Bluetooth is a popular wireless technology standard designed for data exchange over short distances. Bluetooth is so common that it’s now the part of smartphones and comes in lots of embedded devices. Many wearable devices also use Bluetooth to pair with their accessories or co-devices. The Bluetooth interface uses UHF Radio wave in ISM band from 2.4 GHz to 2.485 GHz. It was invented by telecom vendor Ericsson in 1994 and developed by Bluetooth Special Interest Group. A Bluetooth connection has a range from 10 M to 100 M.
Making embedded devices Bluetooth enabled is a popular trend. The HC-05 Bluetooth Module is a commonly used and widely available Bluetooth module that can be added to an embedded project to make it Bluetooth enabled. The module can work as both Master and the Slave. The module connects with a microcontroller through serial communication. It is basically a 2.4 GHz Radio Transceiver with V 2.0+ Enhanced data rate of 3 Mbps modulation. The module can operate in two modes –
1. Automatic Connection Work Mode
2. Order Response Work Mode
In automatic work mode module can work in either of the three roles – Master, slave, and Loopback. In this mode, module follows default way to establish connection and exchange data. In Order response mode the user can set control parameters by sending AT commands. To enter into the AT mode, the 34th pin of the module needs to be connected to the power supply.
The modules have six commonly used pins apart from which there are programmable input/output pins and pins for communication over UART, SPI, USB and Synchronous PCM. The 34th pin is a programmable input/output pin which is designated as the Key pin.
For setting the module in AT Mode, the key pin of the module needs to be wired with the microcontroller. It should be set to LOW logic initially and once the module is powered on, should be set to HIGH logic for entering the AT mode. If the key pin is initially at HIGH logic, the baud rate for serial communication with the module will be set to 38400 bits per second even before the module is ready for entering the order response work mode. The desired baud rate for the initialization of the module is 9600 bits per second and is set to the value when Key pin is set HIGH after powering of the module.
In this project, the Arduino Pro Mini is used to pass the AT commands to the Bluetooth module. The Arduino board connects with the Bluetooth module and virtual serial port of a desktop computer. The AT commands are passed from a hyper terminal application to the Arduino Pro Mini. The Arduino board write these commands to the Bluetooth module. The responses from the Bluetooth module are serially read back and passed on to the hyper terminal application on the desktop.
The Arduino sketch simply creates and open two serial communication ports for data exchange between the Bluetooth module and the desktop computer. The Arduino code is written on Arduino IDE and burnt to the board using AVR Dude.
Components Required –
1. Arduino Pro Mini
2. HC-05 Bluetooth Module
3. Desktop Computer or Laptop
4. USB Cable
Software Tools Required –
1. Arduino IDE
2. Any Hyper Terminal Desktop Application like Arduino Serial Monitor
Circuit Connections –
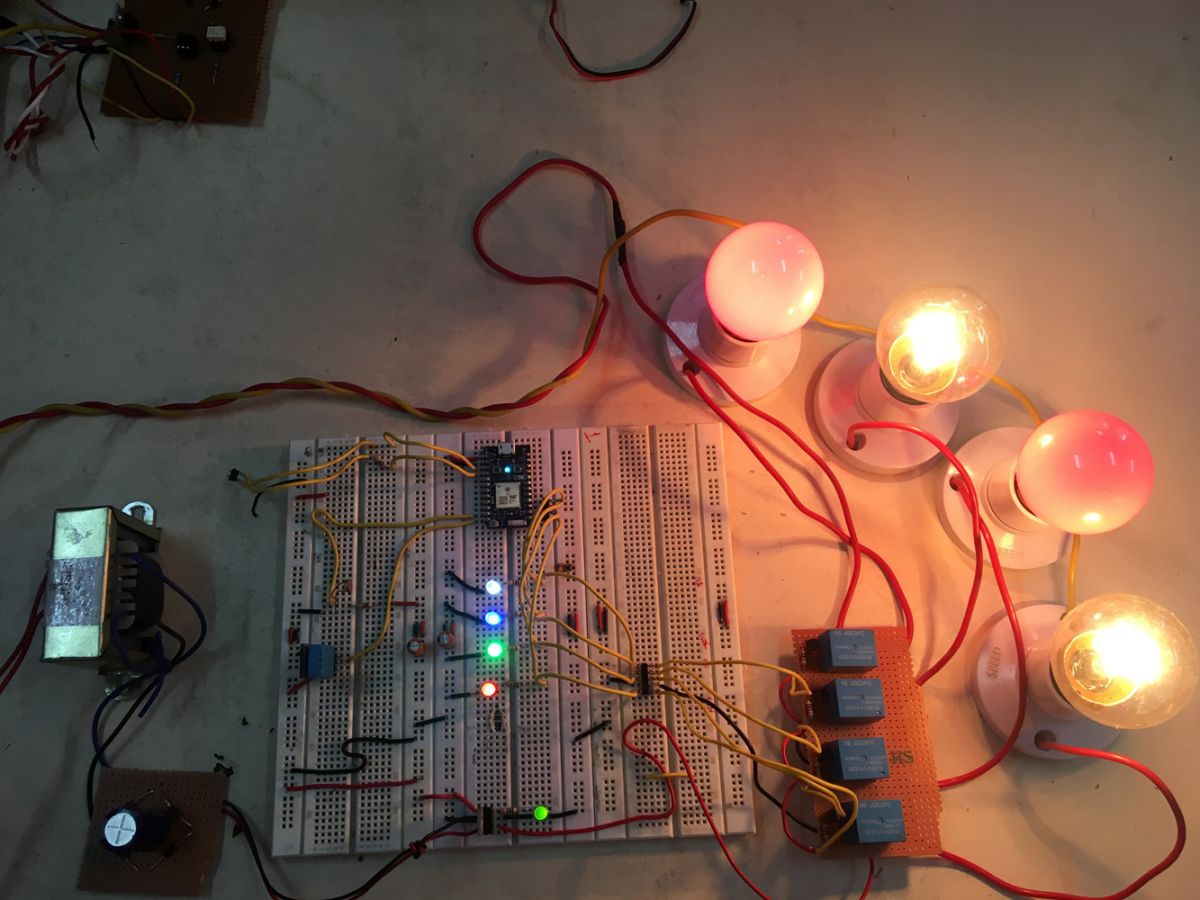
Fig. 1: Prototype of Arduino based Bluetooth AT Commands Test Project
The Arduino Pro Mini manages the exchange of data between the serial application on the desktop computer and the Bluetooth module. The circuit is assembled the following way –
Power Supply – The circuit is powered by a battery which directly supplies to the Arduino board and the Bluetooth module.
HC-05 Bluetooth Module – HC-05 Bluetooth module is serial port protocol module. It operates on ISM band 2.4GHz with V2.0+EDR (Enhanced data rate). It can work in both Master and slave modes. The Bluetooth module has six pins – Enable, VCC, Ground, Transmit Data (TxD), Receive Data (RxD) and State. The Enable and State pin are unused and so not connected in the circuit. The VCC and Ground pins are connected to the common VCC and Ground. The TxD and RxD pins of the module are connected to the pins 10 and 11 of the Arduino Pro Mini respectively. These connections are summarized in the table below –
Fig. 2: Table listing circuit connections between HC-05 Bluetooth Module and Arduino Pro Mini
Apart from these connections, the 34th pin of the module is wired to the pin 9 of the Arduino Pro Mini.
Desktop Computer – The computer is connected to the Arduino board through USB cable and transfers serial data to the board through Virtual serial communication using a hyper terminal application.
How the project works –
The project device receives the user entered AT commands from the hyper terminal application. The commands are serially read over virtual serial communication and passed to the Bluetooth module. The Bluetooth module responds to the AT commands and the responses are again serially read and transferred to the desktop application.
The HC-05 Bluetooth module supports the following AT commands –
|
|---|
Fig. 3: Table listing AT commands of HC-05 Bluetooth Module and their response
During the testing of the Bluetooth module, the following commands were passed for which the response given in the table below were received.
Fig. 4: Circuit Diagram of Arduino based Bluetooth AT Commands Test Project
These responses were observed on the Hyper Terminal Application. If the responses are not received on the desktop application, the circuit connections should be checked and baud rate must be verified. During testing, it was observed that baud rate needs to be set to 9600 bits per second initially but later it needs to be set to 38400 bits per second for running the AT commands.
Check out the Arduino code to learn how the Arduino board manages serial data between the desktop and the Bluetooth module.
Programming Guide –
For enabling virtual serial communication, SoftwareSerial.h needs to be imported. An object of Software serial type is instantiated and mapped to Arduino pins 10 and 11.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
SoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
The setup() function is called in which the baud rate for communication with the PC is set to 9600 bits per second. The pin 9 which is connected to the 34th pin of the Bluetooth Module is set to digital output and set to HIGH logic using pinMode() and digitalWrite() methods. Some initial messages are sent serially to the hyper terminal application and baud rate of the software serial port is set to 38400 bits per second for communication with the Bluetooth module.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(9,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(9,HIGH);
Serial.println(“Engineers Garage:”);
Serial.println(“Enter AT commands:”);
mySerial.begin(38400);
}
The loop() function is called in which the response from the Bluetooth module is checked and if available is written to the serial port. Similarly, if any AT command from the desktop is available, it is read and written to the Bluetooth module.
Note: Get the complete code in the code section.
This completes the Arduino sketch for the Bluetooth Module Testing Project. Get a computer, assemble the circuit, launch a hyper terminal application and get hands dirty. It’s time to test.
You may also like:
Project Source Code
###
//Program to #includeSoftwareSerial mySerial(10, 11); // RX, TX void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(9,OUTPUT); digitalWrite(9,HIGH); Serial.println("Engineers Garage:"); Serial.println("Enter AT commands:"); mySerial.begin(38400); } void loop() { if (mySerial.available()) Serial.write(mySerial.read()); if (Serial.available()) mySerial.write(Serial.read()); } ###
Project Video
Filed Under: Tech Articles
Filed Under: Tech Articles







Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.