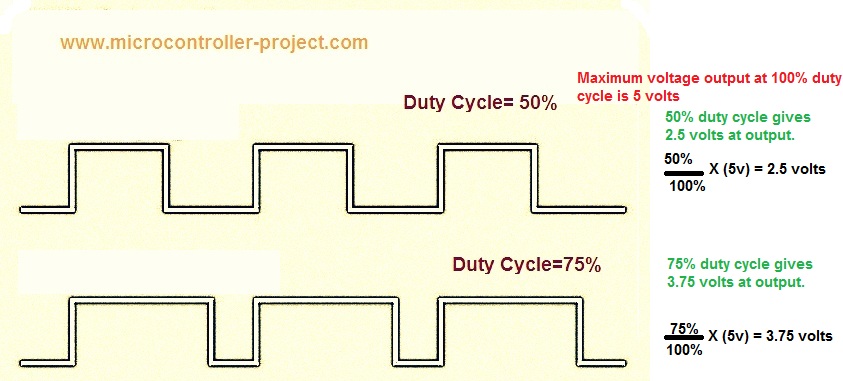
How to control led brightness?To fade and control brightness of led we have to provide different voltage signal levels to led. Each voltage level glows led according to the voltage value. For example you have an led whose rating is 5 volt. To fade it we have to provide voltage ranging from 0.1 to 5 volts. At 5 volts input led will glow at its maximum brightness. Decreasing voltage from 5 will decrease the led brightness. If we speed up the brightness cycle then led will show a fading effect.
|
Typical led brightness control method
How to fade led using microcontrollers?
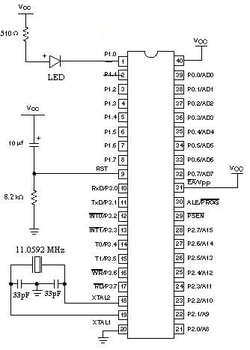
89c51 led fading circuit diagram
PWM(pulse width modulation) signal generation using 89c51 microcontroller timers
How to use internal Timers of 8051(89c51,89c52) microcontroller?
I am using Timer-0 of 89c51 microcontroller in 16-bit mode. Their are two variables most important in my code. They are high-low and h1-l1. high-low is associated with the high period of signal and h1-l1 is associated with low period of the signal. high and h1 are associated with TH0 register of 89c51. I am generating 20 different waves for achieving pwm. 20 different waves means 20 different duty cycles. In the code a for loop is running 20 times, duty cycle logic is placed in that for loop. Initially duty cycle is low for a little duration then it goes high and high up to 100%. Actually timers are loaded with 20 different values and they run for 20 different values, but at a time timer runs on a single value.
In the code initially TH0 is loaded with 0xFF(high) and TL0 with 0xFF(low), this combination is for high signal. Timer runs with this combination for 100 times and at the same time for low signal TH0 is loaded with 0xEB(h1) and TL0 0xFF(l1). TH0 is loaded with 0xEB because initially we want low signal for some long duration. Now when this for loop runs, signal for high wave increases and signal for low wave decreases. Due to which we receive a PWM signal as output on the pin and we can see led fading and brightness is increasing and decreasing continuously.
Note: 0xEB gives a gap of 0xFF-0xEB(hexadecimal)=20(decimal). So we are increasing and decreasing our signal levels equally on both sides(High and Low). h1 increases from 0xEB and it goes to 0xFF after 20 increments and high decreases from 0xFF to 0xEB after 20 decrements. You can increase the PWM frequency by using a crystal of high value.
Filed Under: 8051, Electronic Projects, Microcontroller Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.