GPS is position and location tracking technology based on the Global Positioning System (GPS) used for determining and tracking the precise location of a person, vehicle, or any other asset. The system uses a GPS receiver that calculates the distance from multiple satellites by measuring the time it takes for the signals to reach the…
What is GPIB and is it obsolete?
The bus, codified as the IEEE 488 standard, continues to find use in legacy test-system upgrades and in calibration labs. The General-Purpose Interface Bus (GPIB) began life as the Hewlett-Packard Interface Bus (HP-IB). Hewlett-Packard, whose electronic test-and-measurement business has evolved into today’s Keysight Technologies, created the interface in the 1960s to connect multiple instruments in…
What is the Modbus protocol and how does it work?
Modbus is a popular low-speed serial communication protocol widely used in the automation industry. The protocol was developed by Modicon (now acquired by Schneider Electric) in 1979 for its own programmable logic controllers. The protocol served as a link between PLCs and intelligent automation devices. Now an open protocol maintained by Modbus Organization, the Modbus…
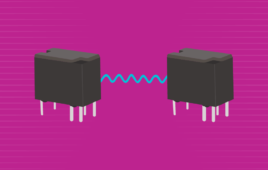
An overview of signal relays
Signal relays are devices that are commonly used to control the flow of electrical current in a wide range of applications, from simple household appliances to complex industrial systems. Their simple design has made them a go-to component for safely and reliably controlling circuits from a distance. Signal relays are typically tasked with switching current…
What’s a protective relay and what does it protect?
A protection relay is a smart device that receives inputs like current, voltage, resistance, temperature, or even light, compares them to set points, and provides outputs such as visual feedback in the form of indicator lights and/or an alphanumeric display, communications, control warnings, alarms, and turning the power off and on. They are used for…
What is an Actuator Sensor Interface (AS-i)?
The Actuator Sensor Interface is a standard Fieldbus interface for connecting binary actuators and sensors in a PLC, DCS, or PC-based automation system. It is the only worldwide standardized bit-oriented Fieldbus. Traditionally, actuators and sensors were connected to a PLC controller or other controller using parallel wiring. The complex nest of wires was hard to…
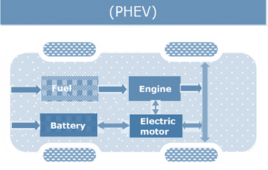
What are the different types of electric vehicles?
Electric cars are the present and future of the automotive industry, yet it may not be easy to believe the first electric cars were introduced in the 1880s. The electric technology in automobiles was shunned due to cheaper gasoline cars and the unexpected developments and innovations in internal combustion (IC) engines. Electric vehicles, a greener…
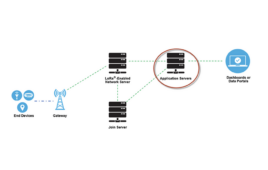
What is the LoRaWAN network and how does it work?
LoRa (“long-range”) is an excellent wireless communication solution without networking capabilities. It’s a reliable, energy-efficient, encryption-secured, low-cost wireless connectivity technology. And as its name suggests, it offers an extremely long range. LoRa operates at the physical layer of an OSI model and is implemented at the chip level — excluding the network management protocol. This…
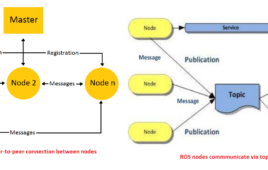
What is a Robot Operating System (ROS)?
Usually, when we talk about robotics, the first thing that flashes into mind is robotic manipulators equipped with end-effectors, driven by actuators, guided by sensors, and controlled by microcontrollers. The mechanical hardware always impresses viewers, but it is the robotic software underneath, that brings these magnificent machines to life. Most of the small robots are…
What is FreeRTOS?
Embedded devices are the soul of the Internet of Things. Any IoT network is inherently a medium to connect microcontroller-powered “things” via the internet. Microcontrollers at the heart of most IoT devices are simpler, resource-constrained, low-power chips that cannot run a standard operating system. Microcontrollers are often flashed with minimal firmware codes intended to execute…
What is Light Fidelity (Li-Fi)?
Imagine data transferring over your local wireless network at the speeds of light. Light Fidelity or Li-Fi is a ground-breaking innovation that has made it possible. Data communication through optical fibers has already made data communication available at light speeds over long distances. Light Fidelity has filled the space for optical communication in the wireless…
What are the different types of integrated circuits?
Integrated circuits (ICs) are synonymous with electronics. Wherever there are any electronics, there are definitely one or more ICs. There are no electronics without ICs. Electronics became so popular, widely acceptable, and ubiquitously applicable, all due to the invention of integrated circuits. Integrated circuits are miniaturized integration of complete electronic circuits on a single semiconductor…
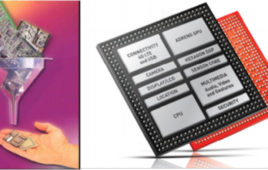
What is an SoC?
A System on Chip or an SoC is an integrated circuit that incorporates a majority of components present on a computer. As the name suggests, it is an entire system fabricated on a silicon chip. The beauty of an SoC is that it integrates all the components on a single substrate. In semiconductors, a substrate…
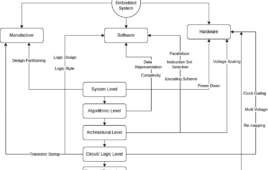
What is a low power design?
Low power design is a system using a collection of techniques and methodologies for the purpose of optimizing battery life and reducing the overall power dissipation of the system. To optimize the power there are many low power techniques that depend on the level of the design selected, ranging from semiconductor technology to the higher…
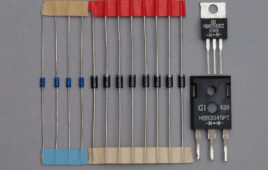
What is a Schottky diode?
A diode is a two-terminal device that acts as a one-way switch. The Schottky is a metal-semiconductor diode known for very low forward voltage in which the metal forms the anode and the n-type semiconductor acts as the cathode. The diode is named after German physicist Walter H. Schottky. It is also called Schottky barrier…
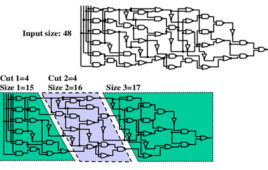
What is an Integrated Circuit? Specifications to tapeout
An integrated circuit, or an IC, is a miniature circuit made up of thousands or even billions of transistors. It can be described as a set of electronic circuits fabricated on a semiconductor material. Usually, this material is silicon. The integration of MOS transistors leads to chips being faster, smaller in size, and less expensive…
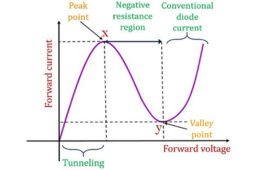
What is a tunnel diode?
A tunnel diode—also called Esaki diode because Leo Esaki invented it in 1957—is a heavily doped PN junction diode that exhibits negative resistance and high conductivity due to the tunneling effect. In signal diodes (small signal diodes and rectifier diodes), charge carriers gradually overcome the depletion region. In a tunnel diode, the charge carriers spontaneously…
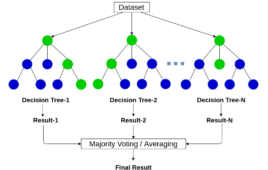
Classification of machine learning algorithms
Machine learning is the future of computer theory and computational electronics. In the past decade, advances in machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence have changed how computing power is utilized. In the future, the developers may not be writing specific user-defined programs. Instead, they will be fabricating algorithms to let the computers perform assigned…
What is TinyML?
Data science has not just remained a field of scientific computing and research. In the internet-connected world, data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence are far more applicable than ever imagined. No doubt, the very first leap in the practical applications of machine learning and artificial intelligence happened when enterprise websites, including social media platforms,…
How load cells work
Mass is one of the seven basic physical quantities. In real-world applications, mass is often realized in the form of the object’s weight. The weight is the force of gravity acting on a body due to its mass. How is the weight of an object measured? It is done by sensing pressure exerted by it…