As per recent research and experimentations, the scope of informatics and machine learnings seems infinite. The range of its applications goes from healthcare to medicine to saving marine animals like whales. This advanced iteration of artificial intelligence is actually solving several problems in the most innovative and inherent manner. If you consider the recent discoveries, the machine learning-informatics duo is improving the efficiency of new materials discovery as per required features. The researcher’s team, for this purpose, deliberately used nickel-titanium-based shape-memory alloys. The implications can, however, be applied to any other class of materials or for targeting any specific set of properties.
This system can also be used for a number of other applications that may range from optimization of processing conditions in latest manufacturing or optimizing several other properties of a process. In the nickel-titanium alloy preparation the makers needed a transition temperature quite above the normal temperature along with low dissipation.
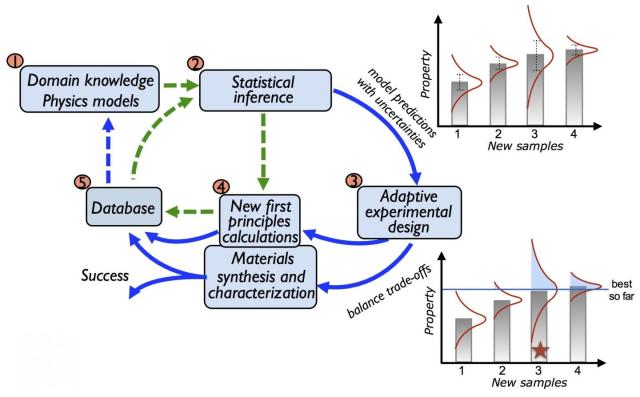
The biggest advantage of machine learning lies in research assistance. The reason being, increasing complexity of chemicals outdates the age old trial and error method. Even if you keep aside solid solutions, multi-component compounds, and defects, it is almost impossible to run thousands of quantum mechanical calculations over chemical, micro, as well as macro characteristics of new things. This task can be easily accomplished by machine learning.
Machine learning is, basically, a method of data analysis that utilizes algorithms that learn to automate the analytical model building from data in an iterative manner. Resultantly, computers having machine learning capabilities gain capability to find insights without taking explicit instructions from the user. Informatics can then use the resulting data in generation of meaningful results for researchers. While experimenting, the researchers build a structure that makes use of uncertainties that can guide upcoming experiments in an iterative manner. These alloys are very useful in improving the fatigue life for engineering applications.
In words of Turab Lookman, the materials scientist and physicist at the Los Alamos National Laboratory, “The goal is to cut in half the time and cost of bringing materials to market. What we have demonstrated is a data-driven framework built on the foundations of machine learning and design that can lead to discovering new materials with targeted properties
Filed Under: News


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.