Cloud Computing

Figure1: Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is an internet-based computing that delivers services like servers, storage, networking, analytics, databases, and software. It offers shared computer processing resources and data to devices on demand. The cloud computing solutions enable individuals as well as business enterprises to store and process their data in third-party data centers instead of the involvement of local servers.
Almost all internet users avail cloud computing services and apparently, it’s counted among the emerging technology trends. Even though you may not realise it but even the usage of e-mails to store important information is an example of cloud storage. The first cloud computing services were introduced one and a half decade ago but now it has evidently become quite popular among all kinds of enterprises including startups, government organisations, NGOs, and MNCs. It is used for the following purposes-:
• Creating new apps
• Store, back up and recover data
• Web-hosting
• Delivering on-demand software
• Streaming audio and video
Service Models of Cloud Computing
As per the National Institute of Standards and Technology, there are three standard service models of cloud computing, namely- IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. These are also called cloud computing stack as they are built on top of one another. It’s important for the business enterprises to understand each of these models to so as to accomplish the business goals. Let’s take a quick look at these models.
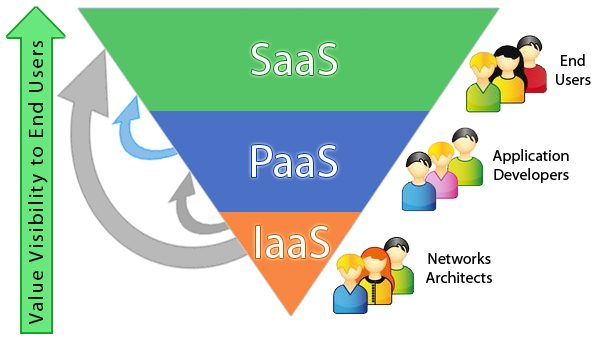
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
This is the most basic category where the users rent IT infrastructure services (servers, virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems) from a cloud provider and make the payment as per the usage. Here the consumer can control the operating system, storage, and deployed applications.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
It refers to the services supplying on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. It makes convenient for the developers to create web or mobile apps without having to manage the underlying infrastructure which is needed for the development.
SaaS (Software as a Service)
This model aims at providing software applications on demand over internet, usually on a subscription basis. With this service, the cloud providers manage software applications and take care of software upgrades as well as security patching. The users can connect to the application over a web browser through their devices like tablet, smartphone or PC.
Cloud Computing Trends to look forward to in 2017
In the last five years, there has been a remarkable surge in cloud adoption owing to a variety of benefits that this technology brings with itself. With the hike in the number of enterprises, there is an abundant amount of data that needs to be stored and the virtual world of storage in the form of clouds has become the ultimate destination for all such databases. It not only brings down the hardware cost but also allows the organisations to focus on the efficiency of their business as they don’t have to worry about managing loads of data through servers.
We are currently witnessing a phase where almost every entity and business unit is aware of the concept of cloud computing. It’s no more a concern whether one should make use of the cloud facility or not. Rather, it’s time to make decisions regarding the right time to adapt to the technology and choose the type of solution suiting the needs of one’s business.
As we have almost stepped into 2017, here are a few trends that are going to affect the usage of cloud computing in the years to come. Let’s have a quick glance at these cloud computing future trends.
Hybrid Cloud Approach
After experiencing the adoption of private and public clouds, a lot of enterprises are switching to hybrid clouds. This enables them to store sensitive data on private clouds while they can still run applications on public clouds relying on that database. Thus the organisations have the choice to avail the facilities on a public cloud and that too without offloading the entire data to a third-party.
Besides, the deployment of SaaS platform leads to data fragmentation which in turn affects the agility of operation. So instead of avoiding the adoption of SaaS, entities are embracing hybrid cloud approach so as to re-claim the single view of data assets.
IT Orientation and Training Programs
Owing to the intense competition in the market, employees need to be aware of all the emerging technology trends. As a result, cloud adoption has become an integral factor in determining the success of each and every organisation. Owing to the growing popularity of clouds, the IT department is required to focus on the cloud-based training and orientation programs regarding the hard skills as well as new workflows.
These programs are aimed at teaching cloud security, hosted databases, and infrastructure as a service. Moreover, the managers are required to search and recruit candidates who are experienced in DevOps practice and have already worked on cloud platforms such as Azure or AWS.
Shifting the load of Data Complexity
With the adoption of cloud computing, enterprises are able to shift the data complexity from the applications on to the platform, thereby significantly bringing down the lead-time for developers. Building strategies for the complexity management, leads to the creation of an environment that enhanced development and supports product innovation.
Besides, it creates time and gives rise to opportunities whereby the business concern can take on experiments, which otherwise is neglected. In the next few years, the focus is going to shift from developer’s productivity towards exploring their creativity.
Managing Multiple Cloud Vendors
Now is the trend where companies are seeking multiple cloud vendors instead of relying on just vendor as they all are configured differently and cater to different needs. This has led to the emergence of companies offering cloud management services i.e. cloud monitoring as a service (CMaaS) so that the users can manage their vendors simultaneously.
These services integrate, manage and monitor all the cloud facilities contracted by the organisations. Besides, they also provide facilities like incident and problem management, asset management of devices and infrastructure, along with the escalation to third parties, if needed.
Cloud Architecture

Figure3: Cloud Computing Architecture
Building the architecture of a cloud or devising and optimal method for migrating among the existing cloud services requires a completely different skill as compared to the core IT infrastructure design. Because of the presence of public cloud platforms, the companies are not free to configure each element in a unique way so as to suit their preference; rather they have to select the basic building blocks that can’t be changed. It’s expected that from now on the organisations are going to make efforts in developing such architecture skills so that they can easily migrate from one service to another.
Migration between Cloud Providers
As of now, not many organisations are shifting their workload among different providers but in the next few years, it’s going to be a common practice. This is because with each passing day, not only more and more enterprises are seeking cloud services but the numbers of cloud vendors are also increasing thereby giving the users a wide variety of options to choose from.
This would also lead to providers offering competitive prices. Owing to this situation, the organisation would be demanded to design more flexible cloud services which support different platforms in a faster manner and that too with minimum swapping risk.
You may read our Blog and Article section for more topics on electronics engineering, industry, and technology.
Filed Under: Tech Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.