When developing a USB enabled custom device, a controller chip needs to be selected. The selection of chip depends on various form factors like-:
• Ease of Availability
• Cost
• Functions Supported
Components of USB Controller
For functioning as a USB device, the controller chip has the following building blocks -:
• USB Transceiver
• Serial Interface Engine(SEI)
• Buffers to hold USB data
USB Transceiver: It provides hardware interface between the USB connector of the device and the circuit that controls USB communication. Usually, the transceiver is present on the same controller chip but sometimes external transceiver is used.
Serial Interface Engine: It is an intermediate unit that handles the transmission and reception of the packets. The unit does not check or manipulate the data but just sends the data that has been provided by the controller chip or stores the received data. The typical functions of serial interface engine are -:
• Send packets
• Detect incoming packets
• Detect and generate SOP(Start of Packet), EOP(End of Packet), Reset and Resume signals
• Encode and decode the data in required format. Generally, NRZI (Non Return to Zero Inverted) with bit stuffing
Buffers: They are used for holding received data or the data that needs to be transmitted. In some controllers, a portion of data memory is reserved for buffers while in other registers are used. Buffers work in FIFO (First in First out) order. The Controllers in which buffers are located in data memory, the data is read/write from lowest address to highest address. Some controller chips have two parallel buffers in order to enable faster transfers. For example, when the first buffer is transmitting data the second buffer can hold the next block of data to be transmitted. In reception, while the firmware is processing the data from the first buffer, the second buffer can hold the next block of data received. Some controllers support four buffers.
Configuration, Status and Control Information: USB controller chips have inbuilt registers for holding information. These registers are mainly used for storing information related to -:
• Number of bytes received
• Number of bytes ready to transmit
• Suspend state status
• What endpoints are enabled
Clock: The controller chip needs clock signal for USB communication. The sources of clock can be Crystal Oscillator, Ceramic Resonator or On-Chip Clock
USB Device Requirements
A number of factors need to be considered while the selection of a controller chip -:
Data communication speed
A USB can support three different speed modes – low, high and full. Some controller chips support only low speed, some support low and high while some support all the speed modes. The selection of controller chip has to be done according to the data transfer rate required. In projects, where, only low speed is required, the unnecessary inclusion of full or high-speed controllers will add surplus cost to the device. Also, the circuit components and manufacturing of full and high-speed controllers are costly.
Length of the cable
For low-speed devices, the length of the cable can be no longer than three meters, while full and high-speed cables can be up to five meters long.
Power drawn
A peripheral device can draw a maximum current of 500mA in USB2.0 while in USB3.0 it can draw up to 900mA current. In cases where current requirement exceeds the USB standard, the external power supply is needed.
Transfer Types
All USB controller chips support Control Transfer. The other transfer types (Isochronous, Interrupt, and Bulk) have their own specific applications. The controller chip may support all the transfer types. The controller chip has to be selected depending on the transfer type required to fulfill the purpose of the device. For example, a mouse only needs Interrupt transfer apart from the control transfer. The proper chip selection can save from incurring additional cost.
Firmware
Some controller holds firmware in their flash memory or EEPROM. Hence these controllers provide the functionality of removing, upgrading or changing the firmware as per the requirement. While some controllers have dedicated memory for keeping firmware which cannot be easily erased or re-written. In that case, the controller chip has to be replaced with another whenever a firmware upgrade is made.
Other functionalities
In addition to a USB interface, a controller chip can provide other functionalities like GPIO (General Purpose Input Output) pins, Timers, Counters, ADC(Analog to Digital Convertor), Interrupts, SPI(Serial Peripheral Interface), TWI (Two Wire Serial Interface) and other microcontroller features. Selecting a USB controller chip with the extra feature can remove the need for external IC or components in a project.
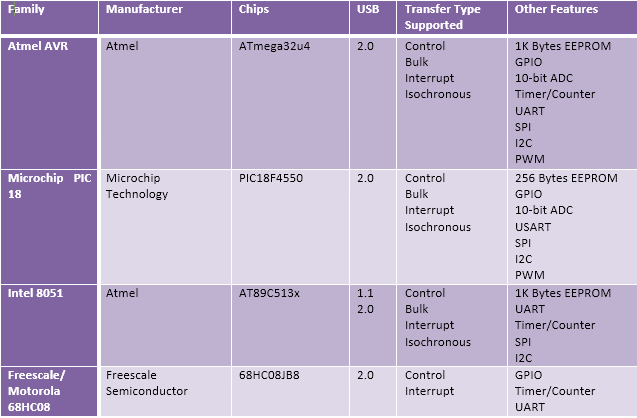
Common Controller Chips
There is a large variety of controllers available which provides USB interface as well as other features. Using ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) is also an option for application specific devices like mouse or keyboard. Some of them are listed in the table:
Controller and External CPU
There are USB controllers available that can be interfaced with external CPU or microcontroller. The interfacing can be done using parallel or serial protocols. This means an obsolete CPU or microcontroller that does not support USB, can be provided a USB interface using USB controller. In the end, the device will contain two separate chips, a USB controller chip, and a CPU/Microcontroller chip.
Using two separate chips can add cost to the device whereas using one USB controller with embedded CPU like PIC18f4550 will be less costly.
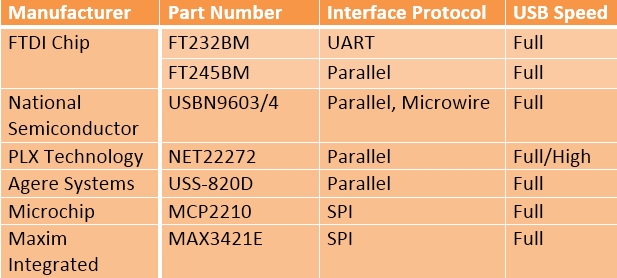
Some of the USB Controllers that can be interfaced with external chips are listed below:
This completes the USB series. It’s now the time to get hands dirty and start implementing projects using USB interface and protocols.
You may also like:
Filed Under: Featured Contributions, Tutorials, USB






Questions related to this article?
👉Ask and discuss on Electro-Tech-Online.com and EDAboard.com forums.
Tell Us What You Think!!
You must be logged in to post a comment.