This security alarm circuit can be used to protect your valuable documents and jewellery from theft or intruder. Just put the switch under the mat or in front of locker so that when unauthorised person come it will walk over the switch and this will trigger the circuit and alarm start sounding. Main advantage of this circuit is you can use it in two places because both switches produces different sound.
[[wysiwyg_imageupload:9927:]]
Fig. 1: Prototype Of security alarm circuit on Breadboard
This simple circuit is based on transistor, diode, resistor and switches with few more components.
1. Resistor– Resistor is a two terminal passive component used to control the flow of current into the circuit. A current through resistor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across resistor terminal.
Resistor comes in two variety –
1.Fixed resistor means they have fixed value of resistance.
2. Variable resistors means there value can be changed like if you have variable resistor of 5K then you can vary the resistance from 0 to 5 K Ohms.
We can calculate the value of resistor with the help of multimeter or we can do it with help of color code available on resistor.
2. Diodes– Diode is a two terminal device with a asymmetric characteristic means it allows low resistance to current flow in one direction and high resistance in another direction. Therefore it allows current to flow in one direction and blocks the current that flows in opposite direction. The two terminal of the diode are refer to as anode and cathode. Because of its unidirectional behaviour they are used to convert alternating current to direct current.
3. Transistor– Transistor is a three terminal electronic device used to amplify weak input signals. A transistor consist of two PN junction diode connected back to back. Transistor are of different type such as bipolar junction transistor, Field effect transistor and photo transistor. They are mostly used in electrical appliances due their smaller size and light weight. In addition they posses less power hence have greater efficiency.
4. Speaker- Speaker is a transducer which produce sound in response electrical audio signal applied at input.
5. Capacitor– A capacitor is a two terminal passive component which stores electric charge. Capacitors consists of two conductors which are separated by a dielectric medium. It works when potential difference applied across the conductors polarizes the dipole ions to store the charge in the dielectric medium. Capacitor comes in two variety-
1.Polarised capacitor- They have polarity means + and – sign. They are basically used to store charge. As they store charge they should be carefully discharge before troubleshooting the circuit.
2. Non polarised capacitor – They does not have polarity and can be mounted any way. They are basically used to remove the fluctuation present in conversion of AC to DC.
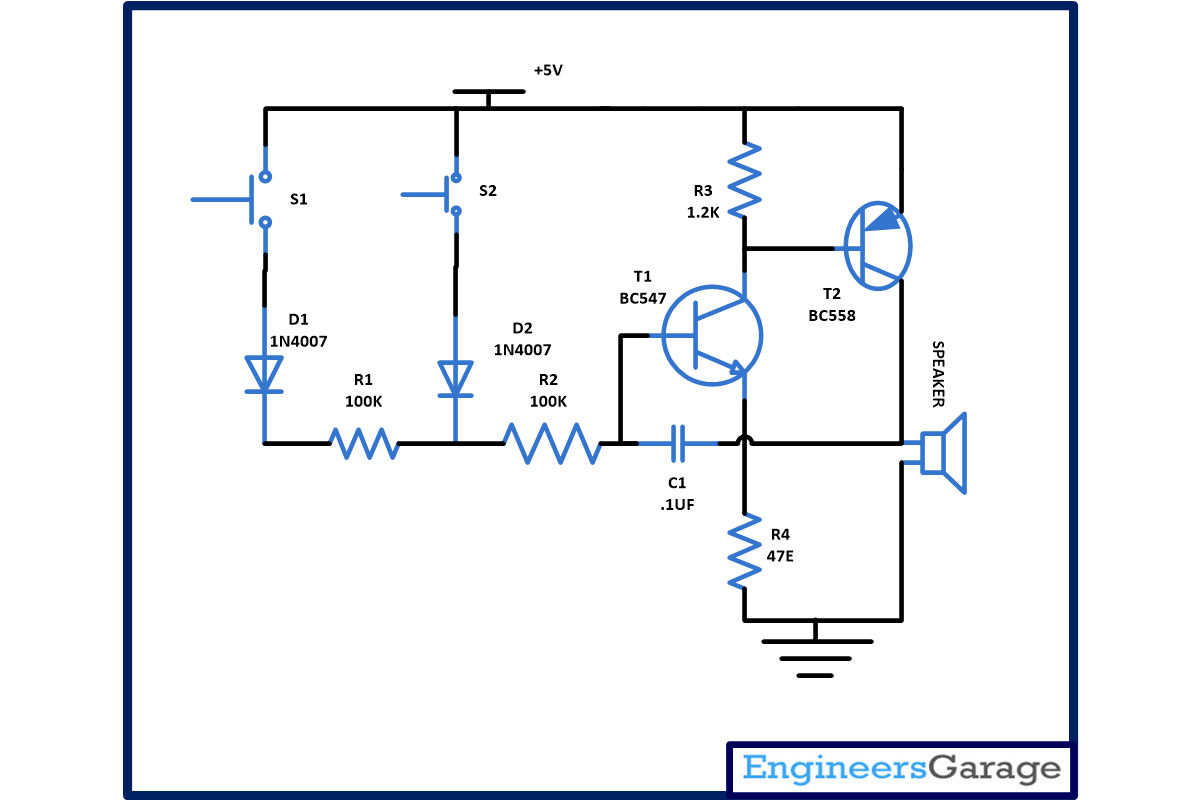
Working of the transistor based security alarm circuit
In this circuit two switches S1 and S2 are used for two places like one can be used on front door and another can be used in front of locker. When S1 is pressed diode D1 connected to it start conducting because of that transistor T1 and T2 connected through resistor start conducting. Capacitor C1 is used to provide positive feedback to transistor T1 and T2 for oscillation. When S1 is pressed low frequency tone is generated indicating that intruder is present on door.
Similar kind of phenomenon happen when you press the switch S2. Diode D2 connected to it start conducting which provide power supply to the working of transistor T1 and T2 and the speaker connected to it start sounding. But this time it produces a high frequency tone indicating that intruder is present near the locker. Once alarm start sounding it can only be off by disconnecting power supply.
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.