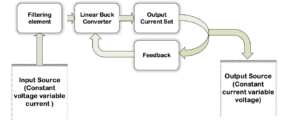
Voltage and current sources are two fundamental types of electrical sources used in electronic circuits. A voltage source, such as a battery, is commonly used in many devices. It’s a two-terminal device that maintains a constant voltage across its terminals, regardless of the current flowing through the source.
A current source is typically less discussed and more difficult and costly to design. It’s also a two-terminal device, but it maintains a constant current through its terminals, regardless of the voltage across the source. This means it’s used to ensure a steady current even if the load fluctuates.
In this experiment, we’ll design a constant current source application using a linear buck regulator.
Specifications
- The LM338 linear buck regulator
- Input voltage range – 1.2 to 32V
- Maximum output current – 5A
Block diagram
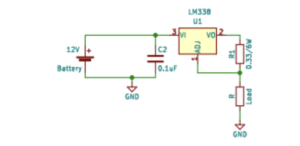
Circuit diagram
Principle
When using any linear regulator as a current source, the circuit works on the principle of a feedback loop.
The regulator consists of a feedback pin (the adjust pin) that feeds the output back to the regulator and maintains a fixed voltage at the feedback network. This network is a resistor, which determines the output current at the output.
Circuit design
Here are the steps for the circuit design.
1. Input source – 24V DC
2. Linear buck converter – LM338 IC
Features of the LM338
- Overload protection – in case of overloading, the device will reduce its output current until the overload is removed
- Thermal regulation
- Output short-circuit protection
3. Output current set – the output current is based on the feedback network, which is the resistor
The equation for calculating the feedback resistor…
By applying famous Ohm’s law, we get: . Vref = voltage reference of the regulator
. Vref = voltage reference of the regulator
LM338 regulator, Vref =1.25V
Desired constant output current, Iout = 4A
Feedback resistor, Rfb = Vref / Iout
Rfb = 1.25/5
Rfb = 0.33E
4. Feedback resistor power rating
The equation for calculating power rating of the resistor…
PR = I2*Rfb
PR = (4*4)*0.33
PR = 5.28W (minimum)
5. Filtering – the capacitor, which is at the input, grounds all of the ripples and spikes from the source. To reduce the total ESR, we can connect a ceramic capacitor along with an electrolyte.
6. Cooling system – the heat sink must be mounted with the regulator because we’re drawing a large amount of current. This will produce a lot of heat at the IC surface and can ignite it. So, it’s important to use a cooling fan or a heat sink to reduce its temperature.
How the circuit works
In our constant current source, the feedback loop maintains a fixed output voltage across the feedback resistor. As per Ohm’s law, with a fixed value of voltage and a resistor, a constant amount of current will flow.
This will generate a constant current at the output, irrespective of the load.
Output current regulation
All current sources provide a regulated current but only for a specific load range.
It’s possible to calculate the load limit for the linear regulator by using the following equation…
Vout = 12 – 3
Vout = 9V…………………………Eq.2
VR = 5*4.7
VR = 23.5V
The regulator is unable to provide 23.5V at the output. So, we must first calculate the output load limit using the equation below…
The maximum value of resistive load, RL = 2.25E
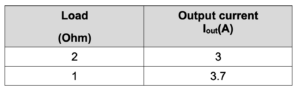
Testing results
Initially, we designed the current source for 5A since the IC is rated for 5A output current. However, the IC could not maintain a constant 5A output current and began dropping its value even with a heat sink and cooling fan.
This might be because of the IC’s internal thermal regulation, which tries to maintain its temperature and drops the current if in a high-power dissipation state.
So, instead, we tried the circuit using a 3.7A current, and it worked perfectly with the heat sink.
Observation
The output current begins stabilizing at a load of 1 Ohm. The difference in the output current is due to the resistor’s tolerance values.
Circuit limitations
- Input source – A high-voltage input source is needed to increase the maximum load limit
- Cost – A high power rating feedback resistor increases the cost
- Efficiency – There’s less efficiency because of high-power dissipation across the feedback resistor
Thermal management
For extra heat dissipation, heat is connected to the IC. It’s also possible to use a fan to disperse the hot air.
Applications
- Battery charging
- In transistor biasing
- Lighting systems
- Regulated supply
Precautions
- Ensure the feedback resistor’s power rating is per the product requirements.
- Always put a load under the limits of the current source.
- A capacitor should be connected between the input pin and ground to regulate the DC input voltage.
- The circuit’s capacitor must have a higher voltage rating than the input supply voltage. Otherwise, the capacitor will leak current due to the excess voltage at its plates and burst.
- Ensure all the capacitors are discharged before working on a DC power supply.
- Do not give a higher voltage at input than its operating input voltage range.
- Always connect a heat sink or a cooling fan for heat dissipation around the IC.
Video
You may also like:
Filed Under: Tutorials











Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.