Definitely, mosquitoes are annoying and it can spread diseases also. The best way to destroy mosquito is electronic killing using Swatter. It eliminates the use of toxic chemicals. The mosquito coils and liquids do not kill mosquito but they repel them only. Mosquitoes will return back when the chemical disappears from the atmosphere. 
Fig. 1: Image of Mosquito Racket
The swatter is commonly called as Mosquito racket and is meant for killing the mosquito and not for repelling. Since each mosquito lays thousands of eggs, destroying a mosquito equals destroying thousands of mosquitoes.
Some Mosquito Biology
There is no doubt, mosquitoes and mosquito bites are annoying. The nuisance mosquitoes bother people around homes or in parks and recreational areas and everywhere. They reduce real estate values, adversely affect tourism and related business interests, or negatively impact on livestock or poultry production. Above all these, mosquitoes transmit fatal diseases like Dengue fever, Malarial fever, Filariasis, Chikungunya, Encephalomyelitis etc.
Swarming in Mosquito
Mosquitoes are Crepuscular (Twilight active- Evening and early morning) and they show mass migration (swarming) in places where human beings are located. Mosquito has feeble flying ability so that they can fly only 10-20 meters distance and up to a height of 20-25 meters. They usually fly above the ground level around 2-3 feet. That is why we get more mosquito bites in the legs. Mosquitoes prefer legs since they get sufficient blood from the legs, because the veins in the legs are large and are located just below the skin. The mosquitoes biting us are the members of the local population . That is, the mosquitoes reared in our own home. Mosquitoes from long distance will not migrate to our home for biting.
Ultrasound detection
Male mosquito produces characteristic ultrasound vibrations to attract females. After mating, female mosquito avoids the presence of males by detecting the ultrasound from males. This is the principle in Ultrasound mosquito repellents that produces 22-38kHz ultrasound to simulates the sound of male mosquito. The female mosquito considers the device as a male mosquito and avoids its presence.
Human detection
Mosquitoes have complex methods for detecting the hosts and different types of mosquitoes react to different stimuli. Most mosquitoes are active at dawn and dusk, but there are also day biting mosquitoes. There are many factors that attract mosquitoes towards you.
1. Body Temperature
The exact body temperature sensing depends on the type of mosquito. Many mosquitoes are attracted to the slightly cooler temperatures of the extremities (hands, foot, nose, and ear) of the body.
2. Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide content in the body attracts mosquitoes. Carbon dioxide content in theclosed room also attracts mosquitoes.
3. Moisture
Mosquitoes are attracted by perspiration because of the chemicals it contains and also because it increases the humidity around your body. Interior plants, aquarium etc attracts more mosquitoes.
4. Lactic Acid
Lactic acid content of the body is another attractant. Lactic acid content in the blood increases after exercise and also after eating salty and high potassium food materials.
5. Perfumes and Flowers
Perfumes, floral decorations, cosmetics, fragrant cloths etc attract mosquitoes.
6. Dark Clothing
Dark cloths attract mosquitoes because they can easily locate the host from the surroundings. They have feeble vision. Mosquitoes rests the on removed clothes due to the presence of body smell believing that human is there.
Mosquito bite
Mosquitoes have chemo sensors which enable them to detect the humans or any other animal by the odor, heat etc released by the body and also the carbon dioxide exhaled by the humans and the other animals. Mosquito bites are caused only by the bite of a female mosquito. The female mosquito feeds our blood by piercing the skin with the proboscis a modified mouth part. While sucking our blood, mosquito deposits some saliva into the skin. The saliva contains anticoagulant proteins that remain in our body and react with the body chemicals, resulting in the characteristic itching and bump. Both Male and Female Mosquito are Plant juice feeders but female mosquito bites human beings to getblood protein for the maturation of their eggs. On the first day of emerging from the pupa, female mosquito do not bite and on the second day, it mates and starts feeding human blood. After two or three days it lays thousands of eggs in water and die off.
Mosquito Swatter
It is an electronic device that produces high voltage around 300-400 volts in the nets. When the mosquito passes through the outer and inner nets of the swatter, its wings short out and sparks which will destroy it. The mosquito swatter circuit consists of three sections.
1. AC to DC converter
AC is directly step-down using the AC capacitor and rectified through full wave Diode Bridge. A low value smoothing capacitor is also present. This DC is used for charging the battery in rechargeable types. But in non rechargeable types, AC-DC conversion is not present.
2. Oscillator
A transistor based oscillator is present to generate pulses. The transistor switches on and off rapidly to create a rising and falling voltage for the transformer to step up.
3. A step-up transformer to generate high voltage AC by inverting the DC to AC.
4. Net or Grid – The high voltage low current pulses passes into the net. The grid set up has three nets. Two outer nets are negative and the middle one is positive.
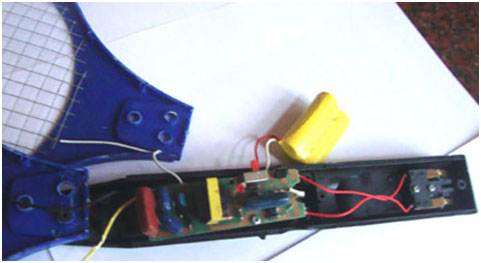
Fig. 2: Image of Mosquito Swatter Structure
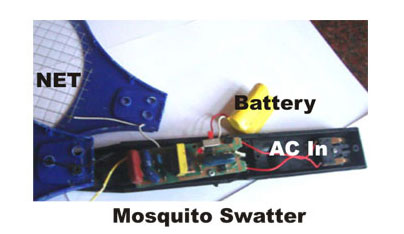
Fig. 3: Image of Inside the Mosquito Swatter
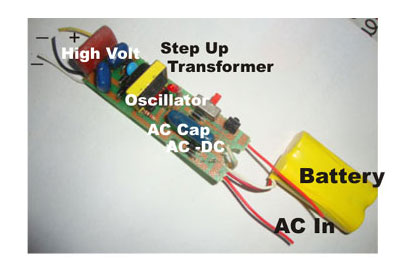
Fig. 4: Image of Mosquito Swatter Circuit
When the mosquito swatter is switched on, and gently swings, the electric field from the net attracts the mosquitoes and they try to move though the net which gives a fatal shock.
Probable reasons for Failure
1. Battery failure
In rechargeable type swatter, the battery should be properly charged. It is a 3 volt battery which discharges deeply if the unit is used for 10-20 minutes continuously. So after the use, it should be plugged in for charging. In non rechargeable types, frequent battery replacement is necessary.
2. Shorting the Grid
Grid shorting is another important cause of failure. During the use, the grid may mechanically vibrate and hit on furniture and walls. The nets are very delicate and if they make contact each other, shorting occur which destroys the internal circuit.
3. Solder point break
The output from step-up transformer is connected to the grids using wires. These wires are soldered to the grid. When the mechanical vibration is too strong, the solder points may detach.
4. Contact with water
If water is spilled on the net, dry it immediately in sunlight. Do not try to push cloths into the net to wipe water. It will destroy the net.
5. Charging
Take care while charging the Swatter. If the inbuilt plug is loose in the socket, there is chance for sparking which can destroy the internal circuit. If the plug is loose, the swatter may fall from the wall mounted socket. So if the pin is not fitting in the socket firmly, try to charge in an extension cord with the swatter placed in the horizontal plane.
6. Do not introduce any metal tools like screw driver into the net. It will destroys the net through shorting and also give a shock (mild but can burn) to you. Do not touch the net when the switch is pressed.
7. Do not give the swatter to children. They will play badminton considering mosquito as ball. During the play, there is definite chance for a hit- not on the mosquito but on the wall or furniture. This can damage the swatter permanently.
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.