Mosquitoes have been a big problem in urban and rural areas. Carriers of deadly diseases like malaria, dengue and chikungunya, mosquitoes pose a serious health threat to humans. Among the several toxic and non toxic methods that have been devised to keep the mosquitoes away, mosquito repellents are one of the most economic and widely used. Using a simple electrical heater, a refill that contains a liquid which disrupts normal activity of mosquitoes, one can get relieved from these small creatures within minutes.
Quite simple to use and refill, liquid mosquito repellent is a common house gadget whose working is ambiguous to most of us. This insight will detail with the various outer and inner features of a repellent, its refill and working. Against mosquito bites, prevention is always better than cure, let’s find out what makes this little machine a good prevention.
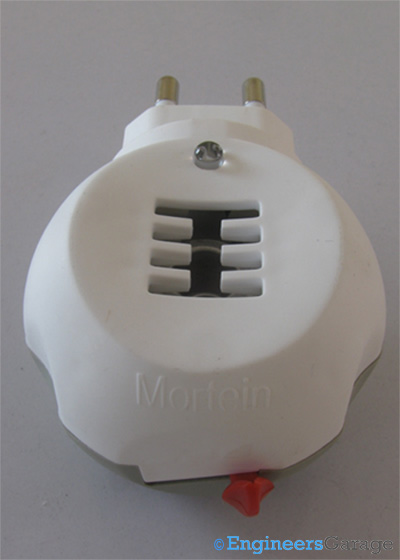

Fig. 1: Image of Electrical Mosquito Repellant Machine
Outer Structure
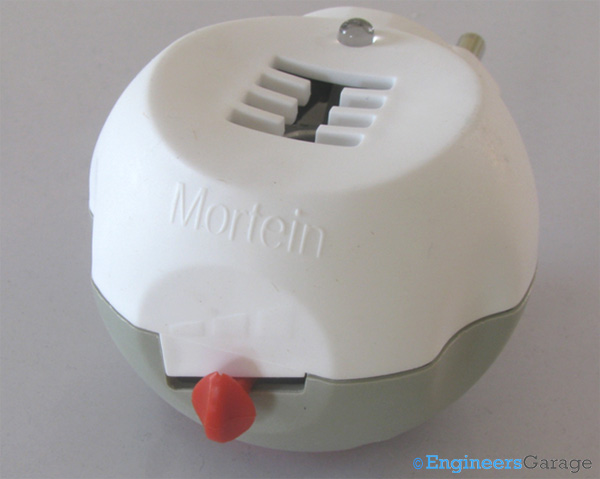

Fig. 2: Image Showing Outer Body of Mosquito Repellant and its Various Parts
Shown in the image above is the front of a conventional portable mosquito repellent. Made of light weight plastic, this is a simple electrical device that holds the repellent refill. A slider knob is there through which the user can regulate the quantity of liquid to be vaporized. The vapors are released through a small rectangular opening on the top of the repellent.
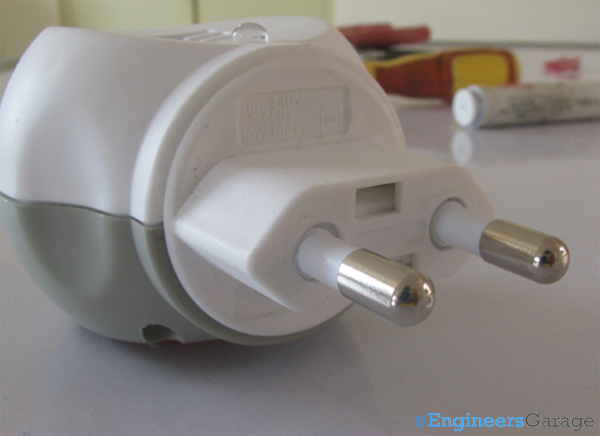

Fig. 3: Back Side View of Repellent—Electrical Plug Switch and LED
The back side of the repellent shows the electric plug seat and an LED which glows when the repellent is in use. The plastic body of the repellent can withstand the temperature increment when the machine is in on state.
The portion of the wick that is covered by the heating element of the repellent machine is directly proportional to the amount of liquid vaporized. The more the portion of wick near the heating element, higher the vaporizing rate.
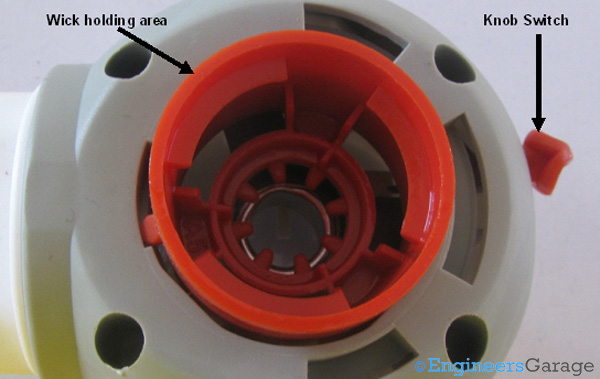
Fig. 4: Knob Switch and Wick-Holding Area at Bottom of Repellent Device
The image above shows the bottom part, where the liquid bottle is inserted & mechanically held by the machine. To help the user in controlling the amount of liquid to be vaporized, a knob switch is present. More is the area of the wick under the heating element, the more will be the vapors.
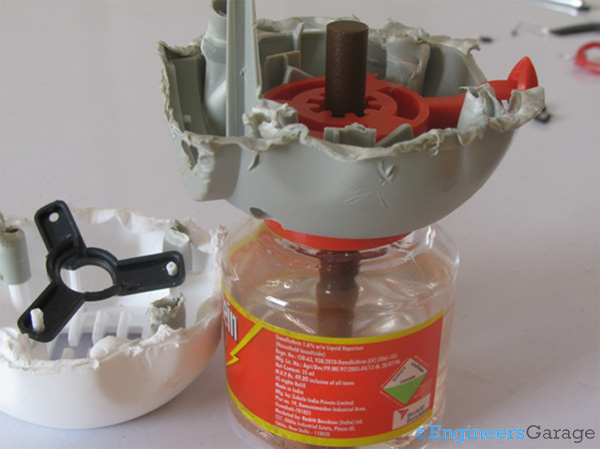

Fig. 5: Image Showing How Wick Holds Liquid Bottle
The image above shows how the wick is held in the machine. Slider helps in increasing the area of the wick under the heating element. Moving the switch changes the area of the wick under the heating element thereby regulating the speed at which the machine is working. The area is changed by mechanical motion of the red part of the assembly shown in the image above. There is no electronics involved.
Internal Structure & Heating Element
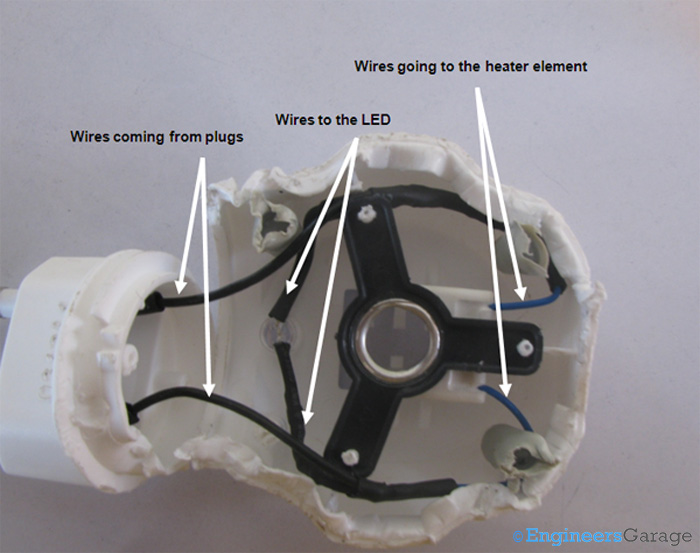
Fig. 6: Image Showing Wire Layout of Repellent Machine
When the plastic body is opened, the internal wiring of the repellent can be seen. The two wires coming from the plug seat are split into four. Out of these four wires, two connect to the LED to illuminate it while the other two are used to heat the element which helps in evaporating the liquid in the refill.
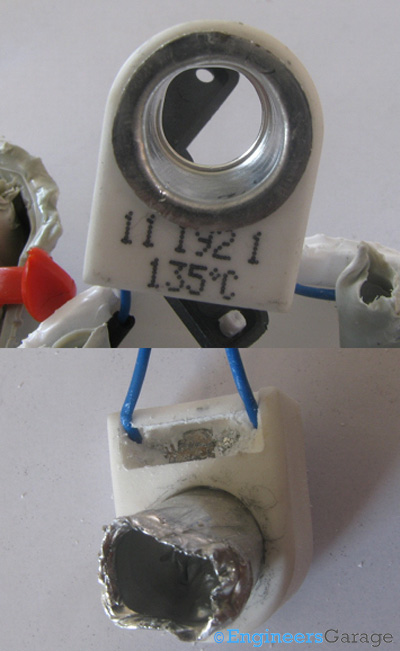
Fig. 7: Two Images Showing Heating Element of Repellent Device
The image above shows the heating element in the mosquito repellent machine. It is a ceramic Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistor having a hollow metallic cylinder at its center. When heated, the resistance of a PTC thermistor increases.
Using a PTC is beneficial as it is an efficient and economic solution to serve as a heating element. The minimum temperature required by the PTC to work to its normal value in this case is around 135°C. They are able to reach this temperature in a short span of time, thus having a fast response time. They also have the tendency to limit current, making usage of repellent machine possible for longer duration of time. The hollow metallic cylinder aids in heating the wick of the refill instantly.
Heating Element Contd…
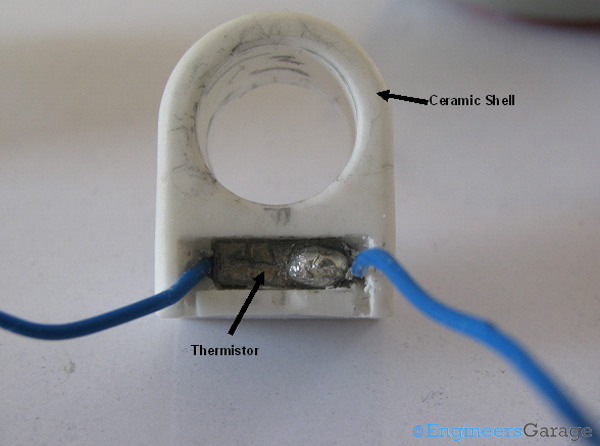
Fig. 8: Thermistor and Ceramic Shell of Heating Element
The image above shows the thermistor and its ceramic shell. The thermistor has metallic layers over it that allows the wires to solder on it.
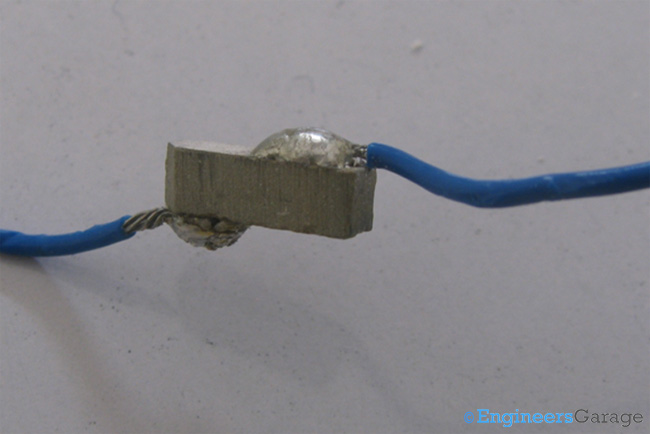
Fig. 9: Thermistor with Wires Soldered
The image above shows the positive temperature coefficient of the thermistor with the wires soldered on it. To ensure uniform heating, the wires are placed at opposite sides.
Wick
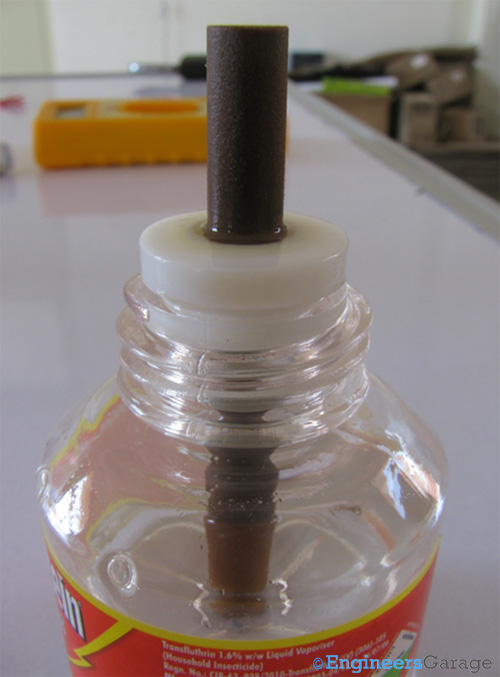

Fig. 10: Mosquito Repellent Liquid Bottle
The image above shows the refill of the mosquito repellent. Enclosed in a plastic bottle, the liquid is a mixture of chemicals that primarily include transfluthrin, a stabilizer (Butlyated hydroxytoluene BHT in this case) and a perfume. All these chemicals are dissolved into deodorized kerosene so that they can be easily vaporized when subjected to temperature.
The mixture is toxic as it can cause a variety of reactions such as dizziness, headache, skin allergies, irritation and other physical reactions. Transfluthurin is the most important part of the mixture. It passes through the skin of the mosquitoes and cause paralysis making the movement of the mosquitoes slower, thus damaging their nervous system.
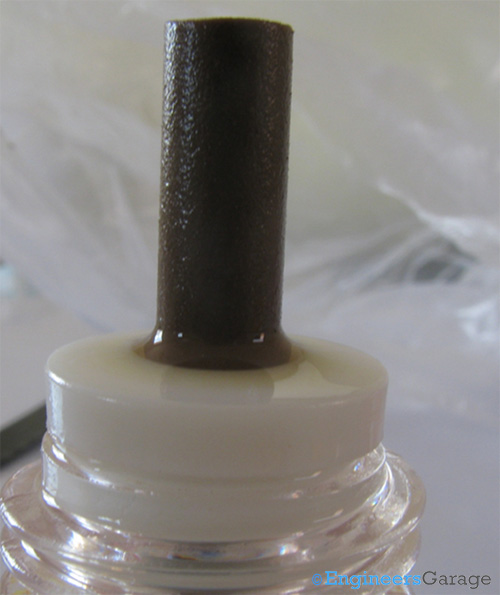

Fig. 11: Wick of Liquid Bottle
The wick is the only way through which the liquid reaches the repellent machine for vaporization. The wick absorbs the liquid and when inserted in the machine, the top most part gets heated. This vaporizes the liquid and which in turn spreads to the room.
Filed Under: Insight


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.