When a communication is to be established, that too wirelessly, with a remote device, we typically employ optical radiations or radio waves or sometimes, acoustic waves (for underwater applications). These three types of wireless communications basically differ in their frequencies. All frequencies starting from frequency bands like LF, HF, VHF, UHF and so on, extending up to microwaves and millimeter waves are referred to as radio waves. Acoustic waves use ultrasonic portion of frequency spectrum. Optical Radiations use visible and infrared portion of the spectrum.

Fig. 1: Image Showing Wavelength Range of Infra red Rays in UV Spectrum
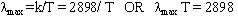
Fig. 2: Equation of Wein’s Displacement Law
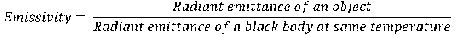
Fig. 3: Equation Defining Emissivity
What is PIR Sensor?

Fig. 4: Image Showing Working of Passive Infrared Sensors
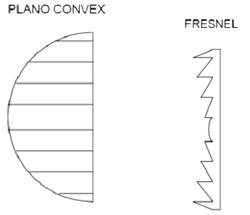
Fig. 5: Frensel Lens

Fig. 6: Image Showing Structure of A Typical PIR Sensor
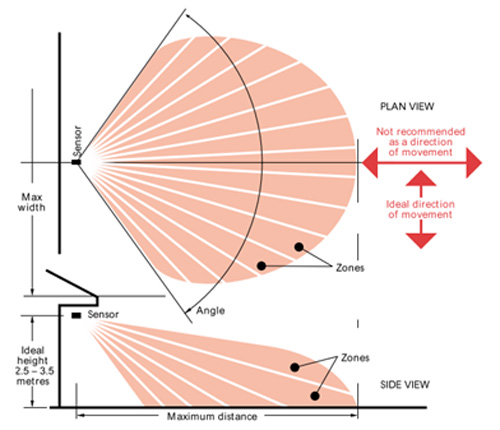
Fig. 7: Diagrammatic Presentation of How PIR Sensors Work
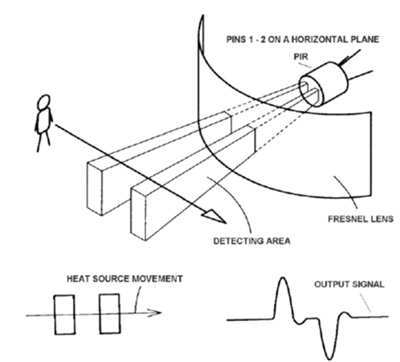
Fig. 8: Image Showing How Signal Is Produced In A PIR Sensor
Passive Infrared Detectors : Classification
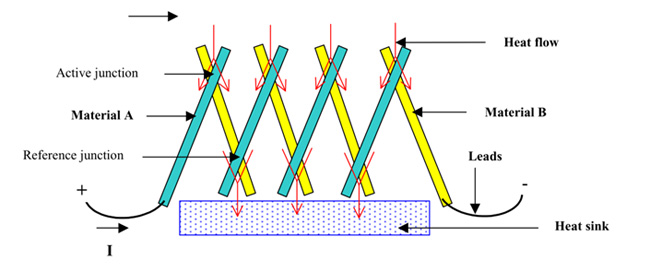

Fig. 10: A Typical Thermopile
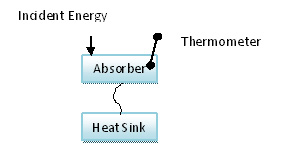
Fig. 11: Image Showing A Normal Bolometer

Fig. 12: A Pyroelectric Detector
Quantum type PIRs
Filed Under: Articles


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.