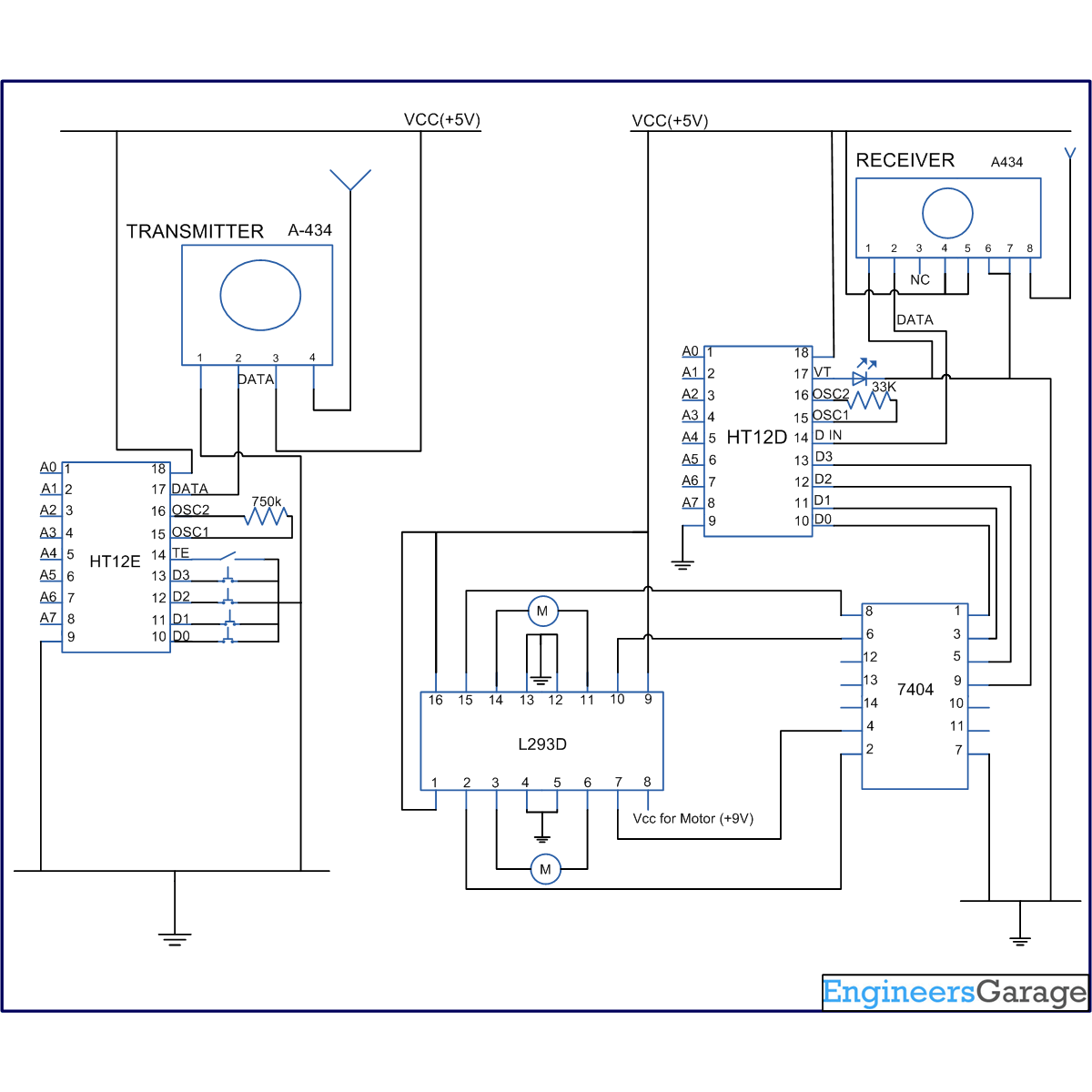
Wireless remote controlled toy cars work on the concept explained in this project. Motor control through RF communication is a very interesting application and is widely used in robotics, electronics toys, automation systems etc. This topic covers the way DC motors can be driven by using the controls from a distant place. The controls are transferred from one end to another by employing an RF module.

The circuit of this project uses RF module to control DC motors through a motor driver IC L293D. Transmission is enabled by giving a low bit to pin14 (TE, active low) of encoder HT12E. The controls for motor are first sent to HT12E. Pins 10 and 11 (D0-D1) are used to control one motor while pins 12 and 13 (D2-D3) to control another motor. The data signals of encoder HT12E work on negative logic. Therefore a particular signal is sent by giving a low bit to the corresponding data pin of encoder.
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.