Bus States
The Bus state refers to the signal voltage level on the USB bus or the conditions that these voltages signify -:
Single Ended Zero: This state is also known as SE0. It occurs when both D+ and D- are logic low. The SE0 state is used by bus when entering the Disconnect, Reset and EOP (End of Packet) states.
Single Ended One: Also known as SE1. It occurs when both D+ and D- are logic high. This state can be taken as a compliment of the SE0 state. SE1 should never occur as it is an invalid bus State.
Idle: This state occurs when bus remains idle or there is no exchange of packet. For a full speed device, the voltage at D+ will be more positive than D- while for a low-speed device, the voltage at D- will be more positive than D+
Data J and Data K: Data J and K states are used to define the Data States like the Differential 0 and 1 that refers to the bus states. They are defined by Differential 0 or 1 state and the speed of the bus.
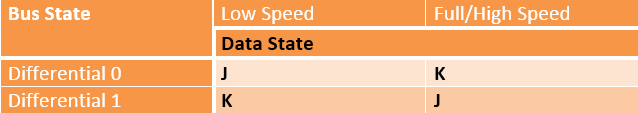
Fig. 1: Table listing Flip-Flop Status for Differential 0 and Differential 1 Bus States
The data states are used to describe an event even when the voltages at data lines are differential. For example, a Start of Packet state exists when the bus changes from Idle to the K state.
Start of Packet: Also known as SOP. This state occurs when there is a change from Idle to K state. Every transmission of the packet begins with SOP.
End of Packet: Also known as EOP. This state occurs when SEO state occurs for two-bit times, followed by a J state for 1-bit time.
Disconnect: A downstream port at which the device is connected enters disconnect state when an SE0 state has lasted for at least 2.5 uS.
Connect: A downstream port enters connect state when there is an Idle state for a minimum 2.5 uS and not more than 2 mS
Some Other States and Signals
Keep Alive Signal: This signal is represented by a low-speed EOP. The main motive of this signal is to keep the device in an idle state. This signal is sent at least once every millisecond, to keep the device from entering suspend state.
Suspend State: The device enters Suspend state when there is no exchange of packet or the bus remains idle for 3 mS. This state has been incorporated in USB for power conservation. In Suspended state, the device must not draw more than 500 uA of current. A suspended device must recognize the reset and resume signal.
Resume: Resume signal is used to wake the device from Suspend state. The Host wakes the device from suspend state by keeping the bus in K state for at least 20 ms followed by a low-speed EOP.
Reset State: A device enters Reset state if SE0 is applied for more than 2.5 uS. The reset sets the device to its default unconfigured state.
Detached State: This state occurs when the USB device is detached from the Host. In this state, the Host sees both data lines low.
Attached State: This state occurs when the USB device is attached to the Host. The host recognizes this state if it sees either D+ or D- high.

Fig. 2: Table listing conditions for USB Bus States

Fig. 3: Signal Diagram for different USB Bus States
Speed Identification
In USB System, the operating speed of the device is detected by checking which data line is pulled up. The data line is pulled up to 3.3V derived from voltage line. Normally, 1.5-kilo ohm resistor is used for a pull-up.
For Low speed, D- data line is pulled up. While for full speed, D+ data line is pulled up. High-speed devices are initially detected as full speed devices.
Encoding Scheme
The USB employs NRZI (Non Return to Zero Inversion) encoding mechanism to encode the data on the bus. In NRZI encoding, a ‘1’ is represented by no change in level while a ‘0’ is represented by change in level. Together with NRZI encoding, bit stiffing and SYNC field is used for synchronization between host and device.
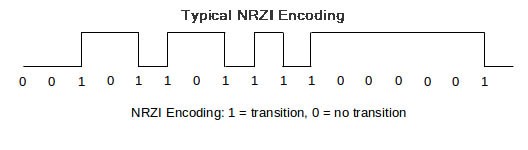
Fig. 4: Signal Diagram illustrating Non Return to Zero Inversion (NRZI) Encoding Scheme
Bit stiffing
When long series of zeros are transmitted using NRZI, it causes a transition in the levels. But when long series of one’s is transmitted, no transition takes place as per NRZI encoding scheme. No transition in levels for a long time can confuse the receiver and makes it desynchronized.
Bit stiffing is a process in which a zero is inserted in raw data after every six consecutive ones. The inserting of zero causes transition in level. The receiver must recognize the stuffed bits and discard them after decoding the NRZI data.
In case if no transition takes place in NRZI signal after six consecutive one’s, then the receiver decides that bit stiffing has not been done and discards the data received.
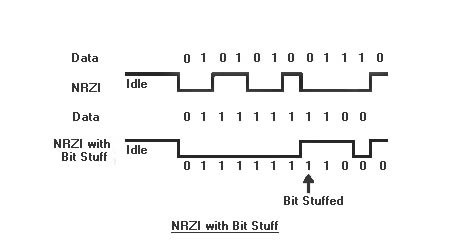
Fig. 5: Signal Diagram showing Bit Shifting in Non Return to Zero Inversion (NRZI) Encoding Scheme
SYNC field
The bit stiffing alone is not enough to take care of the synchronization between transmitter and receiver. To keep transmitter and receiver synchronized, SYNC field is used. In this mechanism, each packet begins with a SYNC field which enables the receiver to synchronize the clock
For low/full speed, SYNC field is of 8 bits: KJKJKJKK. The first k serves as Start of Packet. For high speed, SYNC field is of 32 bits: fifteen KJ repetitions, followed by KK. The alternate Ks and Js provide transitions for synchronizing and the final two KKs mark the end of SYNC field.
End of Packet
The End of Packet that is SE0 for 2-bit times followed by J state for 1-bit time marks the end of packet.
This is all needed to know about the signal and encoding schemes implemented in the USB system. In the final part of the series, selection of a controller chip for developing USB enabled custom devices is discussed.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Featured Contributions, Tutorials, USB






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.