What is a GSM Modem?
GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications.It is a standard set developed by the EuropeanTelecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to describe protocols for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobilephones.
A Modem is a device which modulates and demodulates signals as required to meet the communication requirements.It modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information.
A GSM Modem is a device that modulates and demodulates the GSM signals and in this particular case 2G signals. The modem we are using is SIMCOM SIM300. It is a Tri-band GSM/GPRS Modem as it can detect and operate at three frequencies (EGSM 900 MHz, DCS 1800 MHz and PCS1900 Mhz). Default operating frequencies are EGSM 900MHz and DCS 1800MHz.
Sim300 is a widely used in many projects and hence many variants of development boards for this have been developed. These development boards are equipped with various features to make it easy to communicate with the SIM300 module. Some boards provide only TTL interface while some boards include an RS232 interface and some others include an USB interface. If your PC has a serial port(DB9) you can buy a GSM Modem that has both TTL and RS232 interfacings in economy.
Sim300 GSM module used here, consists of a TTL interface and an RS232 interface. The TTL interface allows us to directly interface with a microcontroller while the RS232 interface includes a MAX232 IC to enable communication with the PC. It also consists of a buzzer, antenna and SIM slot. Sim300 in this application is used as a DCE (Data Circuit-terminating Equipment) and PC as a DTE (Data Terminal Equipment).
Why use a GSM Modem
GSM Technology has grown so much, that literally there isn’t a place on earth where there is no GSM signal. In such a scenario GSM provides us a wide scope in controlling things remotely from any place just with our finger tips. GSM also provides ease to easily communicate in a more robust way.
Some AT Commands
Sim300 GSM Module can be used to send and receive SMS connecting it to a PC when a SIM is inserted. The GSM Modem can be sent commands to send or receive SMS from the PC through a com port (serial port or an usb). These commands are called as AT commands. Through AT commands we can perform several actions like sending and receiving SMS, MMS, etc. Sim300 has an RS232 interface and this can be used to communicate with the PC. Sim300 usually operates at a baudrate of 9600, with 1 stopbits, No parity, No Hardware control and 8 databits. We shall see at some of the AT Commands necessary for sending and receiving SMS.
|
Command |
Description |
|
AT |
It is the Prefix of every command sent to the modem. It is also used to test the condition of the modem. The GSM Modem responds with an rnOKrn or an rnERRORrn in case of error. where r is the carriage return character and n is a new line feed character).
|
|
AT+CSMINS? |
Command to check if the Modem has a sim inserted in it. It checks if the sim Is inserted. |
|
AT+CREG? |
Command to check if the sim is registered with the network. It checks if the sim is registered and returns the status.
|
|
ATE1 |
Command to turn on the ECHO. The GSM Modem continnously echo’s back the every byte of data sent to modem until a carriage return charater is sensed. It processes the command after a carriage return character is detected. It is usually better to turn off echo to reduce traffic. In this case ECHO is turned on to see how commands are sent and how they are processed.
|
|
AT+CMGF=1 |
Command to set the communication to TextMode. By default the communication is in the PDU mode.
|
|
AT+CMGR=1 |
Command to read an SMS at the index one.Generally the index depends upon the how many number of SMS that a sim can store. SIM Memory is the only memory available when GSM Modem is used and hence the number of SMS’s stored depends on the SIM. It is usually 20. Any message received is arranged in the order of arrival at specific indices. |
|
AT+CMGD=1 |
Command to delete the SMS at the index 1.
|
|
AT+CMGS |
Command to send SMS from the GSM Modem.
|
Some other commands may be device specific and may or might not operate on all the modems. It is better
to use the AT Commands specified for the Modem used.
Using the GSM Modem
We shall first try to communicate with the Modem using PC(Hyperterminal).
1.Setting up a new connection in Hyperterminal

Fig. 1: Screenshot of creating new connection in Hyperterminal
2.Port selection:

Fig. 2: Screenshot of Port Selection on Hyperterminal
Select the COMPORT to which your modem is connected. If you are using a DB9 connector it is COM1 and if you are using a usb connector then it will be shown up in the dropdown menu.
Using UART of ATMega 32
3.COM Properties
Set the com properties as shown in the figure and press OK button.

Fig. 3: Screenshot of COM Properties on Hyperterminal
4.Sending commands to the modem

Fig. 4: Screenshot of AT commands for GSM Modem on Hyperterminal
Now Power on the GSM Modem and wait for Call Ready to appear on the terminal.Type AT and then press Enter button.You’ll see OK on the Hyperterminal. Similarly try out the other commands.

Fig. 5: Screenshot of AT commands for GSM Modem on Hyperterminal
Using the UART of Atmega32 Microcontroller to communicate with the Modem
Atmega32 has three types of serial communication peripherals and they are
1. USART (Universal Synchronous/Asynchronous Rececive and Transmit)
2. TWI (Two-Wire serial Interface) and
3. SPI (Serial Perpheral Interface)
Atmega32 has an USART(Universal Synchronous and Asynchronous Receive and Transmit) peripheral which enables us to perform serial communication either synchronously or asynchronously. Here asynchronous mode is preferred at a normal speed. The Pins Rx and Tx of the GSM Modem are connected to the Tx and Rx pins of Microcontroller. USART of the Microcontroller is configured to work at the baudrate of 9600, with 8 Databits, 1 stopbit and Parity None.

Fig. 6: Circuit Diagram of AVR ATMega32 and GSM Modem Interfacing
Atmega32 serial communication is very much like that of serial communciation in an Atmega16 except a few changes. The interrupt vector table for the Atmega16 and Atmega32 are different, any how since no interrupt is used in the serial communcation the same code is applicable even in here.
Using Watchdog Timer to prevent infinite loops
A watchdogtimer is used to prevent the microcontroller from falling in to infinite loops. A watchdogtimer when set, counts down the specified and when the timer expires it resets the microcontroller. In Atmega32A a watchdog timer with a maximum time of 2 seconds is available.
While reading the data from GSM Modem via UART some times it is possible that we may not receive the expected bytes from the Modem. In such a case the the microcontroller keeps waiting for those expected bytes and keeps on waiting thus falling in to an infinite loop. To prevent such a condition a watchdogtimer is set with a time of 2 seconds(approximately). If expected bytes are received from the GSM Modem then immediately the timer is reset and the watchdogtimer is disabled. if the expected bytes are not received from the Modem then the timer expires and a reset occurs.
Algorithm
The GSM Modem is constantly checked for any new messages to respond and hence it follows the following algorithm.
Initialising the GSM Modem
1. Send AT command and wait for the response.if the response is correct then goto step 2,else the watchdogtimer causes a reset.
2. Send command to check if the sim is inserted in to the modem.if the response is correct then goto step 3,else the watchdog timer expires and causes a reset.
3. Send command to check if the sim is registered to the network.if the response is correct then goto next step,else the watchdog timer expires and causes a reset.
4. Send command to turnon the echo and wait for the response.
5. Send command to communicate in the textmode and wait for the response.
6. Now start reading the messages.
Reading the SMS
i) Send command to read the SMS at index 1.
ii) Read the response
(a) If the response is OK then go to step 3
(b) Else if the response is “+CMGR” then start reading the number and the message.
1. If number is the registered number then process the message.
2. Else discard the message.
3. Delete the message at index 1.
iii) Wait for about 1000ms for the modem to rest
Overall Process
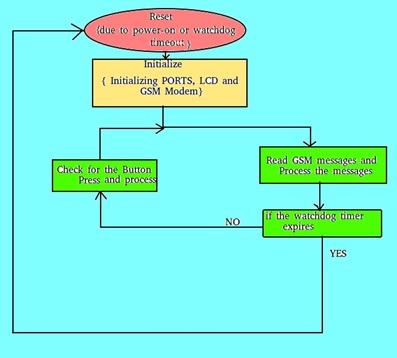
Fig. 7: Flowchart of AVR Code for sending and receiving SMS from GSM GPRS Modem
Hardware used
1. Atmega32
2. LCD and
3. SIM300 GSM Modem
Softwares Used
1. Win AVR : Program compiler for AVR series of microcontrollers.
2. PonyProg : Lanconelli designed third-party programmer software for programming the microcontrollers.
3. HyperTerminal : Windows-Based port based communication software.
Circuit Diagrams
Project Video
Filed Under: Electronic Projects
Filed Under: Electronic Projects



Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.