

Fig. 3: Diagrammatical Image Showing Simplified Device Structure of OLED Screen
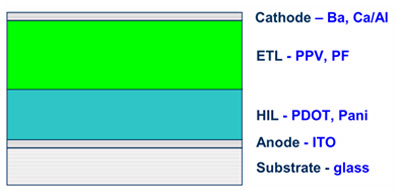
Materials for OLED Polymer based LEDs(PLED)

Fig. 4: Image Showing Multiple Layers of OLED Screen
Polymer based LEDs(PLED)




OLED – How do OLEDs work?

OLED Display – Types
1. Passive Matrix OLEDs (PMOLED)

Fig. 11: Diagram of Passive Matrix OLEDs
Active Matrix OLEDs(AMOLED

Fig. 12: Active Matrix OLEDs
1. Transparent OLEDs
Foldable OLEDs use very flexible substrates such as metallic foils or plastics. Thus they are very lightweight and also durable.
Compared to fluorescent lights, White OLEDs emit brighter, more uniform and more energy efficient. Like incandescent lights, white OLEDs have true-color qualities.
OLED –PROS & CONS
OLEDs offer numerous advantages over both LCDs and LEDs, including:
OLED Products


Fig. 14: Small Molecule Active Matric Display Products

Fig. 15: Polymer based Active Matrix Display Products

Fig. 16: Polymer Based Passive Matrix Display Products
OLED –FUTURE
R&D activities in OLEDs is progressing at a fast rate and soon, OLEDs may be visible in heads-up displays(HUD), automotive dashboards, home and office lighting, for flexible displays. Because of the numerous advantages enumerated in previous sections, this will be the technology of choice for displays.

Fig.17: Image Showing a Typical Futuristic OLED Screen
Filed Under: Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.