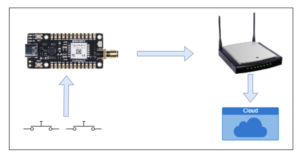
LoRa (long-range) technology ensures reliable long-range communication between a node and gateway, providing long-term, low-power use for devices This article provides an explanation of LoRa node-to-gateway communication while introducing a node equipped with two buttons to control the flags. These buttons enable users to turn on or off specific actions associated with each button and update the status on the gateway.
From home automation to industrial monitoring, this enhanced LoRa communication setup presents several possibilities for Internet-of-things (IoT) deployments.
This tutorial will cover the hardware setup, protocol selection, and gateway configuration, facilitating real-time data transmission and visualization.
Abstract
Here’s what we’ll cover…
1. How to upload LoRa code for the LoRa E5 Mini-Board
2. Circuit diagram to connect a ST-Link and the buttons to the LoRa E5 Mini-Board
3. How to set-up an end node in the gateway
4. The program flow or algorithm with an explanation
Requirements
1. Make sure the LoRa gateway is already installed as shown in this article
2. STM32Cube IDE must be installed on your PC
3. The LoRa E5 Mini-Board by Seed Studio
4. The original ST-Link V2 programmer
5. A tactile switch and some basic soldering knowledge
Compiling the code
1. Download the code and extract it
2. Open the folder and double-click on “.project”
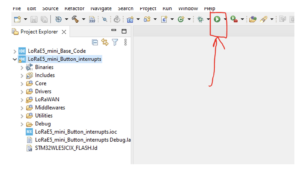
3. The project will be listed in the ‘Project Explorer’ tab on the left of the STM32CUBE IDE. Select the project and click on the hammer Icon on the top bar to compile the code.
4. After compiling the code, there should be zero errors as shown in image below. If there’s an error message, go through the steps again to ensure success.
Uploading the code
1. Locating a genuine ST-Link V2 is necessary for the proper flashing of the LoRa code, as clone ST-Link variants are often not compatible. This means it’s essential to recognize the original ST-Link. One reliable method for identification involves examining the hardware components.
Upon close analysis, a genuine ST-Link V2 has an STM chip, indicating authenticity. The clones are typically imported from China and look slightly different.
This project requires a smooth “flashing process,” which occurs reliably with a genuine ST-Link with the STM chip (see image below). Knowing the difference will ensure compatibility and proper programming.
2. Connect five wires to the LoRa E5 Mini Board as indicated in the below image, including 3V3, SWDIO, SWCLK, RST, and GND.
3. Go back to the STM32 Cube IDE and click on the ‘Play; button as shown below to upload the code.
4. You should receive the message, “Download verified successfully.”
Connecting the buttons
Connect the two tactile switches as shown in this circuit diagram:
Adding a device to the gateway
1. If there is no device profile, add one. If you already have one, this same profile can be used for multiple nodes.
2. To add a profile, open ChirpStack and go to the ‘Device profiles.’
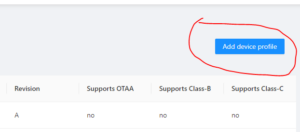
3. Click on ‘Add device profile.’
4. Fill out the general information, and click ‘Submit.’
5. Turn off the OTAA because the device will run in ABP mode. Fill out the RX3 data rate details and frequency.
6. Turn on the Class-C mode as shown below.
7. Add ‘Applications’ next, which contain all of the devices.
8. Click on ‘Add applications.’
9. Fill the details of Application as given below in image.
10. Click on the application that was just created and then click on the ‘Add device’ button. This process must be done anytime a new device is added.
11. Start to fill in the details as shown below. You’ll need to find the Device EUI, which is what we’ll cover in the next step.
Finding EUI and KEYs
1. To find the Device EUI and the Keys, connect the device to a PC via USB cable.
2. Open any Serial Terminal (we’re using Arduino), and select the device port. Open the Serial Terminal with a baud rate of 115200. Press the ‘Reset’ button to see the Keys.
3. Copy the Device EUI from the Serial Terminal and paste it in ChirpStack Add the device section as shown in the image below.
4. Go to the ‘Activation’ section and fill out device’s address, AppSkey, and Network S key, which you can get from the Serial Terminal.
Receiving data
1. To receive data, go to the event section where there is incoming data every 10 seconds.
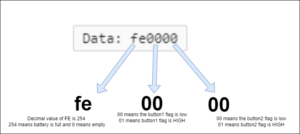
2. The data is in a hexadecimal format. It sends the battery level, as well as the Button1 and Button2 status, in hexadecimal.
3. When Button1 is pressed, the Button1 flag will be HIGH in the data that follows (just click it once with your mouse without holding it down).
4. When Button2 is pressed the Button2 flag will be HIGH in the data that follows.
5. When both buttons are pressed, the flag will be zero.
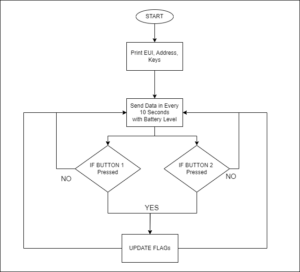
Code algorithm
Code explanation
1. The LoRa-based STM32 code is slightly different from typical codes. The main.c file starts the process to run lora_app.c as main file. So, open the lora_app.c that contains the code.
2. There is a lot happening in the code, but let’s review what’s relevant to this tutorial. The condition below begin a timer, which calls the OnTxTimerEvent function that sends data to the gateway. The default time is 10 seconds, which can be changed by initializing the TxPeriodicity in milliseconds. The below image removes the APP_TX_DUTYCYCLE and places the time delay required in milliseconds.
This function handles all of the interruption that occurs from the interrupt pins. There is a 100-millisecond delay for debouncing purposes.
Integrating smart meters
Smart meters with pulse sensors can be seamlessly integrated into the above code. The pulse sensors generate pulses whenever a meter reading increases, acting like the button interrupts in this tutorial. By configuring a microcontroller (MCU) to recognize these pulses as interrupts, a user can effectively track meter readings in real-time.
Whenever a pulse is received by the interrupt pin, the MCU will increment the meter reading and store it as a variable. The code can then be programmed to send these readings to the gateway at regular intervals, such as every 10 seconds. The transmission frequency can be adjusted to suit specific application requirements.
This integration enhances the functionality of smart meters, enabling accurate and automated tracking of energy consumption. With real-time readings, utilities can efficiently monitor usage, identify patterns, and optimize energy distribution. The versatile code can be adjusted for different pulse sensor setups, so it can work with many smart meter designs.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Tutorials




































Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.