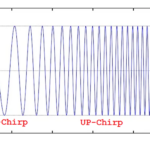
LoRa (Long Range) is a type of wireless communication technology designed to send information over long distances with low power consumption. It uses a special technique called chirp spread spectrum (CSS) modulation, which operates by continuously changing the frequency of a transmitted signal over time.
This varying frequency generates a waveform (resembling the sound of a bird chirping), allowing it to send signals over long distances without using a lot of power.
LoRa was first developed by the French company, Cycleo, and was later acquired by Semtech Corporation. LoRa operates in the license-free ISM (industrial, scientific, and medical) bands, which vary by region, such as
Europe: 868 MHz Band
• Includes European Union countries, such as Germany, France, Italy, Spain, the UK, etc.
North America: 915 MHz Band
• Includes the United States, Canada, and Mexico
South America: 915 MHz Band
• Includes Brazil, Chile, Colombia, and Peru
Asia-Pacific: 923 MHz Band
• Includes parts of Australia, as well as New Zealand, Singapore, Taiwan, Hong Kong, and Japan
Australia: 915 MHz Band
India: 865-867 MHz
LoRa technology provides a low data rate with a high tolerance to interference, making it suitable for low-bandwidth applications that require long-range communication with low power consumption. LoRa is commonly used in both the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) devices. It is flexible and can work in indoor and rural areas, making it ideal for “smart” applications, such as for smart homes and cities.
Common uses
LoRa is often used for IoT devices, which collect data and send it to another device or central computer. For example, a farmer might use IoT devices to monitor the moisture levels in the crop fields, which send that information back to a main computer.
LoRa’s advantage is that it uses low power and can send signals over long distances. It’s an ideal choice for devices in remote areas or hard-to-reach locations and for those that must conserve battery life.
Here are a few typical applications:
1. Smart agriculture: LoRa can remotely monitor crops, soil moisture, and other environmental parameters, helping farmers optimize their yields and reduce costs.
2. Industrial IoT: LoRa can monitor and control machines, equipment, and other assets in industrial settings, enabling more efficient operations and predictive maintenance.
3. Smart cities: LoRa is ideal for smart parking, street lighting, waste management, and other applications that help cities operate more efficiently and sustainably.
4. Asset tracking: LoRa can track the location and status of assets such as vehicles, containers, and equipment, enabling better logistics and supply chain management.
5. Environmental monitoring: LoRa can monitor air quality, water quality, and other environmental parameters, helping to protect public health and the environment.
6. Healthcare: LoRa is useful for remote patient monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to monitor patients’ health conditions and provide personalized care.
7. Home automation: LoRa can be used for home automation applications such as smart thermostats, door locks, and security systems, allowing homeowners to control their homes remotely and save energy.
What is LoRa modulation?
Modulation is the process of converting digital data into analog signals that are transmitted wirelessly. In LoRa modulation, CSS or chirp spread spectrum is used, where the frequency of the transmitted signal changes over time in a specific pattern called a chirp.
This chirping effect allows the signal to have a long duration, which helps overcome any potential interference or multi-path effects. In CSS modulation, data is encoded in the frequency modulation of the chirp signal.
LoRa’s CSS modulation uses a wide bandwidth and a slow chirp rate, resulting in long symbols and an increased resilience to interference. This modulation scheme enables LoRa devices to achieve a long communication range.
Power consumption
There are two main reasons behind LoRa’s ability for low power consumption.
1. Adaptive data rate: LoRa supports an adaptive data rate (ADR), meaning that devices can dynamically adjust their data transmission rate based on the quality of the communication link. This lets devices optimize power consumption by using higher data rates when closer to the gateway and lower data rates when located farther away.
2. Power management: LoRa devices often incorporate power management techniques to minimize energy consumption during idle or sleep periods. This can include sleep modes, duty cycling, and wake-on-radio features, where devices conserve power when not actively transmitting or receiving data.
It’s worth noting that power consumption can vary depending on several factors, including data transmission frequency, duty cycle, and the specific implementation of a LoRa device. It’s important to consider these factors when designing and deploying LoRa-based systems.
Range considerations
There are three reasons behind LoRa’s long-range capacity.
1. CSS. LoRa modulation uses the chirp spread spectrum (CSS), so the frequency of its transmitted signal changes over time in a chirp pattern. This gives the LoRa signal a much longer range than conventional wireless communication methods.
2. Spreading factor. LoRa also uses a spreading factor (SF), which spreads the signal across a wider frequency spectrum. This reduces the effects of noise and interference. By spreading the signal across a wider frequency spectrum, LoRa can maintain a good signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) even over long distances.
3. Frequency: LoRa uses lower frequencies than typical wireless communication methods, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. Lower frequencies can penetrate obstacles and travel further distances than higher frequencies, making them well-suited for long-range communication.
Additionally, the transmitted signal in conventional wireless communication is typically a continuous wave, often subject to interference, noise, and fading as it travels through the air. This can limit the range of the signal, particularly in environments with obstacles or interference.
Overall, the CSS modulation technique used in LoRa technology is the primary reason for its long-range capabilities.
Similar technology
Several other technologies are similar to LoRa in terms of their wireless communication capabilities. Here are a few examples:
1. Sigfox: a low-power, wide-area network (LPWAN) technology. It uses ultra-narrowband modulation to achieve long-range communication over an unlicensed spectrum.
2. NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT): a cellular network technology for low-power IoT devices. It uses narrowband modulation and operates over a licensed spectrum.
3. Weightless: an LPWAN technology that uses various modulation techniques, including CSS and Gaussian frequency-shift keying (GFSK). It operates over an unlicensed spectrum and is designed for IoT applications that require long-range communication.
4. LTE-M (Long-Term Evolution for Machines): a cellular network technology for IoT devices. It uses a licensed spectrum and supports voice and data communication.
CSS
You might wonder if RF could be long-range by using chirp spread modulation. The answer is: possibly.
Such techniques could make RF systems long-range, but they must be optimized for the specific system and its requirements. Additionally, the design of the antennas, transmitters, and receivers must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance.
Chirp modulation is just one technique used in LoRa to enable long-range communication. Adding CSS to a conventional RF system does not guarantee a long-range system.
The reason why LoRa achieves long-range communication is not only because of chirp modulation. It also uses various techniques, including the spreading factor, error-correcting codes, and lower frequency bands. So, it’s a combined effort.
You may also like:
Filed Under: IoT applications, Tutorials






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.