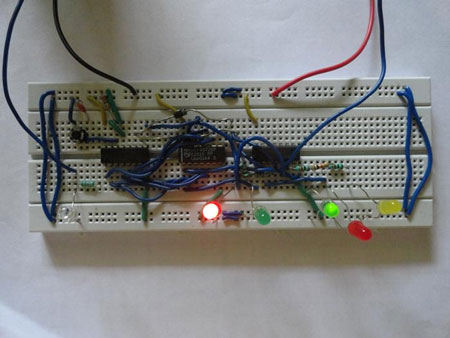
This two way traffic light project described below is a small model of traffic light which we daily see in our life on street. With this circuit you can control two way traffics. There will be lights on both sides, like there is red light on one side and green light will be present aautomatically on another side. It will also have yellow light to alert the passengers or drivers that now there signal are going to open.
This circuit is based on three IC so before understanding the circuit let’s understand the working of individual IC.
1. IC1 used is 4017– CD4017 is a 16 pin CMOS decade counter/ Divider. It take clock signal from the clock input and turn on the 10 output in sequence, each time when it receives clock input pulses. It is the most popular IC and extremely useful in various project like Light Chaser, Matrix Die. It is also useful in many applications like Binary counter/decoder, frequency division, divide by N counting, Alarm system, Automotive etc.
It has 3 input and 10 output pins and one is ground pin and another is used for power supply and one is Carry out pin. Pin diagram of CD4017 is shown below-
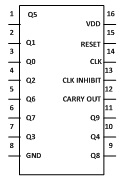
1. Input pin-
a. Reset pin (pin 15) – It is used to reset the counter to zero. If you want the counter to count up to third output then connect the fourth output to pin 15. Now after every third output it will automatically starts counting from zero.
b. Clock pin (pin14) – Whenever pin 14 goes high it will provide you the output. Like for first clock pulse pin 3 will provide you output similarly for next pulse pin 2 will provide output and so on. After 10 pulse it will again start from Q0 output.
c. Clock Inhibit pin (pin 13) – It is used to switch the counter “on” and “off”. When you want to switch off the counter then pin 13 should be high. If it is high it will ignore the clock pulse no matter how many times you press the switch means the count will not advance. In our circuit we have ground the pin 13.
2. Output pin (pin Q0- Q9) – It is used to receive the output in sequential manner. Like for first pulse pin 3 will provide you the output and so on.
3. Ground pin (pin 8) and Supply pin (pin 16) – It is used to provide ground and power supply to the IC for its working.
4. Carry out pin (pin 12) – It is used to connect one or more CD4017 IC’s. Like if you want to add one more CD4017 IC then connect Pin 12 to Clock input of its successor. The carry pin of first CD4017 is connected to clock input of second and the carry pin of second is connected to the clock input of third and so on. In our circuit we have used only one IC that’s why we have left this pin.
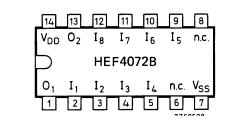
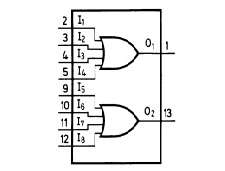
2. IC2 used is 4072– 4072 is a dual 4 input OR gate. Output of OR gate goes high when any of the input goes high and if all input is low then output is also low. 4072 is a 14 pin IC and contain 2 individual OR gate on a single IC. First gate include pin 2, 3, 4, 5 as input pin and pin 1 as output pin. And in second gate pin 9, 10, 11, 12 are output pin and 13 is output pin. Following figure shows the pin diagram and functional diagram of 4072 IC.
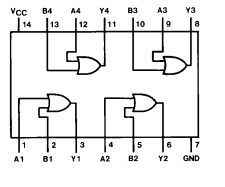
3. IC3 used is 7432– 7432 is a quad 2 input OR gate. In this also output goes high when any of the input is high and goes low when all inputs are low. 7432 contains 4 individual OR gate on single IC. In our circuit we are utilizing only 2 gates. Following figure shows the functional diagram of 7432 IC.
Working
Working of Two Way Traffic Light Circuit
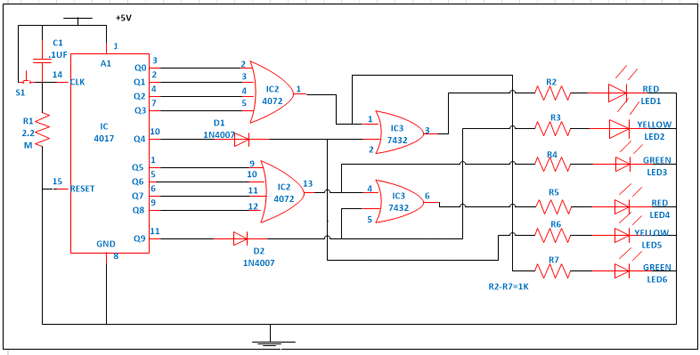
First of all make the connections as shown in circuit diagram. Now provide power supply. In this circuit we are providing input signal to IC1 that is 4017 with the help of switch. So we are manually providing the input to our traffic light you can also use a 555 timer or logic gate IC which will automatically provide signals to on the decade counter/ divider IC4017. When you press the switch S1 counter starts from zero and it advances one each time whenever pin 14 receives a positive pulse. When switch is pressed first time output pin 3 of IC1 goes high. This high is provided to pin 2 of IC2 and from truth table of 4072 IC, if any of the input is high it will provide you the high output. Because of this pin 1 of IC2 become high and Green LED6 will glow. Similarly this high is also provided to pin 1 of IC3 therefore from truth table its output also goes high indicated by glowing of RED LED1. So at one way RED light is there and on another way Green light is on.
When you press the switch next time pin 2 of IC1 goes high. It makes pin 1 and pin 3 of IC2 and IC3 high and RED LED1 and Green LED 6 continuous to glow. Similar phenomenon happens when you press the switch third and fourth time. Because it is making the pin 1 and pin 3 of IC2 and IC3 to go high (this can be verified with the help of truth table). Now when you press the switch for fifth time pin 10 of IC1 goes high and this will make all input (2, 3, 4 & 5) of IC2 low because of that Green LED 6 stop glowing. And Yellow LED5 connected to Diode D1 start glowing. And pin 3 of IC3 is high and Red LED1 continuous to glow. This shows that now another way is going to open.
Now when you press the switch for sixth time pin 1 of IC1 goes high. Which will make the pin 13 of IC1 goes high this will glow the Green LED 3. It will also makes the pin 4 of IC3 high and because of this, pin 6 of IC3 also high and Red LED 4 also glow. This indicates that one side we have Red light and another side we have Green light. When you press the switch next time pin 5 of IC1 goes high. This makes pin 10 and pin 6 of IC2 and IC3 high and Green LED3 and Red LED 4 continuous to glow. Similar phenomenon happens when you press the switch eighth and ninth time. Because it is making the pin 13 and pin 6 of IC2 and IC3 to go high (this can be verified with the help of truth table).
Now when you press the switch for tenth time pin 11 of IC1 goes high and this will make all input (9, 10, 11 & 12) of IC2 low because of that Green LED 6 stop glowing. And Yellow LED2 connected to Diode D2 start glowing. And pin 6 of IC3 is high and Red LED4 continuous to glow. This shows that that now another way is going to open. Therefore you can now see that at a time only one way is open and another have to wait for light to turn Green.
Circuit Diagrams
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.