Transistor biasing is the process of setting the operating voltage across the transistor terminals. BJT (Bipolar junction transistor) has two junctions, one is base-emitter junction and another one is base-collector junction. Depending on the forward and backward biasing of this junction, there are three modes of the transistor. The transistor base to emitter junction depends upon its threshold voltage. When base to emitter voltage level drops below this threshold voltage, the transistor goes into its Cutoff State. When base to emitter voltage level is above this threshold voltage then the transistor is either in its Saturation State or Active State. Theoretically, the value of threshold voltage of the diode is 0.7V but practically, it is 0.65V.
Components Required :
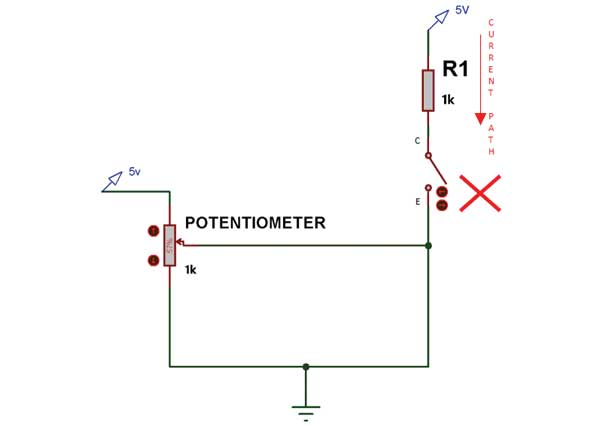
BC547 NPN transistor
Potentiometer of 1k
1k resistance
Some jumper wires
Breadboard
Power supply (+5V)


Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.