The performance of each and every electronic system or electronic circuit depends upon the power supply that energizes the circuit or system. It provides required
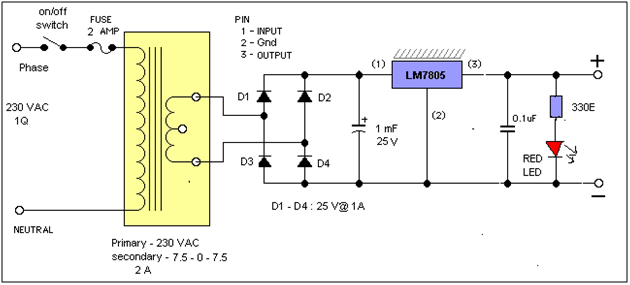
Fig. 1: Circuit Diagram of How to Design a Regulated Power Supply
current to the circuit. Any disturbance noise in this power supply can cause problem in working or operation of circuit. If there is any deviation in this power supply level the circuit may not work properly. The accuracy and precision of circuit operation depends upon it. In some of the circuits all the calibration are done at this voltage level. So all these calibrations becomes false if there is fluctuation in supply level.
There are two types of power supplies: Unregulated power supply, Regulated power supply. Unregulated supply is used in some circuits where there is no much change in required load current. The load current remains fixed or deviation is very less. Read more to know about this interesting power supply project.
The performance of each and every electronic system or electronic circuit depends upon the power supply that energizes the circuit or system. It provides required current to the circuit. Any disturbance noise in this power supply can cause problem in working or operation of circuit. If there is any deviation in this power supply level the circuit may not work properly. The accuracy and precision of circuit operation depends upon it. In some of the circuits all the calibration are done at this voltage level. So all these calibrations becomes false if there is fluctuation in supply level.
There are two types of power supplies
Unregulated supply is used in some circuits where there is no much change in required load current. The load current remains fixed or deviation is very less. Because in such supply
So this kind of supply can not be used where there is noticeable change in load current frequently. But although many circuits works on unregulated supply because it requires very few components and design is also very simple. Also some fluctuation in supply level can be tolerated due to load current change. The regulated power supply is required in digital circuits, the circuits in which the components can not tolerate even 1% change in supply level like micro controller, micro processor etc.
So here I am giving the procedure to design regulated power supply that means which components should be chosen to have required regulated output voltage with required current. The procedure requires calculations based on some designing equations, some assumptions and approximations that we must take during designing.
Consider following notification
Erms : rms value of AC voltage (transformer secondary voltage)
Em : max value of AC voltage
VdcNL : no load DC voltage
VdcFL : full load DC voltage
Ro : internal resistance
IL : full load output current
VLmin : minimum output voltage from unregulated supply
Vrms : rms value of ripple
?Vo : pick ripple voltage
Following equations – relations are used in designing power supply
VdcNL = Em = Erms / 1.41
VdcFL = VdcNL – Ro IL
?Vo = IL / (200 C)
?Vo = 3.5 Vrms
VLmin = VdcFL – ?Vo / 2
So let us start designing
AIM: design regulated power supply for 5 V @ 1 A
Procedure:
We have to design 2 separate sections
1) Regulated section
2) Unregulated section
Design of Regulated section –
Step 1: select voltage regulator chip
Because we are designing regulated power supply, we need voltage regulator chip. There are so many voltage regulator chips available. They are broadly classified into different categories based on
Here we require fixed and positive supply with current capacity 1 A. So we have to choose LM7805 voltage regulator chip.
Step 2: input – output capacitive filter
Input capacitor is required to suppress or minimize any ripple or variation in input applied to regulator chip. Its typical value is 0.33µF as specified in datasheet. This can be neglected if regulator chip is connected very close to filtering capacitor of rectifier. It is only required when the distance between rectifier output and regulator input.
Output capacitor is required to suppress any spike or glitch in fixed output voltage that may occur due to transient change in AC input. Its typical value is 0.1 µF as specified in datasheet.
This completes design of regulated section.
Design of Unregulated section –
It feeds regulated section. Its rectifier + filter. The most required thing is the input given by this section to regulated section must be at least 3 V higher than required output voltage. This is known as ‘headroom’ for regulator chip. This gives us
VLmin = Vop + headroom
= 5 + 3
= 8 V
For this section we have to select transformer, diode and capacitor.
Step 3: selecting capacitor
Let us assume the capacitor is 1000 µF electrolyte capacitor. We need to find out its working DC voltage WLDC, but that depends upon VdcNL as
WLDC = VdcNL + 20% VdcNL
So after finding VdcNL we can calculate it.
From this capacitor value we can find ?Vo as
?Vo = IL / (200 C)
So for IL = 1 A and C = 1000 µF
?Vo = 1 / 200×1000×10-6
= 5 V
From ?Vo and VLmin, VdcFL can be calculated as
VdcFL = VLmin + ?Vo / 2
= 8 + 5/2
= 10.5 V
VdcFL is related with VdcNL as
VdcNL = VdcFL + Ro IL
Ro value is between 6? to 10?. Assuming Ro as 8?
VdcNL = 10.5 + 8×1
= 18.5 V
Now calculate required WLDC
WLDC = VdcNL + 20% VdcNL
= 18.5 + 3.7
= 22.2 V
Always we have to go for higher value than this. So choose capacitor with WLDC of 25 V. So finally our capacitor is
C = 1000 µF @ 25 V
Step 4: selecting diode
Selecting diode means finding current capacity and PIV of diode.
1. Current capacity IC > IL that means Ic can be 1 A or more
2. PIV = VdcNL + 20% VdcNL = 22.2. again going for higher value that is 25 V
Finally required diodes are with
D = 1A @ 25V
All the diodes of series 1N4004, 1N4007, 1N4009 satisfies these criteria.
Step 5: selecting transformer
The rms value of transformer output is given by
Erms = Em / 1.41
But Em = VdcNL., So
Erms = VdcNL / 1.41
= 18.5 / 1.41
= 13.12 VAC
So we may select either
- 1) Center tap transformer of 9 – 0 – 9 or 7 .5 – 0 – 7.5 secondary voltage
- 2) Transformer Without center tapping either 0 – 15 or 0 – 18 secondary voltage
Current rating for secondary of transformer should be at least 1.8 IL. That means the current rating can be 2 A.
Finally select transformer with
T = 230 / 15 VAC @ 2A
Schematic of final design is as shown in the circuit diagram tab.
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.