What is a Resistor?
An electric resistor is a two-terminal passive component specifically used to oppose and limit current. A resistor works on the principle of Ohm’s Law which states that voltage across the terminals of a resistor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.
Types of Resistors:

Fig. 1: Image of Carbon Composition Resistors

Fig. 2: Image of Carbon Film Resistors
Metal Film & Wire Wound Resistors


Thin film & Thick film Resistors

Fig. 5: Image of Thin Film and Thck Film Resistors
Surface mount & Network Resistors

Fig. 6: Image of Surface Mount Resistors

Fig. 7: Symbols of Network Resistors

Fig. 8: Circuit Diagram of Network Resistors
Variable Resistors
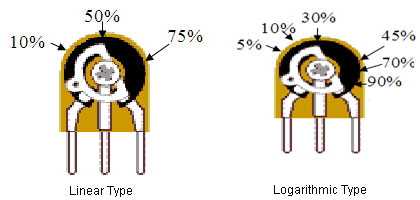
Fig. 9: Diagram of Variable Resistors
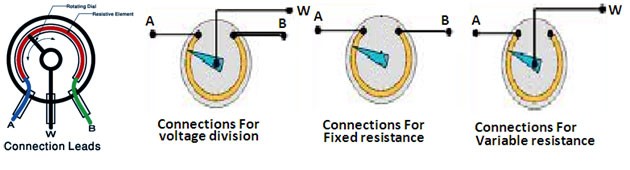
Fig. 10: Image showing applications of variable resistor
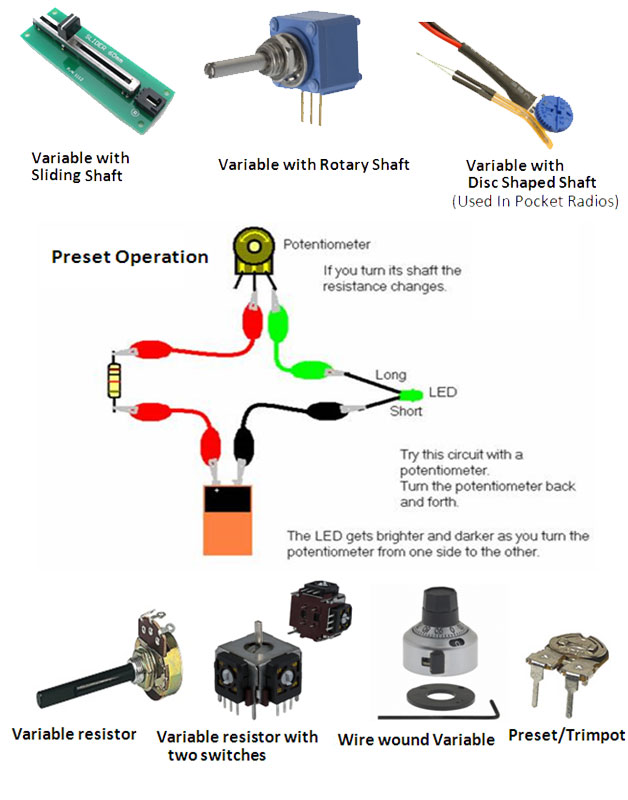
Fig. 11: Image showing different types of variable resistors
Semi Variable Resistors

Fig. 12: Image of Semi Variable Resistors
Special Resistors

Fig. 13: Image of Thermisters

Fig. 14: Image of Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
Resistance Measurement

Fig. 15 :Image showing color coding of Resistors
Measurementn by using Multimeter
General precautions
Circuit Analysis



Fig. 18: Circuit Diagram of star and delta connections of resistors
You may also like:
Filed Under: Tutorials


Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on EDAboard.com and Electro-Tech-Online.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.