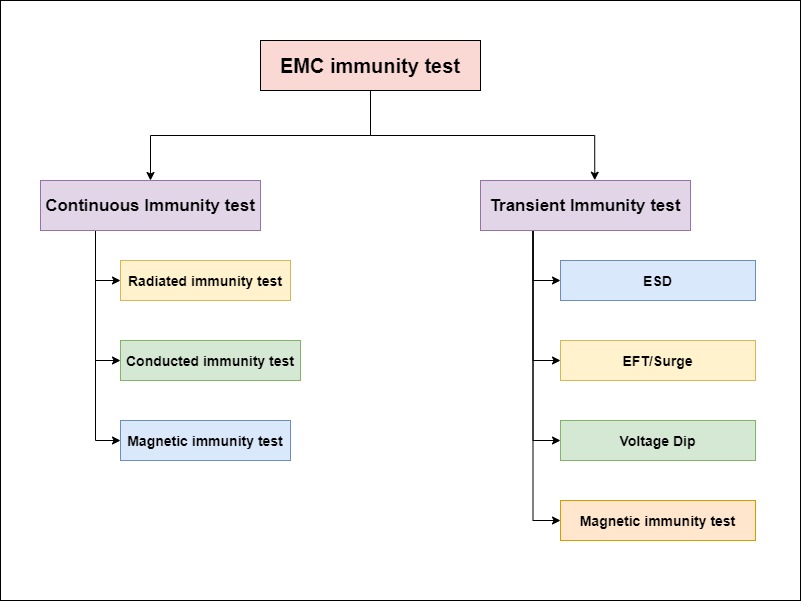
Types of EMC Immunity tests
As shown in the block diagram, there are two types of EMC immunity tests, continuous and transient. Both have their testing methods. Below is the diagram showing the most common immunity tests.
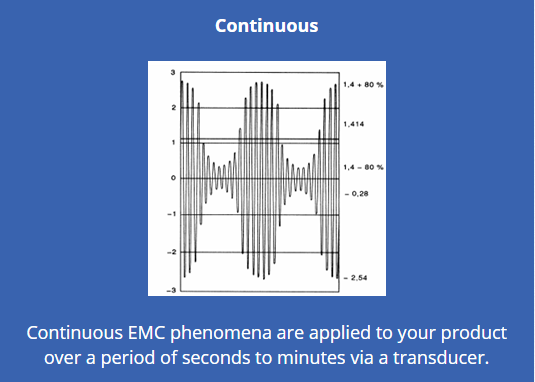
Continuous Immunity testing
In continuous immunity test, the device is placed in an environment where different types of continuous waves are applied to the device for several minutes or several hours. This test simulates the RF interference signal present in the real world. Some common continuous immunity tests are explained below.
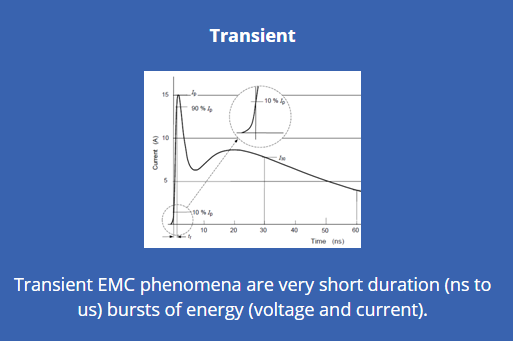
Transient Immunity testing
In a transient immunity test, a short burst of energy is applied to the product – the EUT or equipment under test – for a short time. Like continuous immunity, transient immunity is applied to a product’s signal/data ports, enclosure ports, and power ports.
Types of Continuous Immunity test
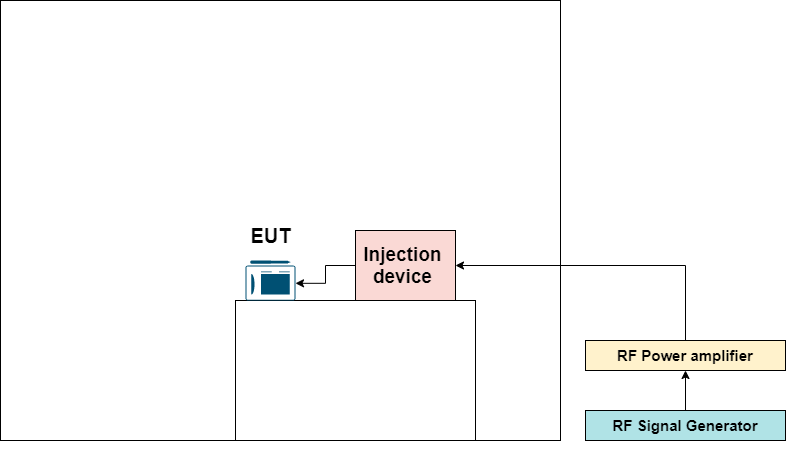
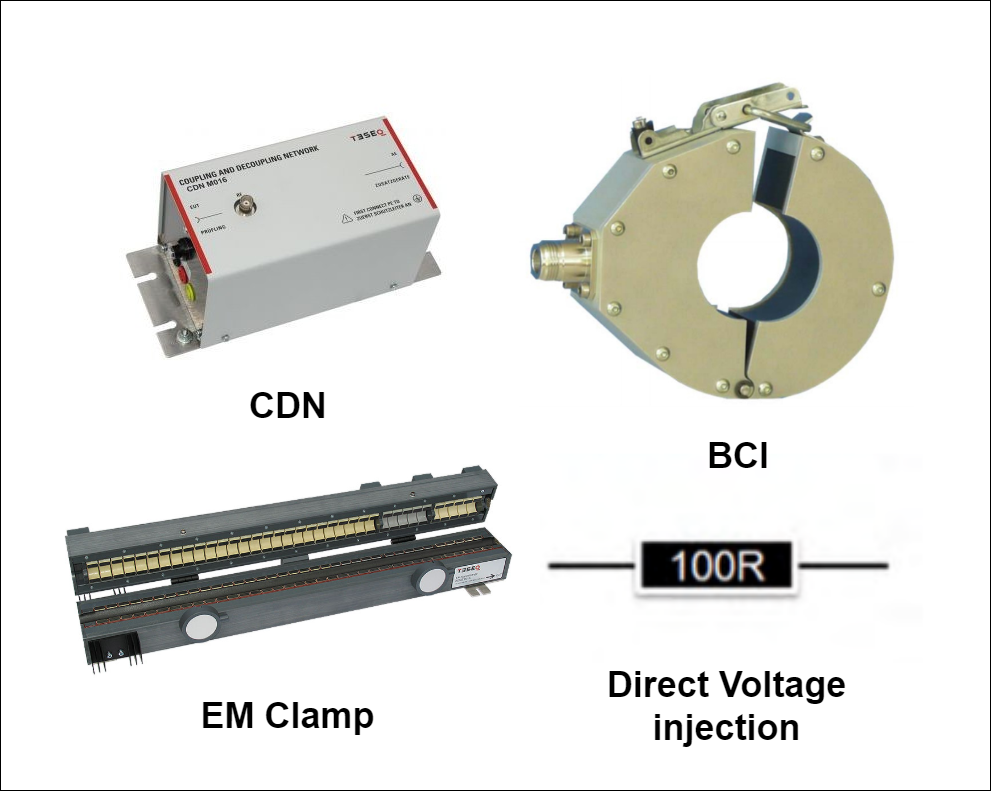
- Conducted Immunity test
An RF signal generator and amplifier generate an electromagnetic field. This electromagnetic field is injected in cables going to the device like signal cable, data cable, or power cable by an injection device. The most common injection device is CDN, BCI probs, EM Clamp, and direct voltage injection equipment. Because this test is continuous, many standards call it “Radio Frequency”. As seen in the diagram, the signal is transmitted to the EUT.
- Radiated Immunity test
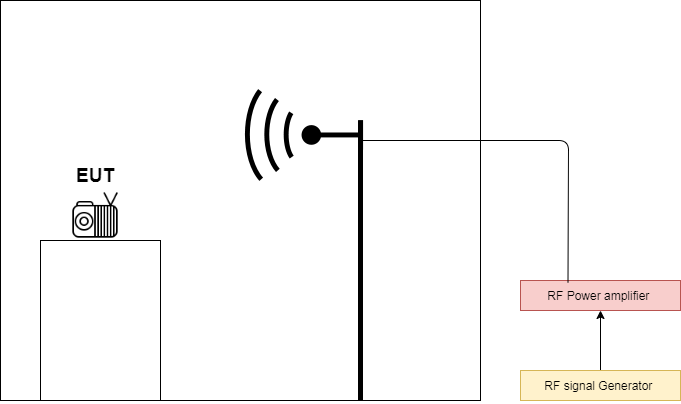
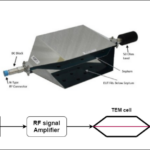
Radiated immunity test is performed to evaluate the ability of the device to perform normally in the presence of electromagnetic radiation generated by other sources through the air. The electromagnetic radiation can vary with different devices like cellphones, wifi routers, microwaves, etc.
The enclosed device and its enclosure and the cables are exposed to generated electromagnetic radiation via an RF amplifier. An RF signal generator is used to generate electromagnetic waves, which are the input of the RF amplifier. The output of the RF amplifier is generated by an electromagnetic field of varying frequency and transmitted via an antenna. As shown in the diagram, the antenna transmits electromagnetic waves for EUT.
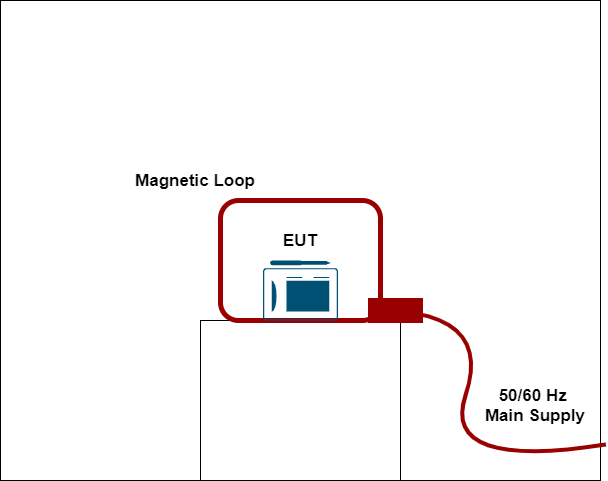
- Continuous Magnetic Field Immunity test
A magnetic field is generated in a loop of wire (antenna). The magnetic field in the wire is varied according to the voltage variation in the mains AC supply. The device is exposed in the loop of wire where a magnetic field is produced. The EUT is exposed in this field to evaluate the product’s performance for a specific time. As shown below, the EUT is placed between magnetic fields, which oscillate according to the mains supply.
Types of Transient Immunity tests
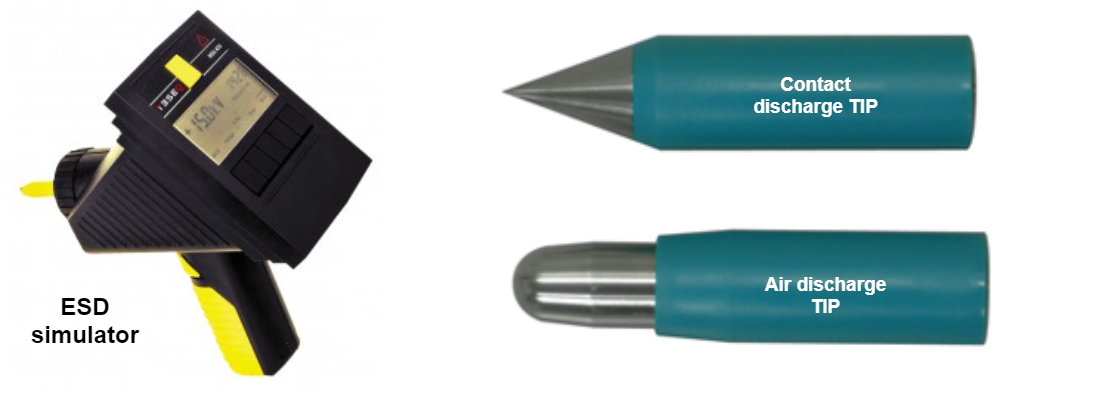
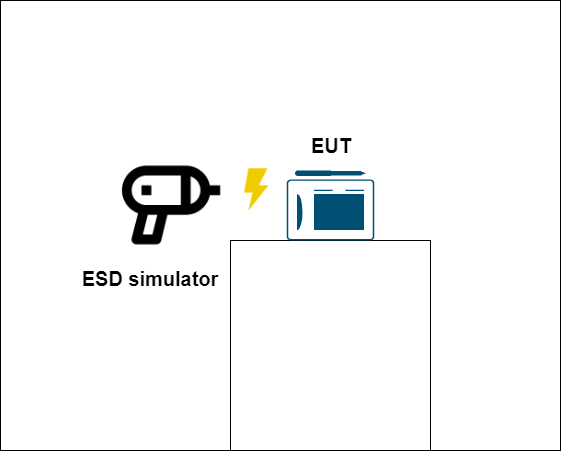
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
When two electrically charged object comes in contact, they discharge electricity such as when the human body comes in contact with an electric device. This discharge produces a short burst of pulse, which can damage electrical components like ICs, LCDs, memory, etc.
An ESD simulator performs this discharge. The ESD pulse is applied to the enclosure of the device or part of the device where humans can touch.
There are two types of tips available: air discharge tip and contact discharge tip. The air discharge simulator discharges through the air with the arc, while the contact discharge simulator discharges through contact with the device. A very common test level is 8kv for air discharge and 4kv for contact discharge.
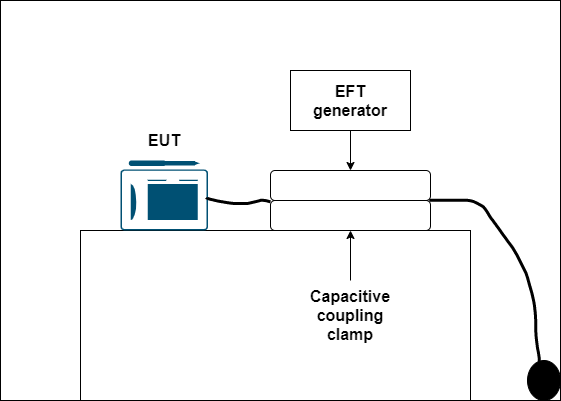
- Electrical Fast Transient (EFT)
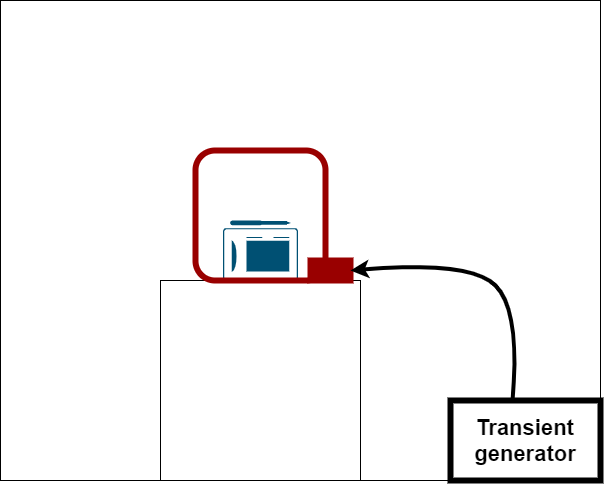
Fast transient is caused by switching inductive loads like motor, switches, and relays. A burst generator is used to simulate the same situation as switching with inductive load. The series of short pulses that are high in amplitude and repetition frequency with short rise time is applied to the EUT. This test applies to AC and DC port and signal cables longer than 3m in length.
As shown in the image, the EFT generator generates the signal, which feeds into EUT with the help of a capacitive coupling clamp.
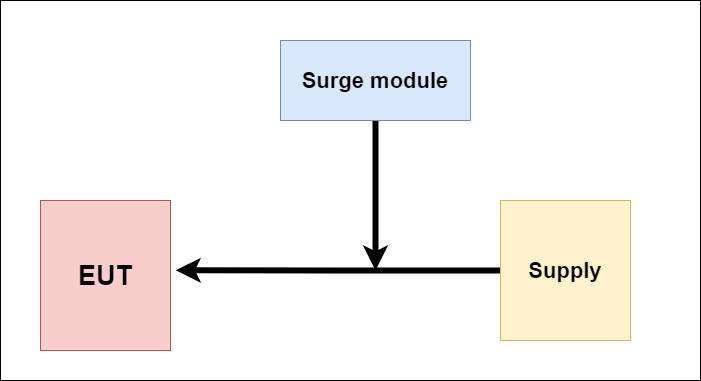
- Surge
Surge can be caused by many factors like high power switching events, magnetic/inductive coupling, and even lightning. A short power surge can lead to arcing, cabling breakdowns, motor damage, and many other problems. Surge testing is mainly applicable on AC ports of EUT or sometimes on DC ports. Some standards apply on signal ports, signal cable longer than 30m in length, or if the cable runs outside of a building.
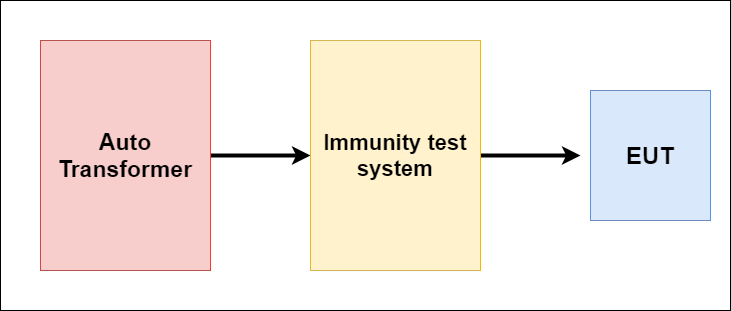
- Voltage Dip test
In the real world, the main AC power supply can fluctuate, or a fault can occur. This fault can occur due to a power cut or by sudden significant changes of loads. The voltage dip is the voltage drop of the main supply or the power supply if cut suddenly. A continuous change in voltage causes a continuous change in voltage dips.
The voltage dip test ensures that the device doesn’t lose functionality in these voltage dips conditions. The image shows that an autotransformer is connected with the immunity test system, which controls voltage dips and switches the supply.
- Transient Magnetic Field Immunity test
This test is similar to the continuous magnetic field immunity test. The EUT is placed in a loop of wire, where a magnetic field is generated. In the continuous magnetic field immunity test, the EUT device is exposed to a continuous fluctuating magnetic field to the main power supply (at 50/60 Hz). In a transient magnetic field immunity test, the EUT is exposed to the magnetic field generated by the transient generator. The amplitude of this pulse is high, but the rise time is short.
Pass/Fail Criteria
The EMC test labs decide criteria according to the performance of the device. These criteria depend upon the standards of the country. Below is data taken from the European standards.
Criteria A
If the product performed perfectly in all the tests, it would fall in Criteria A.
Criteria B
If the device lost its functionality under the test and after the test, it again recovers its normal functionality, then the product falls in Criteria B.
Criteria C
If the device loses its functionality and needs to power it back on, it will fall in Criteria C.
Criteria D
If the device is fully lost its functionality and cannot recover, hardware or software is damaged. Then the device falls in Criteria D.
You may also like:
Filed Under: EMI/EMC/RFI, Tutorials