A countdown timer is a down counter that counts from a specified time to 00:00. It is used in many devices such as washing machine, televisions, microwave ovens, etc. This countdown timer has three states: the running state where it counts down, the pause state where it displays the paused time and the reset state to set the countdown. The countdown is displayed on a set of four seven segment displays using the 8051 microcontroller (AT89C51). A buzzer sounds when the countdown gets over.
The countdown timer keeps the track of time the same way as a simple digital clock does. The control options are provided by means of tactile switches which are active low. This circuit uses five such switches for following operations:
Project Source Code
###
// Program to make a timer similar to the timer in microwave. This countdown timer counts backwards from a set value and raise an alarm when the counting is complete.It also has a feature of pause. #include<reg51.h> sbit dig_ctrl_4=P1^0; //Declare the control pins for the seven segment sbit dig_ctrl_3=P1^1; sbit dig_ctrl_2=P1^2; sbit dig_ctrl_1=P1^3; sbit reset=P1^7; //Reset pin to reset the timer. sbit start=P1^6; //Start pin to start the clock after the time is set. sbit incr=P1^5; //Increment pin to increase the digits for time setting. sbit set=P1^4; // Set pin to set the time. sbit pause=P3^3; // Pause pin to pause the operation sbit buzzer_pin=P3^7; int sel_seg_to_incr=0; int ret_seg_to_incre=0; int recent_incr_seg; int begin; unsigned char dig_disp=0; int min2=0; int min1=0; int sec2=0; int sec1=0; int p; int avi=0; char dig_val[10]={0x40,0xF9,0x24,0x30,0x19,0x12,0x02,0xF8,0x00,0x10};// Hex values corresponding to digits 0 to 9 void delay(int a) // Function to provide a time delay of approx. one second using Timer 1. { int i; for(i=0;i<a;i++) { TL1=0xFD; TH1=0x4B; TR1=1; while(TF1==0); TR1=0; TF1=0; } } int setfn() // Function to select minute and seconds digit to set value. { while(set==0) { switch(recent_incr_seg) { case 1: if(set==0)//select the min2 digit { dig_ctrl_4=1; dig_ctrl_3=0; dig_ctrl_2=0; dig_ctrl_1=0; recent_incr_seg=1; ret_seg_to_incre=1; P2=dig_val[min2]; delay(15); } case 2: if(set==0)//select the min1 digit { dig_ctrl_4=0; dig_ctrl_3=1; dig_ctrl_2=0; dig_ctrl_1=0; recent_incr_seg=2; ret_seg_to_incre=2; P2=dig_val[min1]; delay(15); } case 3: if(set==0)//select the sec 2 digit { dig_ctrl_4=0; dig_ctrl_3=0; dig_ctrl_2=1; dig_ctrl_1=0; recent_incr_seg=3; ret_seg_to_incre=3; P2=dig_val[sec2]; delay(15); } case 4: if(set==0)//select the sec1 digit { recent_incr_seg=1; dig_ctrl_4=0; dig_ctrl_3=0; dig_ctrl_2=0; dig_ctrl_1=1; ret_seg_to_incre=4; P2=dig_val[sec1]; delay(15); recent_incr_seg=1; } } } return(ret_seg_to_incre); } void increase(int a) //Function to set the minutes or seconds digit { while(incr==0) { switch(a) { case 1: // Set the min2 digit. P2=dig_val[min2]; delay(15); min2++; if(min2==6) min2=0; P2=dig_val[min2]; delay(5); break; case 2: //Set the min1 digit. P2=dig_val[min1]; delay(15); min1++; if(min1==10) min1=0; P2=dig_val[min1]; delay(5); break; case 3:// Set the sec2 digit. P2=dig_val[sec2]; delay(15); sec2++; if(sec2==6) sec2=0; P2=dig_val[sec2]; delay(5); break; case 4://Set the sec1 digit. P2=dig_val[sec1]; delay(15); sec1++; if(sec1==10) sec1=0; P2=dig_val[sec1]; delay(5); break; } } } void resetfn() // This function brings the clock to reset or set mode. { IE=0x84; // Disable Timer0 interrupt to stop the display of the clock sel_seg_to_incr=1; recent_incr_seg=1; if(begin==0) { dig_ctrl_4=1; //Enable the min2 digit and disable others dig_ctrl_3=0; dig_ctrl_2=0; dig_ctrl_1=0; } begin=0; P2=dig_val[min2]; delay(5); while(1) { if(start==0) //Check if start pin is pressed { TMOD=0x11; //Reset the Timer0 TL0=0xf6; TH0=0xFf; IE=0x86; TR0=1; break; } if(set==0) sel_seg_to_incr=setfn(); if(incr==0) increase(sel_seg_to_incr); } } void display() interrupt 1 // Function to display the digits on seven segment using multiplexing. { TL0=0x36;//Reload Timer0 TH0=0xf6; P2=0xFF; dig_ctrl_1 = dig_ctrl_3 = dig_ctrl_2 = dig_ctrl_4 = 0; dig_disp++; dig_disp=dig_disp%4; switch(dig_disp) { case 0: P2=dig_val[sec1]; dig_ctrl_1 = 1; break; case 1: P2= dig_val[sec2]; dig_ctrl_2 = 1; break; case 2: P2= dig_val[min1]; dig_ctrl_3 = 1; break; case 3: P2= dig_val[min2]; dig_ctrl_4 = 1; break; } } void pauselock() interrupt 2//Function for pause mode { avi=1; } void main() { pause=1; set=1; //Delaring set, reset, start and incr as input pins reset=1; start=1; incr=1; recent_incr_seg=1; begin=1; TMOD=0x11; //Intialize Timer0 TL0=0x36; TH0=0xF6; IE=0x86; TR0=1; //Trigger Timer0 while(1) // Back counting. { while(min2>=0) { while(min1>=0) { while(sec2>=0) { while(sec1>=0) { p=1; while(min2==0&&min1==0&&sec2==0&&sec1==0&&reset!=0&&begin==0) { if(p==1) { buzzer_pin=0; delay(50); buzzer_pin=1; p++; } } if(reset==0 || begin==1) { dig_ctrl_4=1;//Enable all segments dig_ctrl_3=1; dig_ctrl_2=1; dig_ctrl_1=1; resetfn(); } while(avi==1&&start==1); avi=0; delay(20); sec1--; } sec1=9; sec2--; } sec1=9; sec2=5; min1--; } sec1=9; sec2=5; min1=9; min2--; } min2=5; } }###
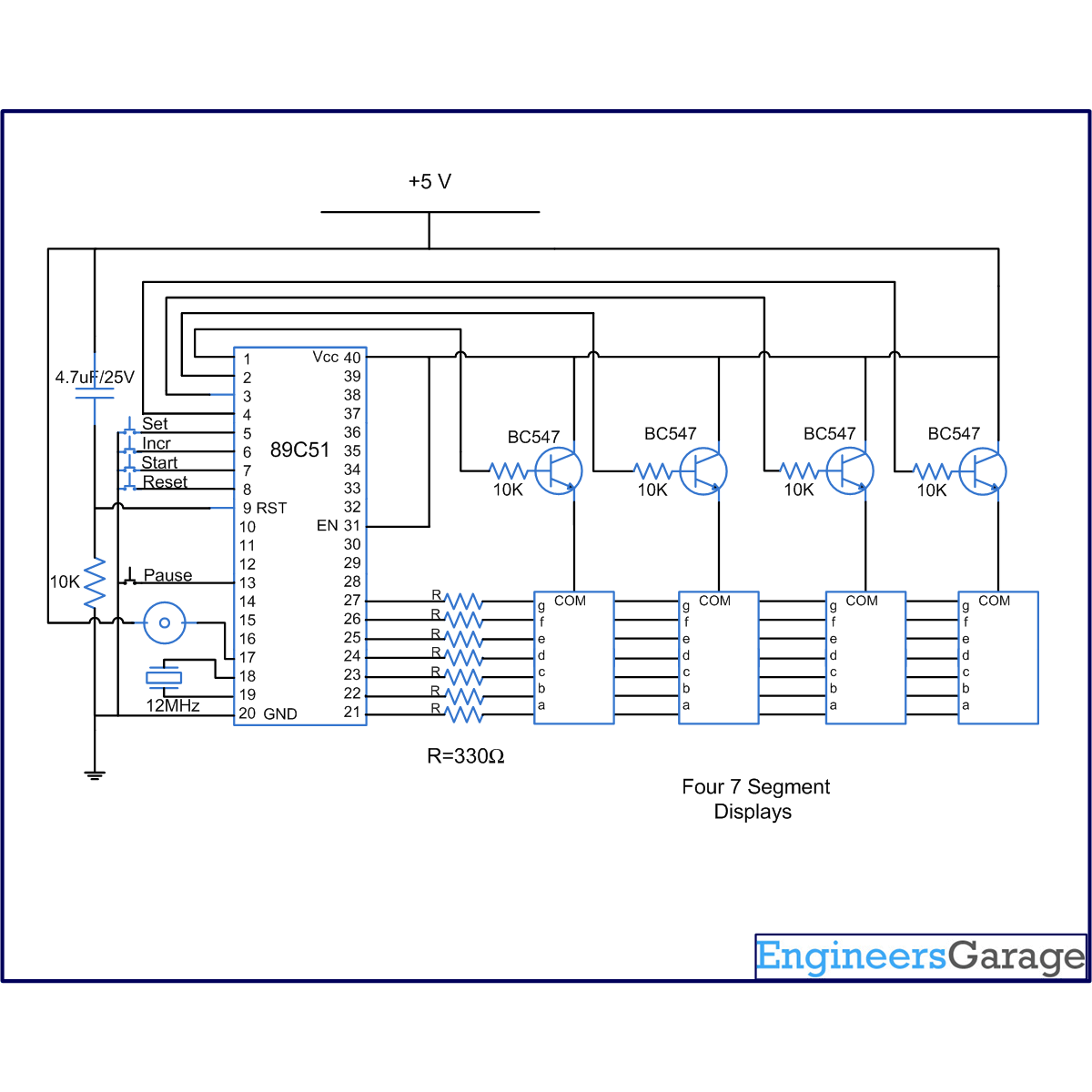
Circuit Diagrams
Project Components
Project Video
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.
Filed Under: 8051 Microcontroller.


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.