Ever imagined how quickly the horn of your vehicle responds? Not even a second or two, just push the button and there comes the sound. You put your hand off the button and it’s back to silent mode. An instant response of these horns is due to what we call “push -button switches”.
Push button switches are those which can be made to work with the force of a finger or two. Not only vehicles but camera, lifts and several other common and uncommon interactions with machines/gadgets involve push button switches applications. But what makes this switch so user friendly? What makes it respond only for the time it is pressed no longer or shorter? How the contacts inside this switch work?
Let us explore the internal architecture of the pushbutton and find out the answers to the questions through this insight.
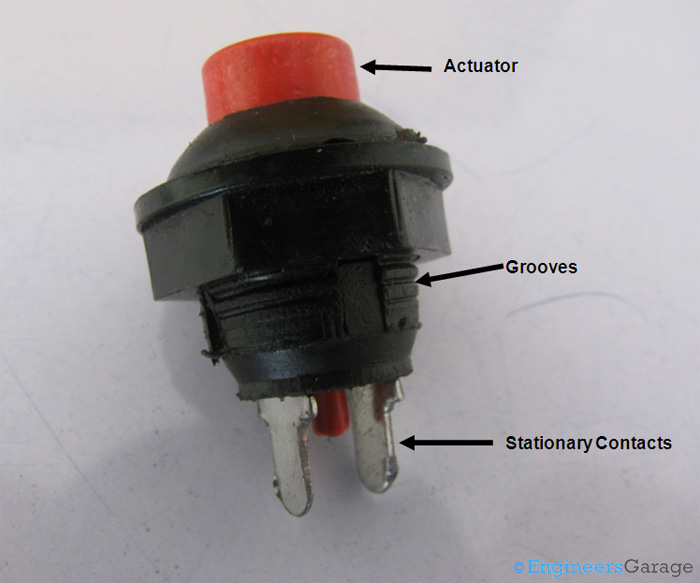
Fig. 1: Image of SPST Push Button Switch
The image above shows the external view of a conventional SPST push button switch. Almost all the parts of the switch can be figured out by observing its external structure. The red colored bulge is the actuator of the switch. The actuator extends towards the bottom of the switch and emerges out as a thin cylinder. Among other prominent extensions are the two stationary metal contacts legs at the bottom. A groovy pattern is also provided for the purpose of easy mounting.
Usually, external body of push button switches is made from polymer plastics and can have multiple shapes, sizes and output terminals depending upon its use.
Actuator & Lower Part
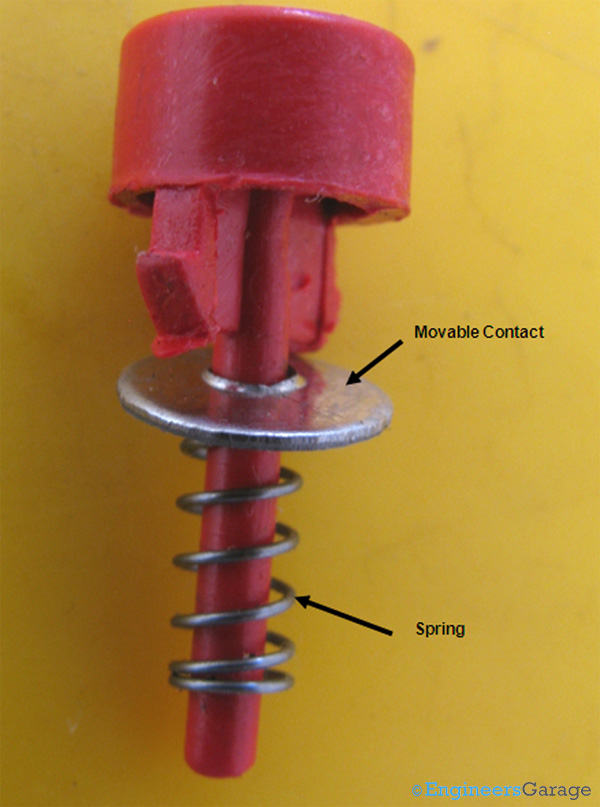
Fig. 2: Push Button—Movable Contact and Spring
The image above shows the movable contact and the spring which is the heart of the push mechanism.
Whenever the actuator is pressed down, the spring compresses; the movable contact connects with the stationary ones. Some switches can have a latch in the internal structure which locks the state when the switch is engaged. When pressed again, the switch gets disengaged and returns to its normal position. Such switches are called push to ON switch. In the switch taken in this article, there is no latch to hold down the switch, hence, as soon as the force is removed from the actuator, spring instantaneously gets decompressed and switch comes back to its rest stage.

Fig. 3: Lower Section of Switch Showing the Grooves
The lower section of the switch has grooves which ease out the process of mounting the switch over a surface.
Open & Close State
The open and closed contact states of a push button switch can be understood with the help of the image below:
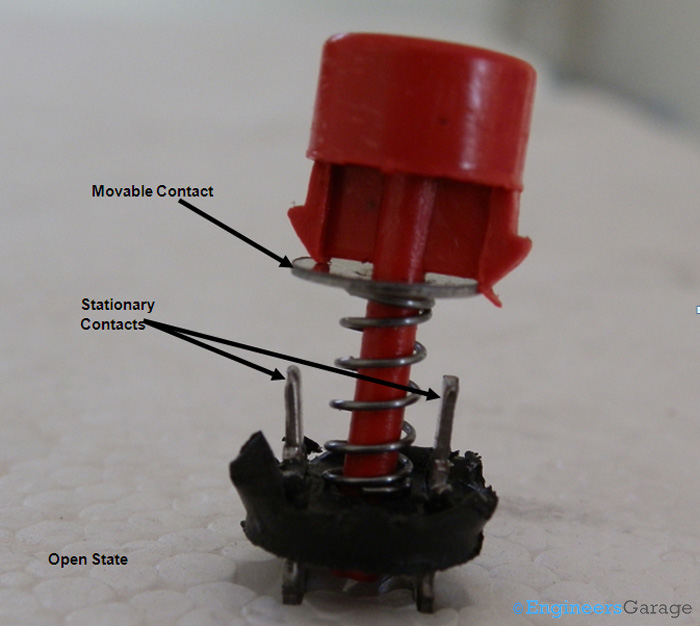
Fig. 4: Open State of Push Button Switch
The image above shows the open state of the push button switch where the spring is at its rest state and the movable contact is not bridging the gap between stationary contacts.

Fig. 5: Closed State of Switch
This is the closed state of the switch where the spring is compressed enough so that the movable contact can connect to the stationary contacts and push button switch starts to conduct.
Filed Under: Insight


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.