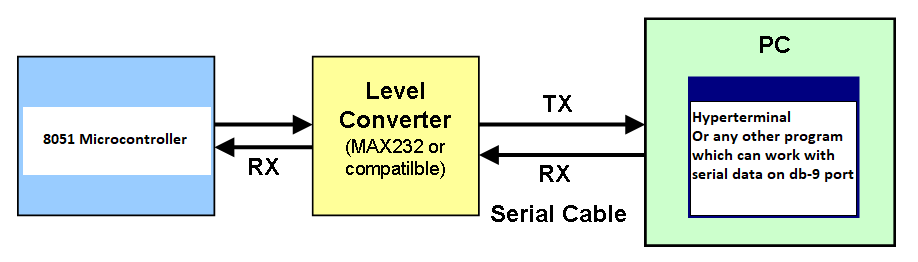
The block diagram of data transfer between 89c51 microcontroller UART port and personal computer is shown below.
Max232 Level converter
8051(89c51,89c52) Microcontroller UART
89c51 microcontroller Uart is used to receive data from PC. You can also use any other 8051 series microcontroller like 89c52 microcontroller. But first be sure it has build in UART(universal asynchronous receiver transmitter)for serial communication.
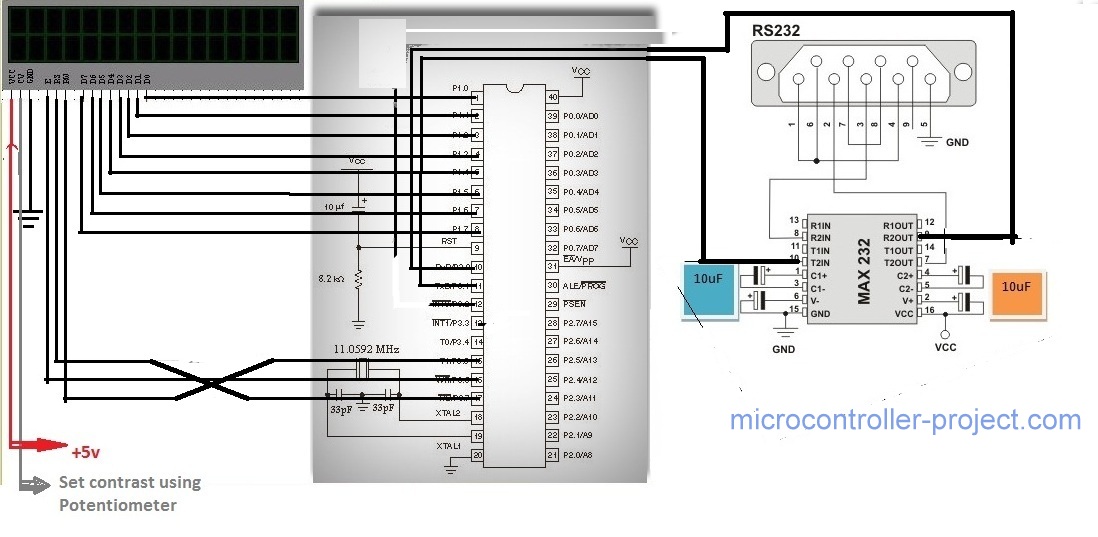
Port-1 of our microcontroller is used as output Port. It is connected to data pins of 16×2 lcd.
- Port-3 pin# 5 is connected to rs(regester select) pin of 16×2 lcd.
- Port-3 pin# 6 is connected to en(enable) pin of 16×2 lcd.
- Port-3 pin# 7 is connected to rw(read write) pin of 16×2 lcd.
If you dont know how to interface lcd with 8051(89c51,89c52) microcontroller here are some good tutorial, just go through them.
Project Code
In the main function i first called the lcdinit() function to initialize the 16×2 lcd. All the commands used in the function are deeply discussed in the above tutorials. Then timer mode is set. TMOD=0x02 means Timer1, Mode2 (8 bit auto reload) is selected. TH1=0xFD is actually timer one high byte, giving 0xFD hexadecimal value to TH1 means setting communication baud rate between 8051 microcontroller and PC to 9600 bps(bits per second). SCON=0x50 is actually setting our serial data bits format Total=8 Data bit with 1 start bit and 1 stop bit. TR1=1 means run timer one. This whole phenomena with full meaning of the statements (SCON,TMOD,TH) is discussed in the below two tutorials. How to calculate baud rate values are also discussed.
while(RI==0) is checking RI(receive interrupt) flag continuously. This flag automatically becomes one when 8051(89c51,89c52) receives any data on its RXD pin(P3^0). when RI becomes 1 it means we have one byte of data in our SBUF(serial buffer) register. So in next statement i picked the Byte from SBUF register and save it in character variable data. Then i made the RI flag low again to receive next byte. The Byte which i saved in data variable is now send to display function to be displayed on the 16×2 lcd.
You may also like:
Filed Under: 8051, Electronic Projects, Featured Contributions, Microcontroller Projects



Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.