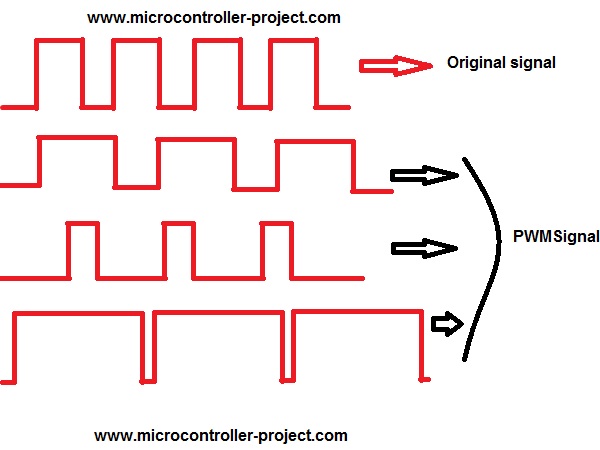
PWM in simple words changes the output voltage on a specified pin on which it is applied by varying the duty cycle of output wave form. Frequency and duty cycle of PWM signal can easily be varied using timers of 8051 microcontroller. Figure below will clear you about PWM signals and duty cycle. Original signal duty cycle is varyied in the below diagram.
What exactly duty cycle is?
Motor speed control with 8051 microcontroller – Project requirements
- Microcontroller 8051(89c51 or 89c52)
- Crystal (11.0592MHz)
- Capacitors 2 (33pf)
- Push Buttons 9
- DC Motor- Fan (Small Toy Motor)
- Power Supply (5v)
- L293D (DC Motor Driver)
Now how to generate these delays using 8051(89c51,89c52) microcontroller timers? Their are two timers in 89c51 microcontroller Timer-0 and Timer-1. You can use them for delay purposes or for counting an event etc. You can use these timers in Four Modes. I am using them in 16-bit mode. To learn more about timers, their modes and initialization go through the tutorial
8051(89c52,89c51) are 8-bit microcontrollers. But you can use their timers as 16-bit. To load 16-bit value in timers you use two registers THx and TLx associated with timers. Where THx represents Timer High Byte and TLx represents Timer Low Byte (Note x is 0 or 1 depending on the timer you want to use). Here i am using Timer-0 so I will use TH0 and TL0 registers.
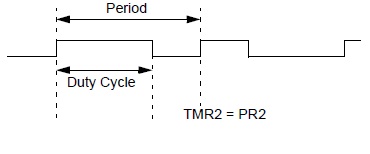
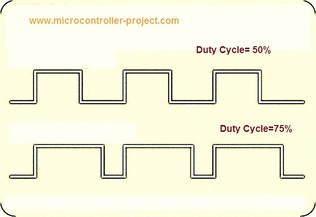
My Duty cycle base is 200 us means at 100 us duty cycle will be 50%. 50% duty cycle means both positive and negative signals are same in length(time). You can see two sine(digital) waves with duty cycles 50% and 75% in the figure at left side. Notice the difference between both waves.
I calculated delay for 00, 20 us, 40 us, 100 us, 160 us, 180 us, 500 us, 800 us and 100 us and loaded the values obtained by the result in TH0 and TL0 registers. Formulas to calculate delay is given below with an example.
|
You can Calculate values of TH0 and TL0 registers for 00, 20 us, 40 us, 100 us, 160 us, 180 us, 500 us, 800 us and 100 us delays using the formula given on the right side. I calculated the values using the same formula.
PWM is generated on Port-1 pin#0. Pin#0 of Port-1 is connected to L293D. To switch between different duty cycles i used Push Buttons. Each push button corresponds to PWM of different duty cycle. Total 9 push buttons are used in the project. Eight are connected to Port-2 and Ninth one is connected to Port-0 pin#7. Apply 5v at Pin#40&31 of Microcontroller. Ground Pin#20. Connect crystal(11.0592 MHz) to pin#18&19 of microcontroller. Connect capacitors in parallel to crystal. |
L293d motor driver with 89c51 microcontroller circuit diagram
L293D motor driver
In the code portion i first included the header file reg51.h. This header file must be included in every project code that is going to be compiled in keil compiler. Some single bits are initialized than. These bits represents push Buttons and Pwm output pin. In the main function first each port is initialized as input or output.
The instruction TMOD=0x01 is initializing Timer-0 in 16-bit Mode. Do not understand take the tutorial.
If-else statement is switching between different duty cycles, depending on the push button pressed. In button statements Pwm_B_20=P2^1, 20 represents the duty cycle corresponding to button. Like in statement Pwm_B_60=P2^4, 60 represents the 60 us high time or 30% duty cycle. Delays greater than 200 us means 100% duty cycle.
Sorry for the poor quality of video
Filed Under: 8051, Electronic Projects, Microcontroller Projects




Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.