Unwanted sound is considered as noise pollution which can cause both behavioral and health problems in human beings. Noise pollution can cause physiological changes in the body like hypertension, high stress level, sleep disturbances etc. It can also cause behavioral changes like annoyance, aggression etc. Normal pleasing sound level is around 30 dB but the normal environmental noise is around 40-60 dB which can be considered as normal. But if the noise level increases above 80 dB, it can affect our psychomotor performance and creates high stress level, loss of attention, physiological changes etc.

Noise pollution can cause many detrimental changes in animals and increase the rate of mortality by changing the delicate balance of prey-predator relationships. Noise interferes with the use of their own sound for communication related to reproduction and migration. Overexposure to high intensity sound affects the hearing ability of many animals. Very high sound causes the reduction in the number of animals in the habitats leading to habitat loss and may lead to the extinction of species.
Impact of noise pollution is very high in industrialized areas and metropolitan cities compared to other parts. Elevated noise in factories, workplaces can cause hearing impairments, hypertension, annoyance, sleep disturbances, decreased attention in children etc.
Safe sound level
Very loud noise of a particular frequency can cause over activity of hair cells of cochlea and the hearing threshold will shift to that frequency. Loud noise of any frequency can have detrimental effects on the normal hearing process. Usually the sensitivity to particular frequencies is only found in young people or in people who have not been exposed to loud music. Personal music systems with in-ear speakers are capable of very high sound levels in the ear, and are believed by some to be responsible for much of the hearing loss in young adults.
Decibel
Decibel (dB) is the unit used to measure the intensity of sound. Decibel is considered as a value between two powers rather than a specific unit. It is the logarithmic unit used to describe a ratio. The ratio may be power, sound pressure, voltage or intensity or several other things. What does 0 dB mean? This level occurs when the measured intensity is equal to the reference level. i.e., it is the sound level corresponding to 0.02 mPa. In this case, sound level is
20 log (p measured/preference) = 20 log 1 = 0 dB
0 dB does not mean no sound; it means a sound level where the sound pressure is equal to that of the reference level. It is also possible to have negative sound levels. For example, – 20 dB means a sound with pressure 10 times smaller than the reference pressure. That is 2 µPa. Sound pressure level is given in units of dB (A) or dBA. Sound pressure level on the dBA scale is easy to measure and is therefore widely used. For sound pressure level, the reference level (for air) is usually chosen as 20 micropascals (20 µPa), or 0.02 mPa.
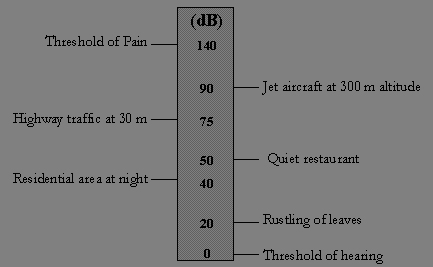
Decibel Chart

Some of the common sound levels in terms of decibel are
1. Weakest sound 0 dB
2. Silent environment with natural sounds 30 dB
3. Normal human conversation 60-70 dB
4. City with heavy traffic 80-90 dB
5. Drilling or grinding machinery 90- 110 dB
6. Get aircraft and explosion 140-150dB
Logarithmic response of Sound
The Human ear is capable of hearing a very large range of sounds. To determine such a range, logarithmic units are useful. Psychologists say that our sense of hearing is roughly logarithmic. That is, we have to increase the sound intensity by the same factor to have the same increase in loudness.
Phones and Sones
The Phon is a unit related to dB by the psychophysically measured frequency response of the ear. At 1 kHz, readings in phone and dB are the same. Sone is defined to be equal to 40 phons. Experimentally it was found that a 10 dB increase in sound level corresponds approximately to a perceived doubling of loudness. The Sone is derived from psychophysical measurements which involved volunteers adjusting sounds until they judge them to be twice as loud.
Noise Pollution and Health
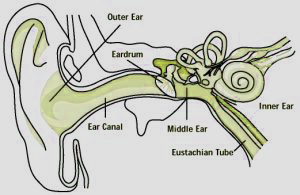
The most important effect of chronic exposure to high sound level is hearing loss. The reason for this is the damage in the stereocilia present in the cochlea of internal ear. The middle ear of human beings along with the ear pinna amplifies the sound by a factor of 20 so that very high pressure reach the internal ear which can create trauma in the cochlear structures leading to irreversible hearing loss.
Anatomy of Human Ear
Tinnitus is another health problem due to noise pollution. It can leads to forgetfulness, depression, panic attacks etc. The maximum sound level is considered as 140 db and permanent damage of hearing tissue occurs when the sound level is above 180db

Stereocilia
Cardiovascular effects
Noise level above 70 db can increase the risk of cardiovascular problems due to hypertension, increased Cortsol production etc. Elevated noise can cause arterial constriction leading to elevated blood pressure and reduced blood flow. Annoyance due to very high sound increases the Adrenaline level which is the most important reason of arterial constriction and elevated blood pressure. Other effects include fatigue, head ache, gastric problems etc.
Annoyance
Sound levels as low as 40 db can cause annoyance in human beings including sleep disturbances, speech or reading difficulties etc. Dysgraphia, the writing learning impairment is commonly associated with environmental stress.
Elevated noise can create stress increase workplace accidents and stimulates aggression and antisocial activities. Elevated noise from air crafts, vehicles, machinery, music systems etc can have many impacts on the normal life activities and behaviour of human beings.
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.