You can easily control the speed of DC motor using Arduino. We know that the Arduino has analog output through which it generates PWM that is used to vary the speed of DC motor. You may have seen speed control of DC motor using potentiometer or joystick or push buttons with the help or Arduino.
What if we want to control the speed of DC motor using remote? Especially normal, readily available, handheld IR remote which we can find in all most all the homes for TV, AC, music systems, DVD or even for STB (set top box). Like, we can run or stop the motor as well as we can vary its speed using such IR remote – any IR remote. Doesn’t this sound great?
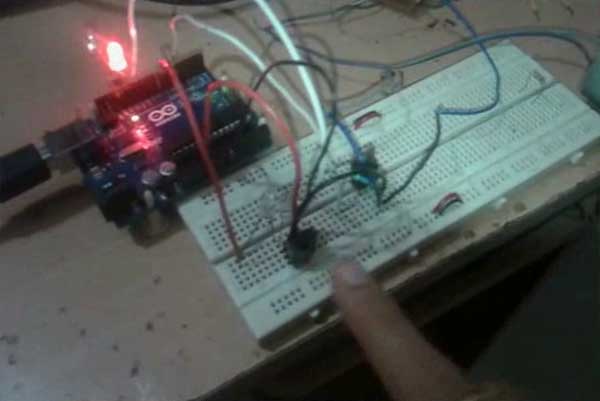

Fig. 1: Prototype of Arduino and IR Remote based DC Motor Controller
The given project demonstrates how to control DC motor speed using any IR remote (like TV, DVD, AC, STB etc) with the help of Arduino. It also runs or stops the motor using a remote. The project uses the normal set top box (STB) IR remote, TSOP IR sensor and Arduino UNO board. Anyone can use any type of IR remote. Just he has to change the remote codes in the Arduino sketch (program) for the remote. This procedure is also described here while explaining the operation. So let us see how this is done. First, see the circuit diagram followed by its description and operation.
As shown in the figure, the circuit is built using 4 components only an Arduino board, IR sensor, RED LED and motor driver transistor MJE3055.
• The sensor TSOP1738 has 3 terminals (1) Vcc (2) Gnd and (3) output. Its Vcc terminal is given 5 V from board and Gnd terminal is connected to the ground of board. The sensor output is connected digital input pin 12 of the board.
• The RED LED is connected to digital pin 11 through the current limiting register of 470E.
• The analog output pin 3 of board drives 12V DC gear motor through MJE3055 transistor. This pin is connected to the base input of transistor through a 2.2K resistor, its collector output drives motor and emitter is connected to the ground of board.
• Motor is given external 12 V supply
Here is the snap of circuit arrangement.
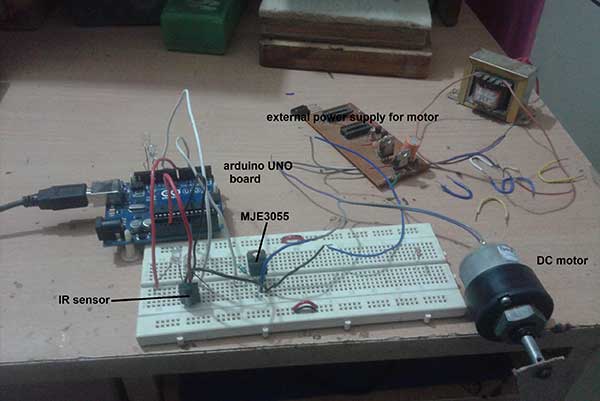
Fig. 2: Image of Arduino and IR Remote based DC Motor Controller
CIRCUIT OPERATION
First, we have to decide, which are the different buttons of IR remote, that we will use to control DC motor. We want to perform following actions.
1. Run or stop DC motor
2. Increase/decrease speed of motor
So we require 3 buttons. I have used set-top box (STB) remote that has many buttons like 0-9 digit buttons, volume control buttons, channel up/down buttons, arrow key buttons etc. From all these buttons I have selected following 3 buttons for above operations.
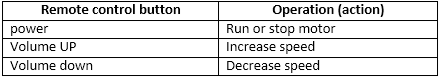
Fig. 3: Table listing IR Remote buttons and their respective functions in DC Motor Control
After deciding the buttons next is to decode the codes of these buttons. As we know when any button is pressed from remote, it will send one code and based on this code the action is performed. So to decode these codes I have used IRremote library for arduino, readily available on the internet.
So download the library and use an example to decode the codes of remote buttons. Upload the program into arduino microcontroller and connect IR sensor as shown in the figure. Now point the remote control towards IR sensor and press the button. Open serial monitor and you can observe the code of pressed button in form of numbers. Note down the codes of required buttons like I have noted the codes as per the following table -:
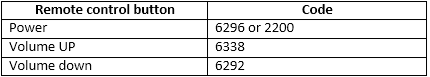
Fig. 4: Table listing IR Remote buttons and respective IR Codes
In the arduino sketch above codes are used corresponding to button pressed to perform an action as per the previous table. Now let us see the actual operation.
• Give the power to board and circuit through USB and to motor through external supply. Initially, the motor is stopped and LED is off. The message is displayed on serial monitor as “IR remote controlled DC Motor”
• Now when the power button is pressed from remote the PWM is applied to motor through pin 3 so motor starts running. The LED is turned ON to indicate motor is running. The message is displayed on the serial monitor as “Motor is running: LED ON”. When the same button is pressed again the PWM applied to the motor is stopped so the motor is also stopped and LED is OFF. The new message displayed on serial monitor as “Motor is stopped : LED OFF”
• Now when volume up button is pressed, the width of the pulse applied to the motor is increased so motor speed increased. The message displayed on the serial monitor as “motor speed increased”. It also displays PWM value from 0 to 255.
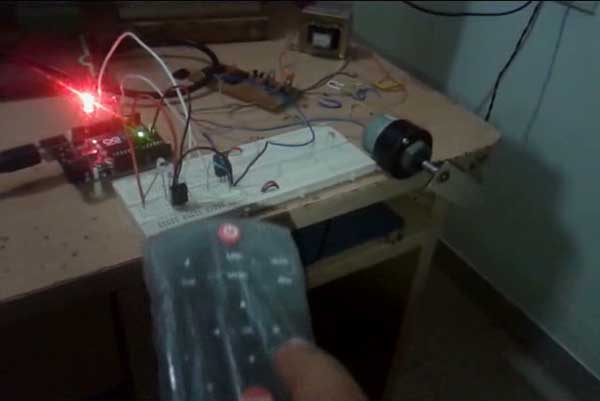

Fig. 5: Image showing working of Arduino and IR Remote based DC Motor Controller
• Now when volume down button is pressed, the width of the pulse applied to the motor is decreased so motor speed decreased. The message displayed on the serial monitor as “motor speed decreased”. It also displays PWM value from 0 to 255.
Thus we can run or stop the DC motor as well as increase or decrease speed of it using any IR remote like of TV, STB, DVD etc with the help of arduino.
Project Source Code
###
#include <IRremote.h> int IRpin = 12; // pin for the IR sensor int LED = 11; int motor = 3; int PWM_value=205; // initial pulse width IRrecv irrecv(IRpin); decode_results results; void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // enable serial communication Serial.println("IR Remote controlled DC Motor"); irrecv.enableIRIn(); // Start the receiver pinMode(LED, OUTPUT); digitalWrite(LED,LOW); } void loop() { while(!(irrecv.decode(&results))); //wait until no button is pressed if (irrecv.decode(&results)) // when button is pressed & code is received { if(results.value==6296) // if code is 6296 { digitalWrite(LED, HIGH); // LED ON and analogWrite(motor,PWM_value); // motor start Serial.println("Motor is running : LED ON"); // display message } else if(results.value==2200) // if code is 2200 { digitalWrite(LED, LOW); // LED OFF and analogWrite(motor,0); // motor stop Serial.println("Motor is stop : LED OFF"); } else if(results.value==6338)) // if code is 6338 for volume up button { if(PWM_value<255) PWM_value+=10; // increase pulse width Serial.print("motor speed increased : PWM= "); Serial.println(PWM_value); // display message analogWrite(motor,PWM_value); // and increase motor speed } else if(results.value==6292)//if code is 6292 for volume down button { if(PWM_value>25) PWM_value-=10; // decrease pulse width Serial.print("motor speed decreased : PWM= "); Serial.println(PWM_value); // display message analogWrite(motor,PWM_value); // and decrease motor speed } delay(200); // wait for 0.2 sec irrecv.resume(); // Receive the next value } }###
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.