Working of NOT Gate using transistor
The NOT gate is the basic logic gate among all the gates. It gives only one output which is the negation value of the corresponding input. When the input is forced to low value it gives high value at the output and vice – versa.
A transistor is used for switching or amplification purpose. Due to this property, we are using it as a switch for NOT gate operation. The transistor used for the design of logic gates depends upon the transistor’s switching speed. There are three modes of transistor operation namely Active mode, Saturation mode and Cut off mode. Out of these, we are using Saturation mode and Cut off mode for NOT gate design.
TRUTH Table of NOT Gate
| A | A |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
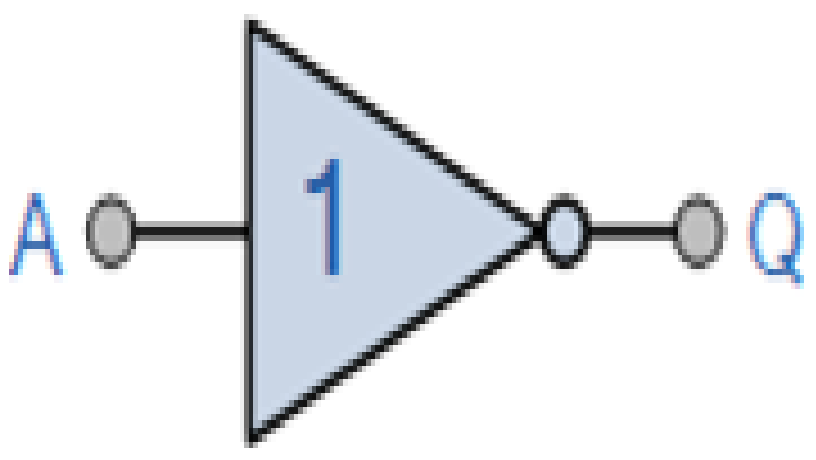
Fig. 1: Symbol of NOT Gate
Symbol of NOT Gate (Bubble shows inversion)
A transistor name reflects the type of semiconductor it is made of and the number of terminals. Here we are using BC547 transistor which is an NPN bipolar junction transistor where prefix BC refers that the semiconductor is of silicon type and is used for general purpose. A bipolar transistor is having three terminals- emitter, base, and collector. You can also use another transistor of BC range (BC548, BC549); they also work well.
The BC547 is used here in common emitter configuration. This transistor utilizes the low power and also has low-frequency. In the common emitter configuration, transistor gives a phase shift of 180 degrees. Due to change in 180 degree in phase shift, it is able to give high at the output when our input is low and vice-versa. The biasing of the transistor is done in a way so that the operating point of the transistor comes closer to the origin in the transfer-characteristic curve of the transistor. This causes an immediate switching of the transistor from its cutoff to the saturation state. Hence when we apply enough voltage at the base of the transistor it immediately reaches into its saturation state and the transistor starts conducting.
Components required :
• BC547 transistor
• 1k ohm resistance
• Two 10k ohm resistance
• 5V power supply or a battery.
• Two general purpose LED
• A toggle switch
• Some jumper wires
• Breadboard
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects



Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.