Summary of LED constant current
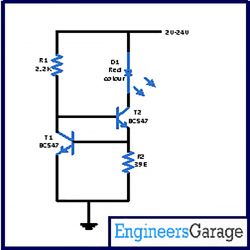
In the circuit when the voltage goes above 2V, large current passes through the collector of T2. Then the base current of transistor T1 goes up so that it can bring this transistor in the conduction stage. However at T1 transistor creates more and more negativity. Exactly same thing occurs with the base of T2. In turn T2 gradually closes and acts against the starting growth of current. That’s how a steady effect is achieved and we get a fixed value of current that will flow from LED.
The power dissipation of R is
P (W) = I2 (A) x R (Ω)
For instance- For a normal LED with 20 mA value of current, 39E of resistor can be used.
For a normal red colour LED value of current depends upon voltage-
5V … 15mA
9V … 18mA
12V … 20mA
18V … 24mA
24V … 27 mA
Note- For the standard LEDs with current rate of approximately 20mA transistor (T2), BC547 can be used. However for large power usage it is advisable to utilize BD135, BD137 or BD139.
Components used in the circuit-
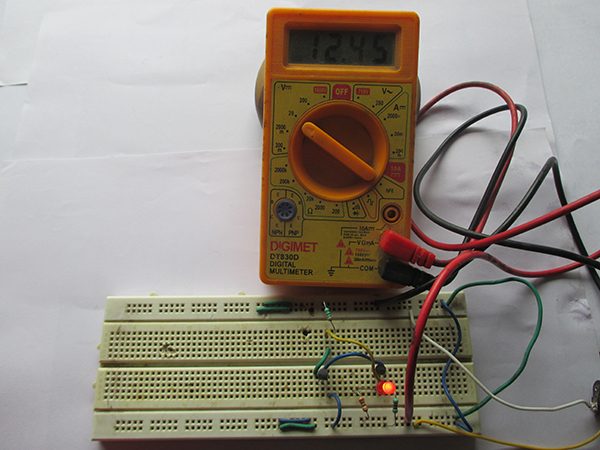

Fig. 1: Prototype of Constant Current Consumption LED Circuit designed on a breadboard
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Filed Under: Electronic Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.