In the previous article, we learned about various performance indicators associated with resistors. Now, let us learn about different types of resistors and how they score over various performance indicators. This evaluation will help in determining the suitability and relevance of different types of resistors for specific electronic applications. There are the following types of resistors:
- Fixed Value Resistors
- Composition
- Film or Cermet
- Wirewound
- Foil
- Semiconductor
- Variable resistors
- Potentiometer
- Digital potentiometer
- Rheostat
- Trimpot
- Dependent resistors
- Light Dependent
- Voltage Dependent
- Thermistors
- Magnetic Dependent
- Strain Gauges
- Power resistors
- Wirewound
- Grid
- SMD
- Water
- Liquid
Fixed Value Resistors
Fixed Value Resistors are supposed to offer a fixed resistance in the circuit. Their resistance cannot be changed in any way. These are two-terminal components that can be connected in series or parallel configuration with respect to another electronic component in the circuit. There are the following types of fixed value resistors available:
1) Composition Resistors – These resistors are made of a mixture of conducting and non-conducting materials. There are two types of composition resistors:
- Carbon Composition Resistors
- Ceramic Composition Resistors
Carbon composition resistors
Carbon composition resistors are the oldest resistor type. These resistors are most commonly used resistors as they are easy to design, inexpensive and are suitable for most of the ‘common’ applications. These resistors are made up of a mixture of carbon dust and ceramic filler material. The mixture is molded into axial resistor package enclosed by an insulating coating with wires or leads attached at the two terminal ends of the package. The ratio of carbon to the ceramic material and distance between the terminal leads determine the resistance of the resistor. Greater is the proportion of carbon in the mixture, less is its resistivity. The ceramic filler used in the mixture is mostly phenolic, which is similar to the plastic. These resistors come available in an axial package with color-coding for an indication of resistor value and tolerance. T
The carbon composition resistors have the following KPIs:
Nominal Value – Carbon Composition Resistors can have very low resistance (1Ω) to extremely high resistance (22MΩ). Their resistance is varied by varying the composition of carbon and ceramic filler in the mixture. The nominal value of these resistors is indicated by color coding.
Power Rating – The power rating of these resistors depends on the physical size of the resistor. Greater is the physical size, greater is the power rating. These resistors are commonly available in 1/4 and 1/2 Watt series. There are also 1/8 Watt series available for low-power, miniature circuits. For power electronic applications, 1 Watt and 2 Watt series are also available, though 1 Watt and 2 Watt series packages are quite big in size.
Tolerance – These resistors have wide tolerance levels from 5% to 20%. Due to wide tolerance, these resistors are not suitable for precision applications.
Voltage Rating – The voltage rating is linked with the power rating of these resistors. Generally, higher is the power rating, higher is the voltage rating. Like 1/4 Watt, 1/2 Watt, and 1 WCarbon Composition Resistors typically have 250V, 350V and 500 V Maximum Rated Voltage respectively. The Maximum Overload Voltage of 1/4 W, 1/2 W, and 1 W Carbon Composition Resistors is 400 V, 700 V and 1000 V respectively.
Temperature Rating – The operating temperature range of carbon composition resistors typically range from -55°C to 125°C. The Full Load Maximum Temperature is usually dependant on the power rating of the resistor series and may vary with the manufacturers. Higher is the power rating, higher is the Full Load Maximum Temperature. The temperature rating is usually indicated by a temperature rating curve for different power rating series from the manufacturer.
Pulse Stability – The carbon composition resistors are known for high pulse stability. So, these resistors are quite suitable for applications that involve high voltage pulses and frequent voltage fluctuations.
Frequency Response, Noise & Stability – The carbon composition resistors offer quite pure resistance and almost negligible inductance or capacitance. So, they typically have good frequency response, low noise, and acceptable stability. This makes these resistors suitable for high-frequency applications as well as low power circuits. However, in overload conditions, they suffer from noise and poor stability due to excessive heat dissipation.
Size – These resistors are medium to large in size depending upon their power rating. These resistors are most commonly available in an axial package, though SMD/SMT packages are also available.
Reliability – These resistors are great at reliability provided they are used in suitable applications. Due to high reliability, low cost and easy availability, these resistors are most common in use.
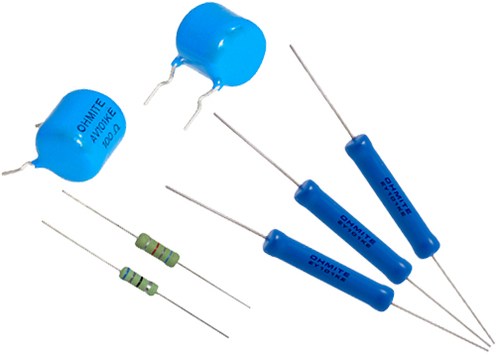
Example of a carbon composition resistor (Source: Ohmite)
Carbon composition resistors have the following pros and cons:
Pros – wide range of resistance, purely resistive, highly reliable, pulse stability
Cons – wide tolerance, physical size, limited operating temperature, available for only low power ratings
Therefore, carbon composition resistors are for common electronics applications where DC or RMS voltage remains below 250V and operating temperature must be -55°C to 125°C, low-power applications, and high-frequency circuits meant to process low power signals like RF receivers. However, they are not for precision applications, high power circuits, circuits to be deployed in extreme environmental conditions, or low power circuits that must be very compact in size.
2) Ceramic Composition Resistors
The ceramic composition resistors are like carbon composition resistors except that they are constructed by solid ceramic composition. This improves their pulse stability and operating temperature range. The ceramic resistors can operate at ambient temperatures up to 250°C. These are typically available in 1/2 Watt, 1 Watt and 2 Watt series with resistance values ranging from 3.3Ω to 1MΩ. There are ceramic composition resistors available with a power rating up to 1000 W. The ceramic resistors offer the advantages of carbon composition resistors (pure resistance, stability, reliability, and pulse stability) in power electronic applications though these too have poor tolerance levels (typically 10%). These resistors are available in many types of packages like axial, tubular, slab, disk and washer, encapsulated, load bank, water-cooled and various custom packages.

Example of a ceramic composition resistor (Source: Token)
Film Type Resistors
These type of resistors are constructed by depositing a film of pure metals or metal oxides onto a ceramic substrate. The deposited film is cut by laser into a long helical resistive path. There are four types of film resistors:
- Carbon Film
- Metal Film
- Metal Oxide
- Cermet Resistors (Thick Film and Thin Film)
Carbon Film Resistors
Carbon Film Resistors are constructed by depositing carbon film on a cylindrical ceramic substrate or rod. Helical cuts are made on the carbon film to create a long helical resistive path between the two terminal leads of the resistor. The carbon film resistors have the following KPIs:
Nominal Value – The helical resistive path of carbon film resistors help in achieving wider range of resistances. These resistors can have resistance in range from a few milliohms to 100MΩ. Their resistance depends upon the thickness and length of the helical path. High-value carbon film resistors have thin film and longer resistive path. The nominal value of these resistors is indicated by color-coding.
Power Rating – Carbon Film Resistors come with power rating from 1/4 Watt to 3 Watt. In high-value carbon film resistors, the resistive path may get open circuit due to excessive heating of the carbon film. So, carbon film resistors are made for only low-power applications (up to 3 Watt).
Tolerance – Due to long resistive path, these resistors have better tolerance than carbon composition resistors. These typically have tolerance between 1% to 5%.
Voltage Rating – Again, the voltage rating of these resistors is related to their power rating. The Maximum Rated Voltage of Carbon Film Resistors range from 200V to 500V while Maximum Overload Voltage range from 400V to 1000V. Greater is the power rating, greater is the voltage rating of these resistors.
Temperature Rating – The operating temperature range of carbon film resistors is similar to carbon composition resistors. It typically varies from -55°C to 155°C. At high ambient temperatures, the high-value carbon film resistors remain at risk of disintegration because of the thin carbon layer. These resistors typically have a negative temperature coefficient.
Pulse Stability – These resistors show good pulse stability like carbon composition resistors.
Frequency Response, Noise & Stability – Due to the helical resistive path, these resistors develop some capacitance or inductance. So, they do not offer pure resistance due to the nature of their design. It is seen that the capacitance in these resistors exceeds the nominal resistance when the value of resistance is less than 100Ω and applied signal has a frequency over 250MHz. Due to reactive nature, these resistors suffer from noise and may not suit ideal for low-power signals. These resistors show stable operation for medium to high-value nominal resistance provided circuit operates at a frequency below 250MHz within limited temperature range.
Size – Like carbon composition resistors, these resistors are also commonly available in axial package. Due to long resistive path, they are slightly smaller than typical carbon composition resistors.
Reliability – These resistors can be considered reliable for medium value of resistances provided circuit operates in limited temperature range, at medium power and limited signal frequency (below 250MHz).
Carbon film resistors have the following pros and cons:
Pros – Low tolerance level, slightly smaller in size, reliable and stable
Cons – Reactive nature, limited temperature range, limited frequency range
Therefore, carbon film resistors are for “Common” circuits where medium value of resistance with low tolerance is preferred. They are not good for power-intensive applications involving high-value resistance, circuits involving low power signals or high-frequency signals, or temperature-sensitive applications.
Metal film resistors
Metal Film Resistors are constructed by depositing a film of metal (Nichrome or Tantalum Nitride) on a cylindrical ceramic substrate or rod. Like Carbon Film Resistors, the coating is cut to a long helical resistive path by laser. The carbon film resistors have the following KPIs:
Nominal Value – These resistors are available for a wide range of resistances ranging from few milliohms to 68 MΩ. The value of the resistance depends on the thickness and length of the resistive path. Less is the thickness and more is the length of the resistive path, higher is the value of resistance. The nominal value of these resistors is indicated by labels instead of color codes.
Power Rating – Metal Film Resistors are available for a wide range of power ratings from 1/20 Watt up to 20 Watt. Unlike carbon film resistors, metal film resistors have better temperature stability.
Tolerance – These resistors typically have tolerance about 1 or 2 percent. There are also precise metal film resistors available that have tolerance as low as 0.01%. However, metal film resistors having precise tolerance often have a lower power rating.
Voltage Rating – The voltage rating of metal film resistors range from 100V to 10kV depending upon the power rating of the resistor series.
Temperature Rating – The operating temperature range of metal film resistors range from -65°C to 250°C. They have a lower temperature coefficient compared to carbon composition and carbon film resistors which gives better temperature stability. Important thing is that these resistors have a positive temperature coefficient.
Pulse Stability – These resistors have similar pulse stability as carbon film resistors.
Frequency Response, Noise & Stability – Unlike carbon film resistors, metal film resistors can be used for high frequency or radio frequency circuits. They do show some reactance but it is far less compared to carbon film types. These resistors have lower noise and better stability.
Size – The size of Metal Film Resistors depend upon their power rating. These are commonly available in axial packages though these have labels instead of color codes.
Reliability – Metal Film Resistors are more reliable than carbon film resistors and can be confidently used in power applications as well as high-frequency applications.

Example of metal film resistor (Source: KOA Speer)
Metal film resistors have the following pros and cons:
Pros – Better temperature stability, low noise, better tolerance, available for wide range of power ratings
Cons – reactive nature, despite advantages, still not best for high power applications
Therefore, metal film resistors are good for “Common” low power signal applications where precise tolerance, low-temperature coefficient, and a wide range of power rating are required without temperature limitations. They are not for typical power applications and circuits involving high voltage pulses.
Metal Oxide Film Resistors
Metal Oxide Film Resistors are similar to Metal Film resistors except that the resistive material in them is a metal oxide (like tin oxide) instead of metal. These resistors have a higher operating temperature range (up to 450°C), lower temperature coefficient (typically 300PPM) and high pulse stability. These resistors are more reliable and stable compared to metal film resistors. These resistors are flame-proof and resistant to ambient heat and humidity. These resistors are typically available in power ratings from 1/4 W to 140 W with tolerance typically 0.5% to 20%. These resistors are available with voltage rating as high as 37.5 kV. These resistors are most suitable for pulse power applications.

Example of metal oxide film resistor (Source: Ohmite)
Cermet Resistors
Cermet resistors are constructed by depositing a conductive paste of Ceramic and Metal onto an alumina ceramic substrate. The resistive path is drawn like zigzag lines between the terminals of the resistor. There are two types of Cermet Resistors – Thick Film Resistors which have about 20 Micrometer wide resistive path and Thin Film Resistors which have only few Micrometer wide resistive path. These resistors are similar to metal film resistors in properties. Though, these are more stable, power-efficient, compact in size, show low noise, and better temperature stability. These resistors come available in both through-hole as well as surface-mount packages. These resistors are commonly used in surface mount chip type packages or resistor networks for high-frequency applications. However, their pulse stability is not much satisfactory. Compared to metal film or metal oxide film resistors, their resistance can be as high as 42.9MΩ (Thin Film SMD), 22MΩ (Thin Film Through Hole), 50GΩ (Thick Film SMD) and 10TΩ (Thick Film Through Hole).

Example of a cermet resistor (Source: TE Connectivity)
In the next article, we shall continue a discussion about fixed resistors. Before that, there are two do-it-yourself activities for you.
Activity 1
In a previous article “Common Mistakes made by Electronics Beginners”, we had mentioned that datasheets are the best friends of an electronics engineer. Try and develop a habit of exploring datasheets from here onwards. Below are some datasheets of resistors randomly chosen from the internet:
Carbon Composition Resistors – Multicomp
Carbon Composition Resistors – Token Electronics
Ceramic Composition Resistors – Tyco Electronics
Carbon Film Resistors – Panasonic
Carbon Film Resistors – Kamaya Ohm
Carbon Film Resistors – RGA
Metal Film Resistors – NTE Electronics
Scrutinize the above datasheets and verify properties of different types of resistors. Look for various technical specifications and graphs like derating curve, temperature rating curve, etc. Try to find out what R-value in “Rating and Dimensions” Table in the datasheet – ‘”Carbon Composition Resistors – Multicomp” signifies; why “the Resistance to Pulse” graph is explicitly given in the datasheet for Ceramic Composition Resistor; and compare derating curves of carbon composition and carbon film resistors.
Activity 2
Check out the various types of fixed resistors available at Mouser, Element14, and Digi-Key. Look for various filters available at these online market places for selection of the desired resistor.
Filed Under: Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.