Varactor diode or varicap diode is a semiconductor diode that changes its junction capacitance significantly with respect to applied reverse bias voltage. Many semiconductor PN junction diodes are designed differently to exhibit specific electrical properties. One of such semiconductor diodes is a varactor diode or varicap diode. It is specifically designed to exhibit unique junction capacitance characteristics. These diodes are useful in RF circuits for tuning signals. That is why, a class of varactor diodes are also called Tuner diodes.
It should be noted that the desired operation of varactor diode is achieved only in reverse bias condition. Why? we will find out later in this article. In reverse bias condition, the internal capacitance of the diode changes significantly with respect to applied reverse voltage. That is why, not the voltage-current, voltage-capacitance is the important characteristic of a varactor diode.
What is a varactor diode or varicap diode?
Varactor diode is a semiconductor diode whose internal capacitance changes with respect applied reverse voltage. It is a voltage-controlled device that acts as a variable semiconductor capacitor. It is also called varicap diode, tuner diode, tuning diode, voltcap, or voltage variable capacitance.
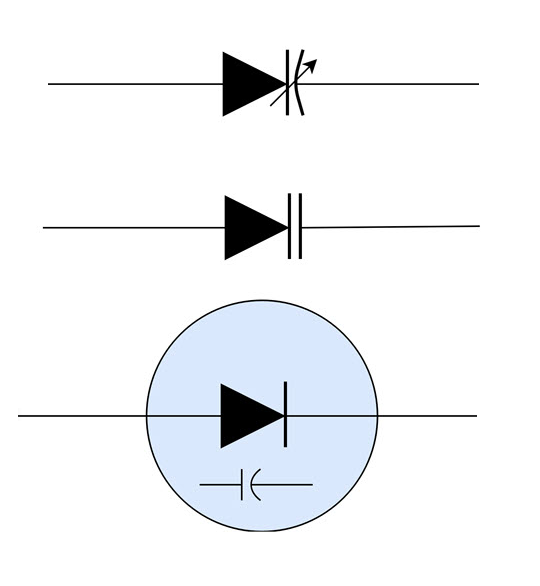
The varactor diodes are shown in electronic circuits by many symbols. The most popular symbols to indicate a varactor diode in a circuit are shown in the following.
Varactor diode construction
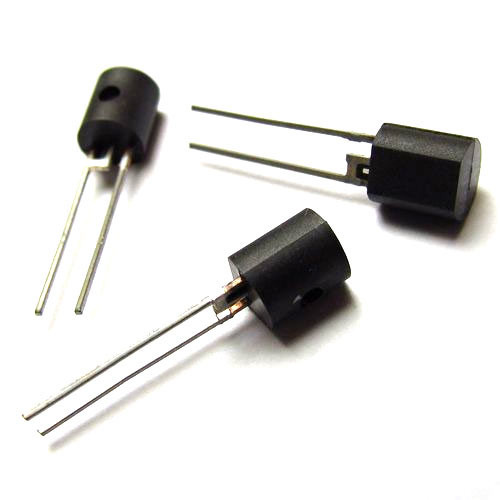
Varactor diodes are designed such that they have a very narrow depletion region. It is just a semiconductor diode with p-type and n-type layers. The n-type layer is connected to a gold plated molybdenum stud via a mesa structure. This work as cathode of the diode. The p-type layer is connected another gold plated molybdenum stud via a gold wire. This works as anode of the diode. Obviously, the polarity of a diode is really important, and that of a varactor diode is even more important as it has to be operated essentially only in reverse bias. The polarity is often indicated by distinguishing the cathode by a dot, or different lead structure or a band.
The varicap are available in both through-hole and SMD packages. The through-hole packages often have cathode indicated by a dot or a distinct lead structure. The SMD packages have cathode indicated by a dot or band at one end. Varactor diodes come in Transistor Outline (TO), Diode Outline (DO), Small Outline Diode (SOD) and Small Outline Transistor (SOT) packages. In some packages, there can be seen three terminals, of which only two need to be connected. Varactor diodes designed for low frequency operation are made of silicon and that designed for high frequency operation are made of gallium arsenide.
One of the unique thing about varactor diodes is their doping. Unlike conventional semiconductor diodes (signal and power diodes) which have uniform doping all across the p-type and n-type layer, in varactor diodes, the concentration of impurity atoms is less near the junction which gradually increases through the rest of the p-type and n-type layers. This type of doping is done to reduce the length of the depletion region.
How varicap diode works
A varactor diode is expected to work as a variable capacitor. A capacitor is an electrical device that stores charge when voltage is applied across it. As the voltage is reversed, the capacitor discharges the stored charge. When a capacitor is charging, current flows through it building a electrostatic field across it. When a capacitor discharges through a load or while negative cycle of an AC signal, it let the current flow through it in reverse direction until its plates are electrically neutralized. The capacitance of a capacitor is nothing but a measure of the charge it can store with respect to applied charging voltage. The capacitor is able to store charge because of the opposition to flow of current through it by its dielectric medium situated between two conducting surfaces.
A diode has transition and diffusion capacitance. The capacitance is shown by a diode because the depletion region is void of free charge carriers acting as a dielectric medium. The layer of negatively charged ions in p-type material and layer of positively charged ions in the n-type material act as conducting surfaces where the charge is stored when there is no bias or reverse bias voltage is applied.
A varactor diode is designed to have a narrow depletion region. Due to unique doping pattern and physical structure of the diode, the length of the depletion region changes drastically on application of reverse bias voltage. The capacitance or charge storage capacity of a capacitor device is inversely proportional to the distance between its conducting surfaces and directly proportional to the area of the conducting surfaces. A varactor diode is designed to have a large junction area and narrow depletion region. This is achieved by the mesa structure of the diode at the cathode end and the unique doping pattern. In unbiased condition, the diode has highest capacitance. In reverse bias condition, as the reverse bias voltage is increased, the length of the depletion region increases and the junction capacitance of the diode decreases. When forward biased, the depletion region is gradually vanished with the forward voltage and diode goes in conduction state. So, operate a varactor diode as a voltage-controlled variable capacitor, it has to be connected in reverse bias.
Varactor diode characteristics
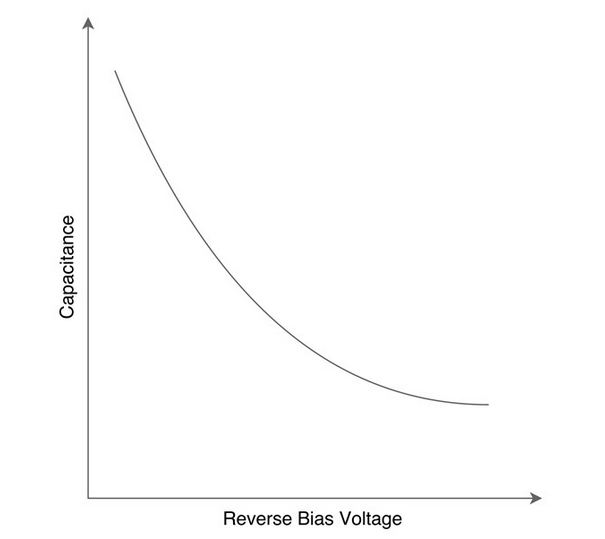
Unlike conventional diodes which have voltage-current as the most important characteristics, for varactor diodes voltage-capacitance is the most important electrical characteristics. The varicap are designed to have an high range variation of capacitance with respect to applied reverse voltage. The typical voltage-capacitance graph of a varactor diode is shown below.
Varactor diode types
Varactor diodes are classified as Abrupt Varactor Diodes and Hyper-Abrupt Varactor Diodes. In abrupt varactor diodes, the doping is linearly increased from the depletion region to diode terminals. As a result, the capacitance is almost linearly decreased with rise in reverse voltage. In hyper-abrupt varactor diodes, the doping is non-linearly increased from the depletion region to the diode terminals. As a result, the capacitance changes exponentially with respect to reverse voltage.
Varactor diode specifications
Some of the important electrical characteristics of a varactor diode are following.
- Reverse current: This is the reverse leakage current of the varicap through its junction for a specified reverse voltage.
- Capacitance ratio: This is the ratio of minimum capacitance to maximum capacitance of the varactor diode. A smaller value of this ratio shows large range of capacitance.
- Diode capacitance: This is the minimum capacitance for a specified reverse voltage and AC frequency.
- Junction operating temperature: This is the maximum junction temperature range that varactor can handle.
- Power dissipation: This is the maximum power dissipated by the diode in its conduction state for a specified ambient temperature. It is also an indication of maximum voltage and current, the varactor can tolerate.
Advantages of varactor diodes
Varactor diodes have several advantages. These are non-mechanical variable capacitors. These can be easily used within a semiconductor circuit. These are small and compact. These diodes produce less noise in comparison to other diode types.
Applications of varactor diodes
Varactor diodes are used in tuning circuits or for frequency modulation. Some of the notable applications of varicap are following.
- FR filters
- Automatic frequency controllers
- High frequency radios
- Band pass filters
- Voltage controlled oscillators
- Harmonic generators
- Frequency multipliers
Varactor diode reference
The following is a list of some popular varactor diodes with notable specifications.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Tutorials, What Is







Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.