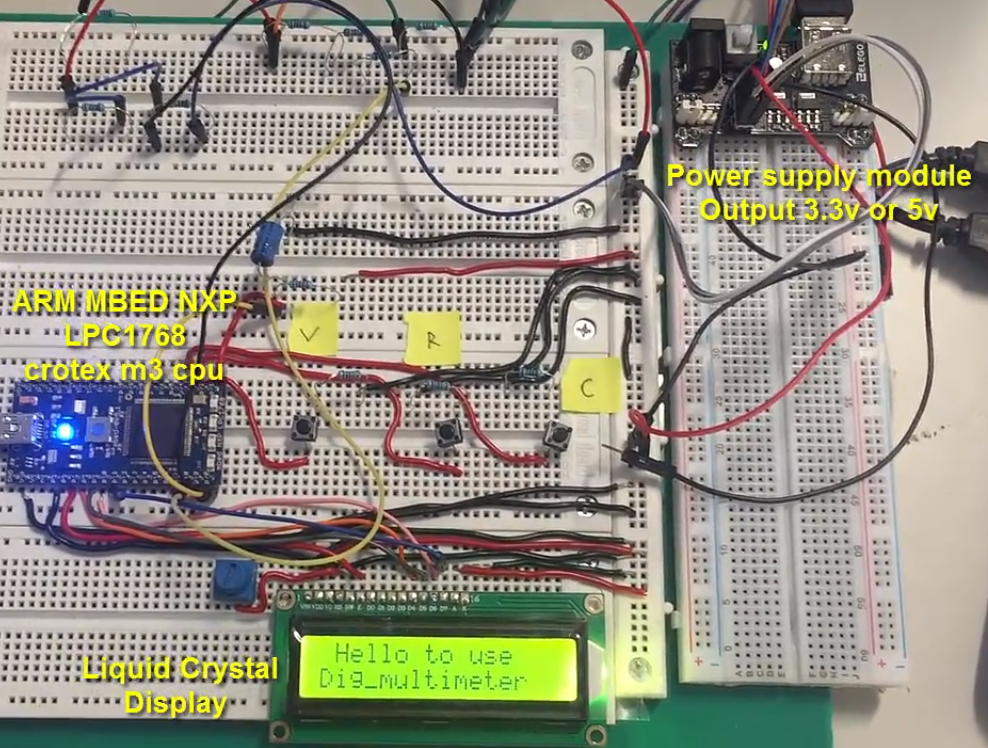
This project by a student of university of liverpool is about building a digital multimeter using mbed microcontroller. Multimeter can measure three parameters voltage, resistance and capacitance. Measured voltage, capacitance and resistance is displayed on a 16×2 lcd display. Its a small and cool diy electronics embedded system project.
How multimeter is made? Mbed microcontrollerMbed microcontrollers are low powered and high performance modules. They posses low latency and high through put. For this particular project their ARM Mbed NXP LPC1768 cortex-m3 variant is utilized. Clock frequency of this particular microcontroller/processor is 96MHz. High clock frequency and through put is what made this microcontroller perfect for digital multimeter application. The mbed microcontroller kit is operating on 3.3 volts.
|
How multimeter is measuring resistance, capacitance and voltage?
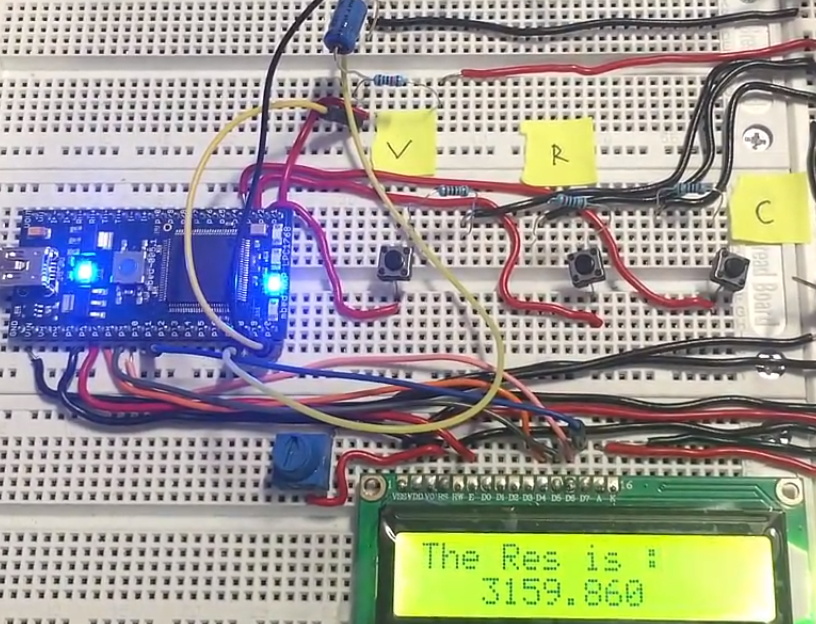
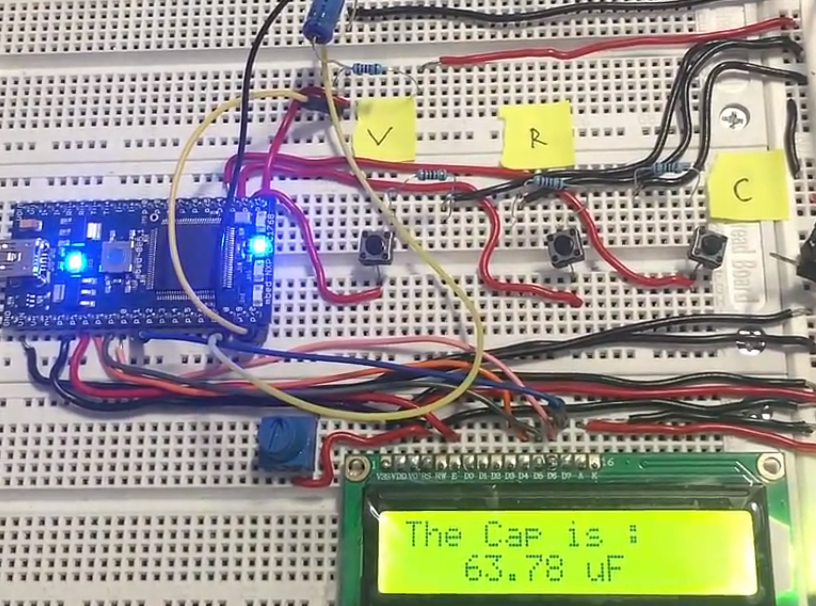
Circuit diagram of the project is given below. A snap shot of the end hardware design is shown in the picture below. A small power supply is mounted on a board and power is taken to other rails using jumper/connecting wires. Mbed microcontroller is housed on an another board along with 16×2 lcd display. To fade or control the brightness of lcd display a variable resistor is installed near the lcd display.
Three push buttons labeled V, R and C sticked with the board represents voltage, resistance and capacitance. Each push button calculates the parameter which is labeled on it.
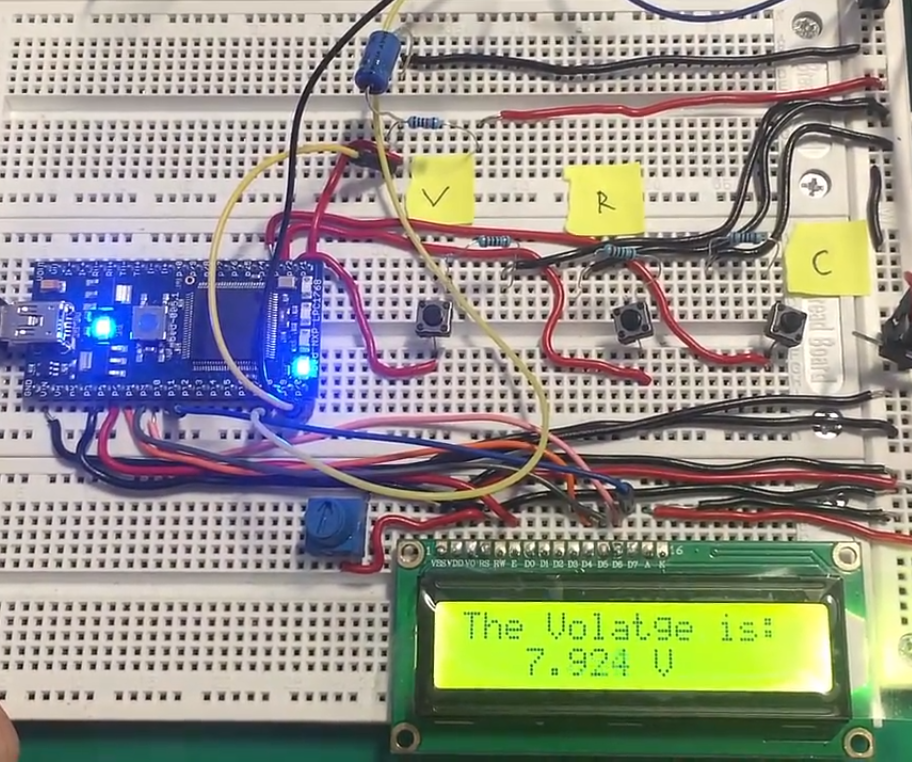
Digital multimeter measuring voltage
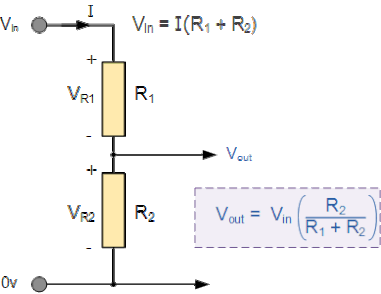
To measure voltage across a point voltage divider circuit is utilized. For example we want to measure a voltage across point and the max voltage which can arrive at that particular point is 12 volts.
|
Mbed microcontroller is operating on 3.3 volts. Its digital as well as analog pins can sink 3.3 volts. Any voltage greater than 3.3 can severely damage the micrococntroller pins. In this case we use a voltage divider circuit. Voltage is divided across two resistances. The voltage divider circuit is designed in such a way that the voltage across one of the resister never increases the 3.3 voltage range. One must pick the resistance according to it. Voltage divider circuit is given on the left hand side. If we take the picture under consideration according to the above scenario. Then at Vin we have 12 volts. At Vr1 8.7 volts must drop and Vr2 must not increase 3.3 volts in any case.
|
We want to measure voltage at point Vin. But since the voltage is higher at this point so in order to lower it we divided the voltage. Now how to accurately predict the voltage? A ratio must be calculated between the two resistances R1 and R2. This ratio multiplied with the calculate voltage across R2 or Vr2 yields the final voltage across Vin.
I made really a nice tutorial on it using arduino i suggest you to go with it for better understanding the method Arduino battery voltage monitor. The result of the voltage measuring is displayed on the 16×2 lcd shown in below picture.
Multimeter measuring resistance like OHM meter
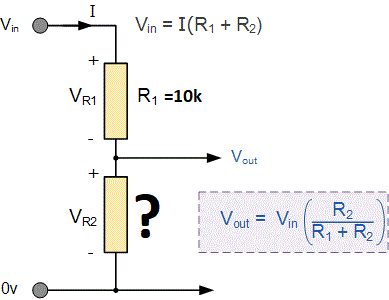
Measuring resistance is same like voltage measurement but this time instead of voltage we calculate the resistance after measuring the voltage drop across R2.
|
In this case Vin is fixed suppose 12 volts. We also know the R1 resistance. We measure the voltage across R2. Now we three parameters Vin, Vout and R1. Substituting these parameters in the formula given on the right hand yields the resistance of R2.
Note: Care must be taken in measuring the resistance. Vr2 must not increase the 3.3 volts limit. I would suggest you to calculate a range of resistance manually which can be measured relative to the R1. Resistance calculation and result is displayed on 16×2 lcd display. Result can be seen in the picture below. |
Multimeter capacitance measurement
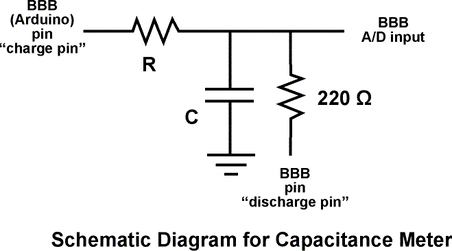
Capacitance is the ability of a discrete electronic component to store charge in it and release when instructed. Capacitors are widely used for this purpose. Capacitor takes time to charge it self. This charge time is proportional to load resistance and capacitor capacitance. Charge time equation is
TC=RC
Where Tc is charge time and RC is product of load resistance and capacitance. If we rearrange the formula and take C on the left hand side then TC/R yields the capacitance of the capacitor. The time constant of a capacitor is defined as the time it takes for the voltage across the capacitor to reach 63.2% of its voltage when fully charged.
Capacitance calculation steps
- Discharge the capacitor. Best method is to used an output digital pin which discharges the capacitor when capacitance is needed to be calculated. An led at the output is recommended for draining the capacitor.
- Charge the capacitor after draining it. At the instance you start charging note the starting time or start the counter in millis().
- When voltage reaches 63% of total voltage across capacitor stop the timer and note the time stamp. Now subtract the start time with stop time. The final value is TC. Dividing Tc with R finally gave us the capacitance value.
Filed Under: Arduino, Microcontroller Projects


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.