STMicroelectronics’ TSZ181H1 and dual TSZ182H1 automotive-qualified operational amplifiers (op amps) deliver high accuracy and stability over a wide (-40° to 175° C) temperature range. The high maximum operating temperature encourages use in harsh environments and in applications with long mission profiles. The op amps have very low input offset voltage, typically 3.5µV at 25° Cm, and input bias…
Audio Filters: The working and classification of microphones – Part 3
In the previous tutorials, physical properties of sound waves and acoustic waves were discussed. Sound or Acoustic Waves are in the form of vibration. Sound needs to be converted into electrical signals so that it can be processed by electronic circuits. So, the sound which is a mechanical energy must convert into electrical energy and must be precisely represented as an electrical waveform (analog) for any signal processing operations. So, there is need of a device which could sense the audio signals efficiently and convert them into electrical signals.
Audio Filters: The working and classification of speakers – Part 4
In the previous tutorial, working principle and classification of microphones was discussed. The microphone is an input transducer which converts sound waves into electrical signals. The audio signals from a MIC are amplified by a preamplifier and transferred to the main audio unit. The audio unit might comprise of amplifier and/or filter circuit or may have other circuitry to store audio to a computer. The amplified or stored audio is reproduced using another type of transducer which is called speaker. The Speaker is a type of output transducer which converts the electrical signal into audio signal. Speakers are enclosed in a rectangular or square shape cabinet. The shape of the box affects the quality of the sound. The cabinet consists of different types of transducers/speakers which produce different types of audio frequency. Each transducer is called as ‘driver’ and the whole cabinet is known as ‘loudspeaker’.
Audio Filters: Understanding the filters – Part 5
In the previous tutorials, two of the most important building blocks of an audio system – Microphone and Speaker were discussed. An audio system is designed to receive audio signals (via microphone), record audio in some storage, transmit audio (through wired or wireless communication channels) and reproduce audio signals (via speakers).
Audio Filters: Designing a two-way audio crossover – Part 6
In the previous tutorial, fundamentals of audio filters were discussed. The audio filters can be passive or active depending upon the use of passive or active components in their designing. On the basis of frequency response, filters can be classified as high pass, low pass, band pass, Notch, band reject, T-Notch, all pass and equalizer filters. In this tutorial, an audio crossover will be designed. The Audio crossover is an electronics circuit which splits the audio signal into two or more frequency bands. These frequency bands are then, sent to the different audio drivers (Twitters, Mid Range and Woofers). A single speaker is not capable to serve the whole range of audible frequencies due to the limitations of its construction. So, different drivers (speakers) are required to deliver different range of audio frequencies.
Audio Filters: Designing an audio equalizer – Part 7
In the previous tutorial, an audio crossover was designed using high pass and low pass audio filter. In this tutorial, an audio equalizer will be designed. An Equalizer (abbreviated as EQ) is an audio equipment which cut or boosts the certain frequency components from the audio signal. This process of adjusting the frequency components is called as Equalization.The equalizers are widely used in the audio systems during recording of sound as well as in amplifiers and mixers. As they are used in the audio system so are called Audio Equalizer.
Audio Filters: Designing an audio mixer – Part 8
In the previous tutorial, an audio equalizer was designed. In this tutorial, now an audio mixer will be designed. The Audio Mixer is an electronic device which combines and modifies the audio signals. The audio signals can be either in digital form or analog form. In digital form, the analog audio signals are encoded so that the audio information in the signal becomes independent of the amplitude of the signal. Both analog and digital signals can be combined by different types of audio mixers. For mixing digital audio signals, digital signal processing techniques are used while for combining the analog audio signals, generally operational amplifiers are used.
Designing a 6 Watt Car Audio Amplifier – 5/9
In the previous tutorial, a Bass Boost Power Amplifier was designed. Now it’s time to start designing power amplifiers suitable for specific applications. In this tutorial, a car audio amplifier will be designed. The cars have been coming with inbuilt audio systems from years. An audio system of a car is one of the important features that shines as unique selling point (USP) for any car in the market. The audio systems have become a vital accessory for any car. Even many times consumers replace the default audio systems came in their car with new one for better driving experience.
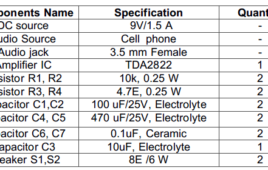
Designing a Stereo Power Audio Amplifier using TDA2822H – 7/9
In the previous tutorials, the amplifier circuits to boost audio from a single channel were designed. Over the last decade, there is growth in the audiophile. This has brought a revolution in the music industry. Now, people like to hear the high resolution surround music just like a 3D video. A surround sound system is designed to create a sound field like the sound is coming from back, front, left and right sides. It can also create the sound above the listener. The surround sound system is used in cinemas and drama theaters to give a realistic feeling to the audience.
Basics of Audio Amplifier – 1/9
Audio is one of the most common media. Here, It refers to the representation of sound which can be perceived by humans. Audio and Video are the essential component of any electronic media. The electronics can be used to receive audio signals (via microphone), record audio in some storage, transmit audio (through wired or wireless communication channels) and reproduce audio signals (via speakers). The audio can be represented and transmitted as either analog signals or digital signals. In this series, analog audio signals are the concern. The audio signals have a frequency range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Designing 250 Milli Watt Audio Power Amplifier – 2/9
In the previous tutorial, basics of audio amplifiers were discussed. It has been already mentioned that on the basis of application, there are two types of audio amplifiers – 1) Pre-Amplifier2) Power Amplifier The pre-amplifiers are used to level up the audio signals from a microphone or audio source to standard voltage levels while the power amplifiers are generally used at the output stage of the audio systems to boost audio signals before they are reproduced by the speakers. In this tutorial, a power amplifier with 250 Milli-Watt output power will be designed.
Designing 1 Watt Audio Power Amplifier – 3/9
In the previous tutorial, a 250 Milli Watt Audio Power Amplifier was designed using LM-386 power amplifier IC. On the basis of application, the audio amplifiers can be categorized into two classes – 1) Pre-Amplifier2) Power Amplifier The pre-amplifiers are used to level up the audio signals from a microphone or audio source to standard voltage levels while the power amplifiers are generally used at the output stage of the audio systems to boost audio signals before they are reproduced by the speakers. In this tutorial, a power amplifier with 1 Watt output power will be designed. The audio amplifier designed in this project will operate in range from 20 Hz to 20 KHz which is the same as of the audible range of frequencies by humans. The amplifier circuit will be designed to have a variable voltage gain in range from 26 dB to 46 dB.
Audio Filters: Understanding sound waves – Part 1
The audio electronics is a branch of electronics that deals with designing of circuits that convert sound into electrical signals or electrical signals back into the sound. These circuits all together form an audio system. Basically, an audio system is designed to receive audio signals (via microphone), record audio in some storage, transmit audio (through wired or wireless communication channels) and reproduce audio signals (via speakers). So, the audio circuits perform signal processing for representing the sound in the form of electrical signals, manipulate the electrical (audio) signals like amplifying, filtering or mixing, reproduce sound from the audio signals, store audio into computer files or reproduce audio from an audio file. All these processes are performed by different audio related circuits or devices.
Audio filters: Understanding acoustic waves – Part 2
In the previous tutorial, sound wave and its properties were discussed. Now it’s time to understand Acoustic Waves. Generally, the term sound wave is used to refer the waves having frequency range audible to humans that is 20 Hz to 20 KHz. The waves having frequency greater than 20 KHz are called Ultrasonic waves and waves having a frequency range in Giga Hertz or higher are called Hypersonic Waves.